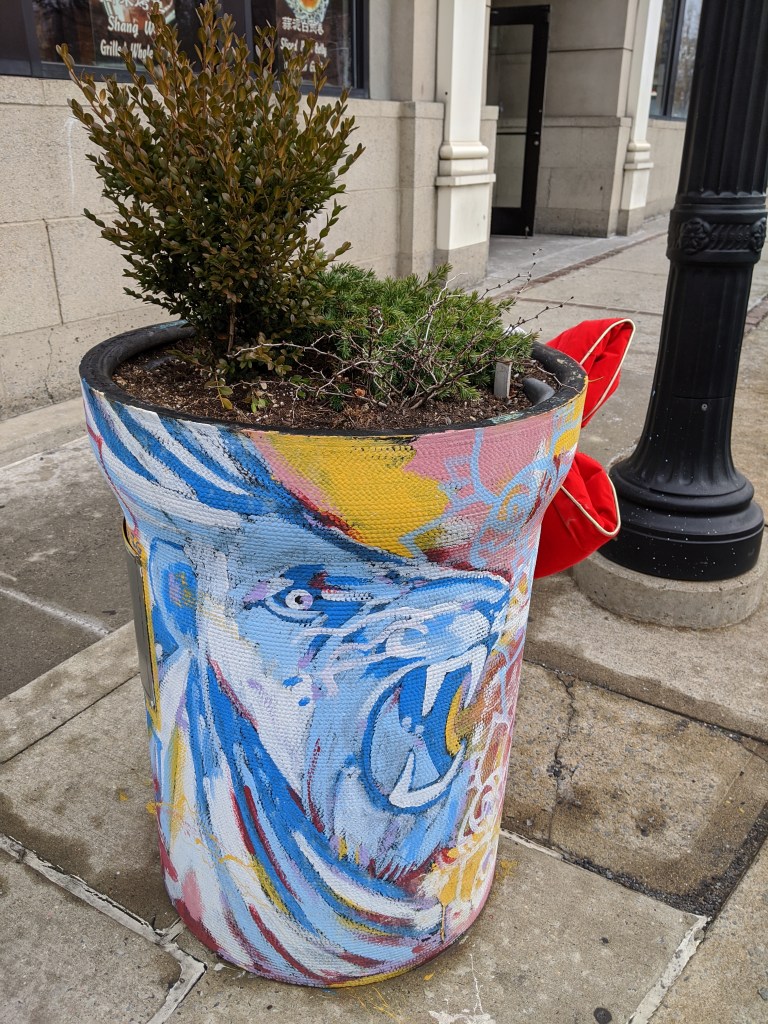Tag Archives: public space
Keeping an Eye on the Lower Hill: Dec. 2020
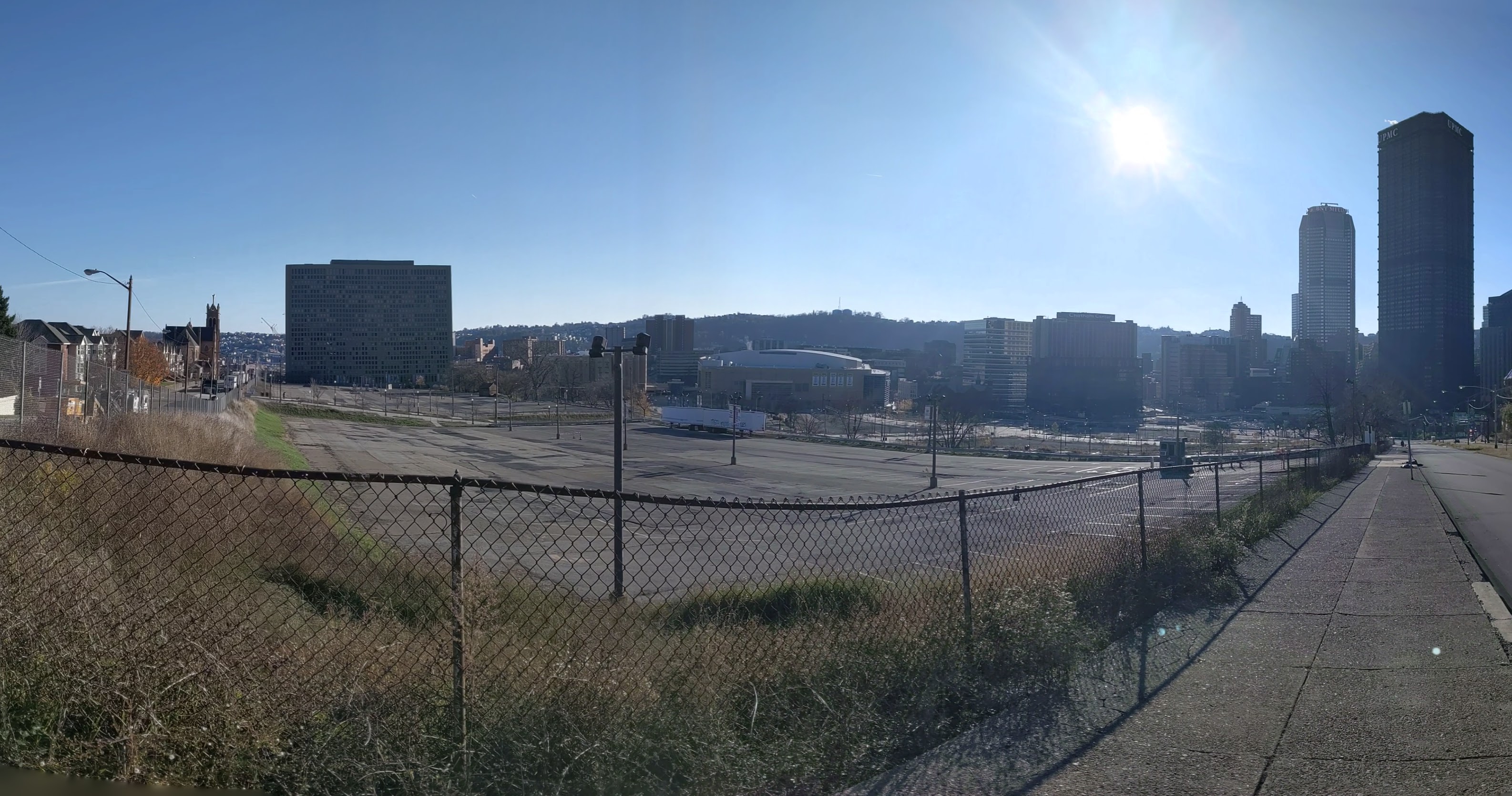
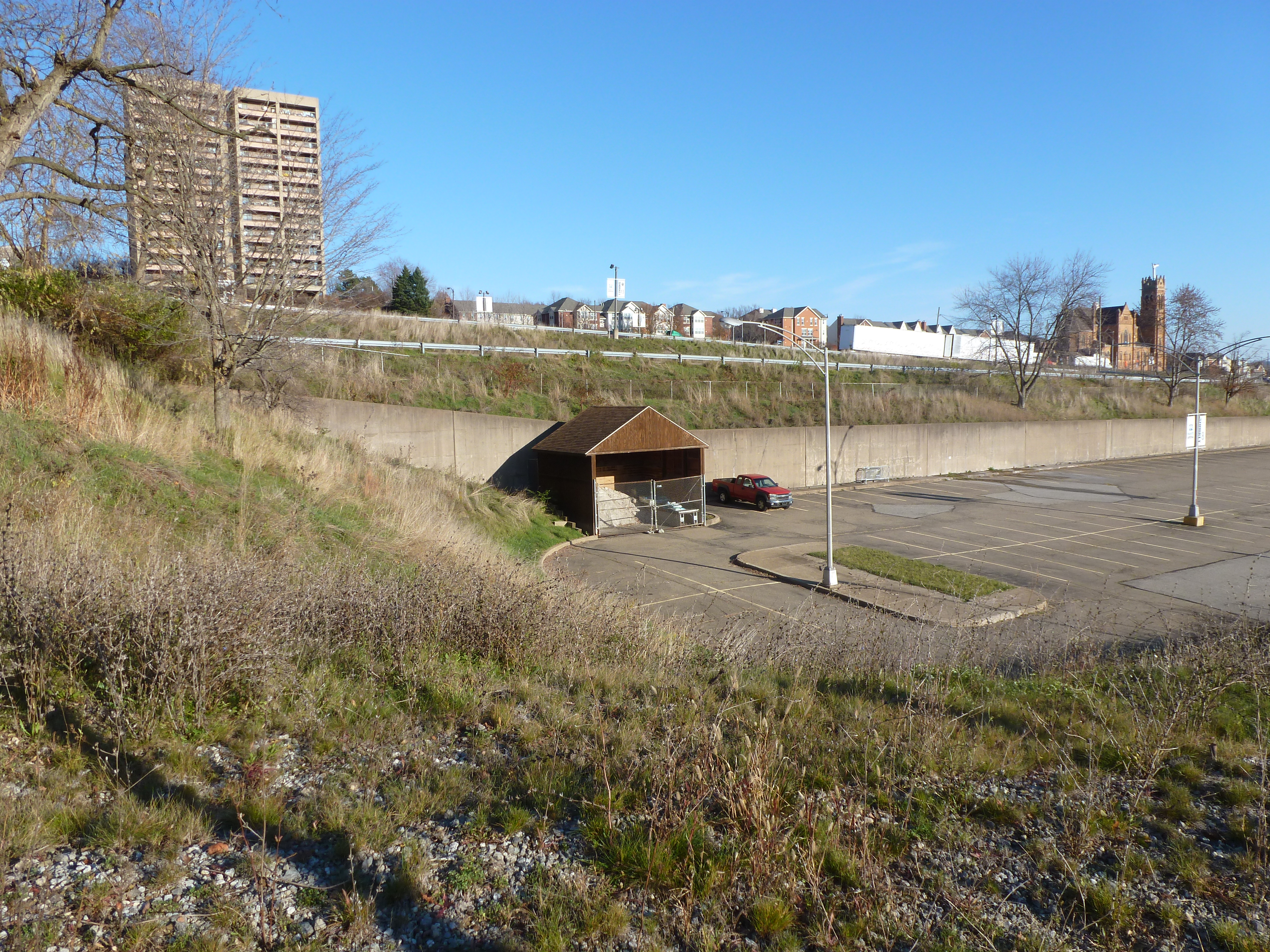
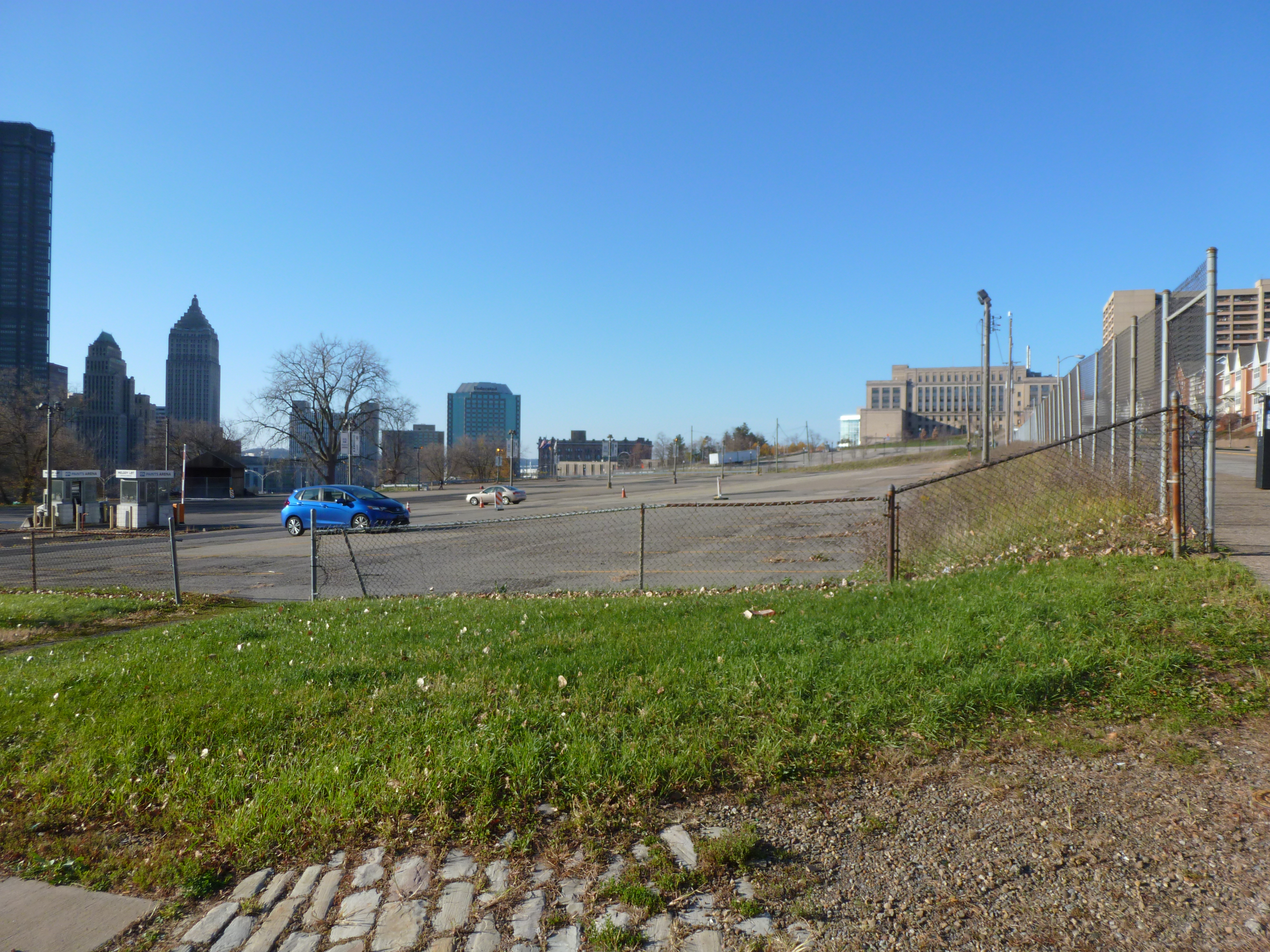
