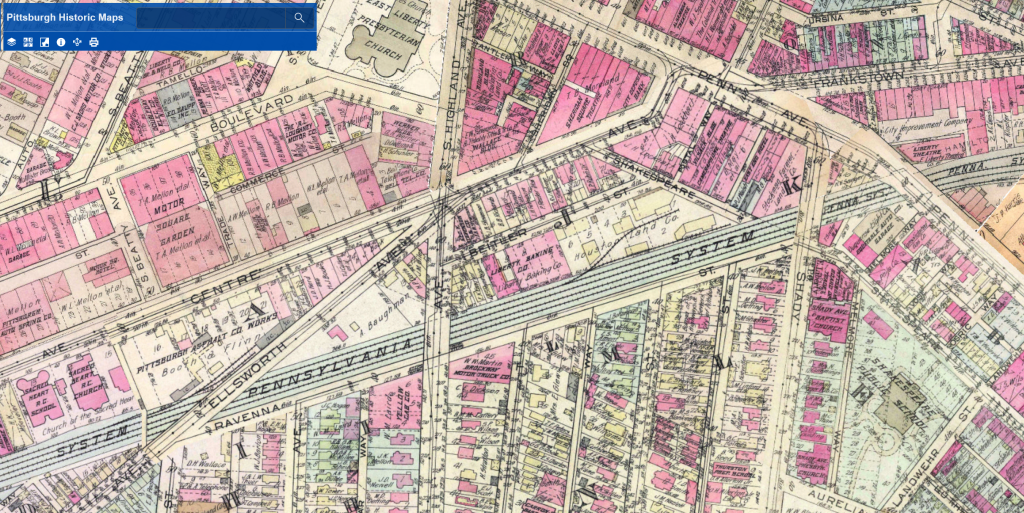
My fascination with World’s Fairs was started when I was a child by Laura Ingalls Wilder and the San Francisco Panama-Pacific Exposition. It has continued as an adult. Chicago’s 1893 World’s Columbian Exposition is the World’s Fair for planners. The “White City” was the first major example of the City Beautiful Movement, an attempt to reduce or eliminate the unhealthy, overcrowded cities of the time.
After years of hearing about the importance of the 1893 Chicago World’s Fair in planning and architecture and after reading Eric Larson’s The Devil in the White City, I made it a goal to visit the fair site. On one trip to Chicago when the weather was beautiful, I rented a bike and rode down the waterfront trail toward what was left of the White City. This was before I had a smart phone which meant I turned around and gave up because I feared that I had misjudged the distance by bike trail. Later, I realized I was probably pretty close and if I had only gone around one more curve, I would have seen my destination.
My next trip to Chicago was the same year I visited San Francisco. This time, I took a bus to the fair location. I picked the bus stop that on the map appeared to be the closest stop to the remaining places of interest from the fair. When I stepped off the bus onto a broken sidewalk, I found a desolate expanse of vacant land, scraggly trees, and pock-marked lawns. A weary walk presented itself every way I turned.
The bus didn’t run frequently out there. The roads that crossed the vacant expanse stretched far and wide, empty except for the random sudden appearance of a single speeding vehicle.
As soon as I had stepped off the bus and it drove off, I felt tired and scared. I wondered how to extricate myself from this horrible environment. I had some additional information that expanded the negative emotions stirred by the conditions around me. I had heard or read somewhere that the former Midway, which was where I got off the bus, was used as a sort of DMZ buffer to keep “those people” (in this case, primarily people with little income or people of color) away from the University of Chicago campus. I had clearly landed in the middle of a land of have-nots.
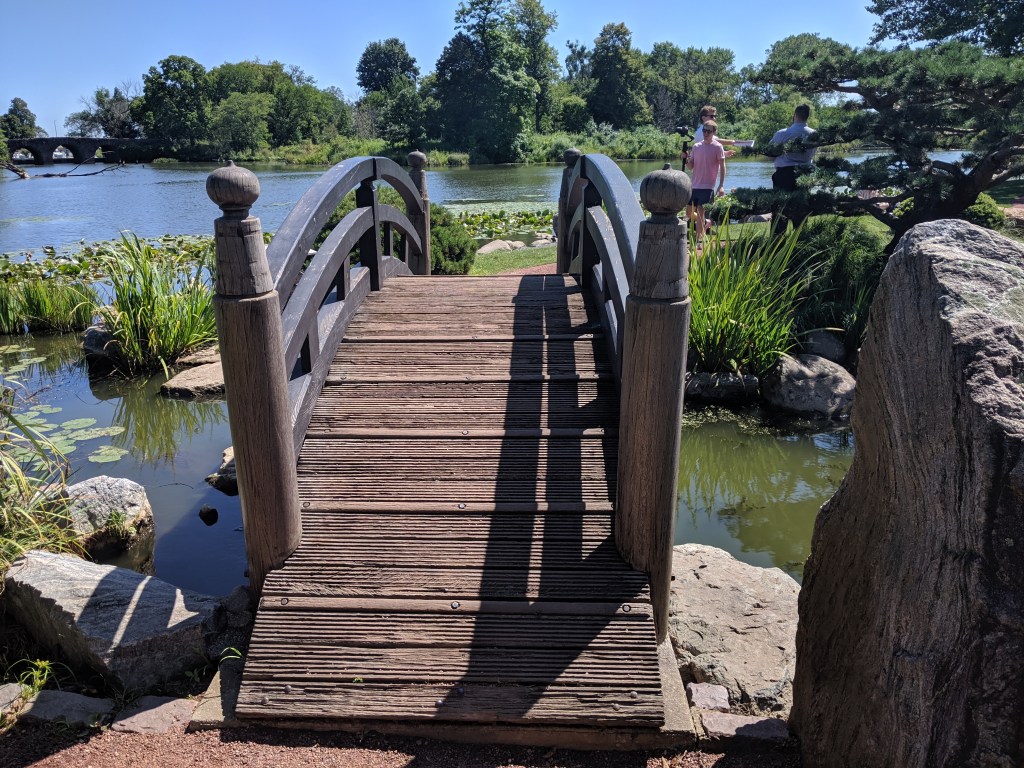
As I had come this far with a purpose and there seemed to be little else to do, I moved forward toward the lake. Migraine-inducing music was blaring from an unseen picnic far away and it followed me wherever I went. After feeling like I had taken my life in my hands by daring to cross the road where at any second a car could come speeding by, I reached a path among experimental plantings. Following random turns, I found the lagoon from the fair. The one white building that remained was on the opposite shore and was surrounded by scaffolding. The walk that once circumscribed the water was shut off by a menacing 6-foot high, chain link fence and a bridge that divided the lagoon seemed no longer safe to cross over, though passing under through the muck and mud was an option.
I eventually found a way forward and reached the Japanese Garden that was developed for the fair and remains a peaceful spot. Prior to that, at the moment of being confronted with a security fence and a broken bridge, the fear and doubt that often accompanies me on my explorations became overwhelming. What if I’m stopped? What if I’m questioned? Do I have a right to explore here and pass this way? Do I have a right to explore places and pass judgement?