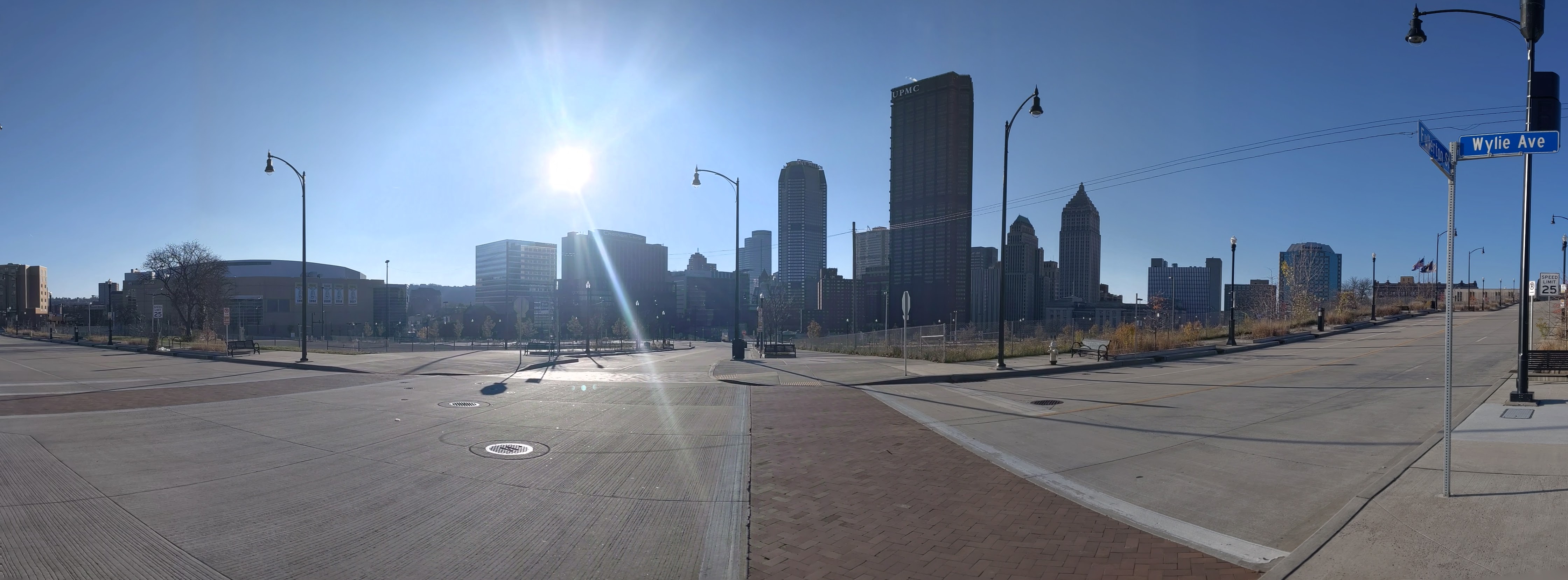
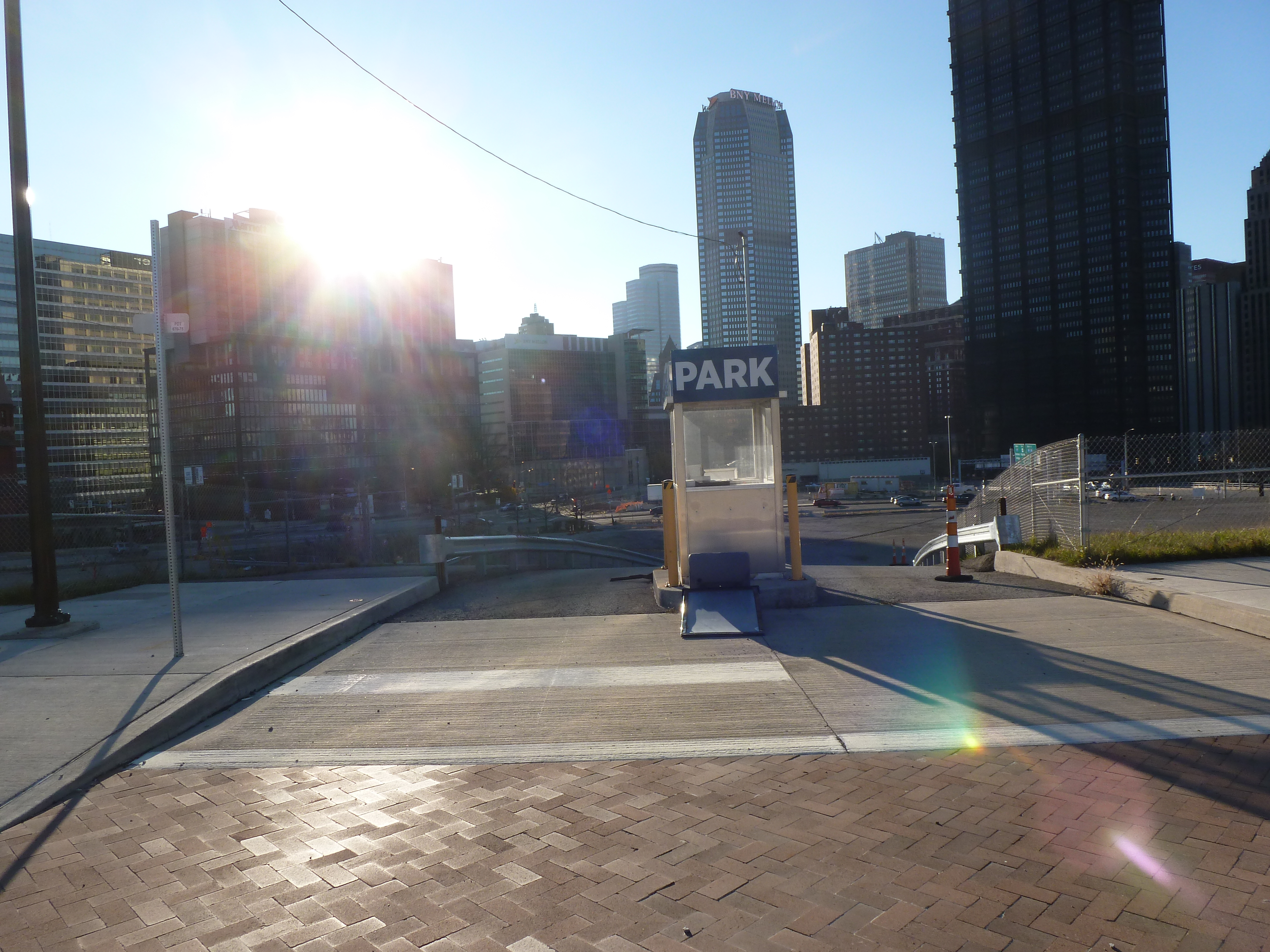



















Lower Hill in the News:
URA board votes in favor of FNB Tower (Pittsburgh Business Times, May 21, 2020)
FNB tower will be among first post-pandemic buildings (Pittsburgh Business Times, May 22, 2020)
The Penguins and FNB Corp provide funds for tech center in the Hill District (Pittsburgh Business Times, August 27, 2020)
FNB and Penguins establish partnership (Pittsburgh Business Times, September 10, 2020)
Funding secured for FNB tower in Lower Hill (Pittsburgh Business Times, October 8, 2020)
Penguins miss deadline; URA considering next moves (Pittsburgh Business Times, November 12, 2020)
Lower Hill commercial redeveloper, Mayor Peduto, and Councilman Lavelle announce partnership (Mayor’s Press Release, November 19, 2020)
New Lower Hill partnership could move project forward (Public Source, November 19, 2020)
Lower Hill redeveloper establishes downtown office and announces local firms and personnel added to team (Pittsburgh Business Times, November 19, 2020)
Previous posts in series:
Keeping an Eye on the Lower Hill: Jun. 2020
Keeping an Eye on the CAP: Dec. 2020
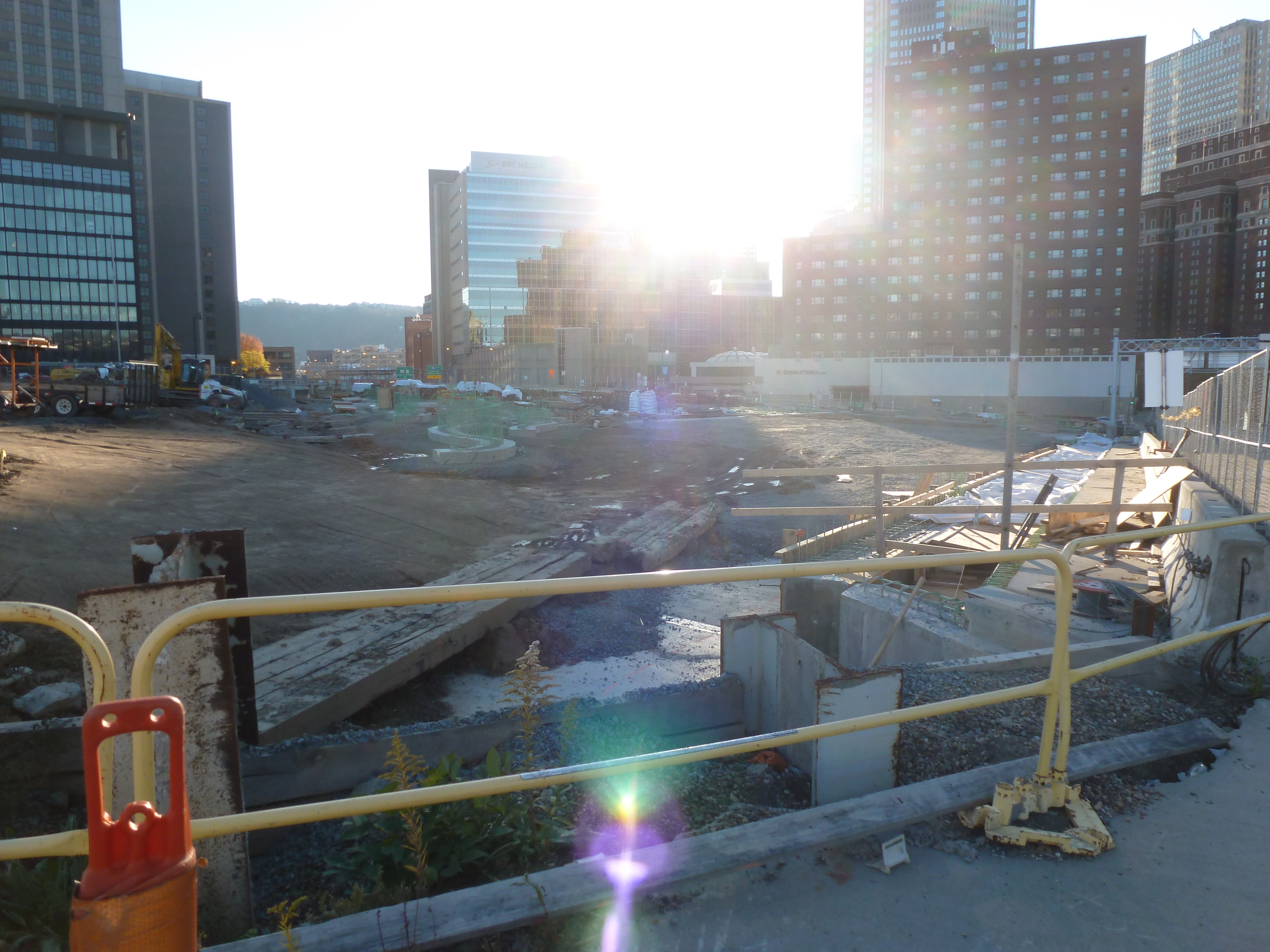
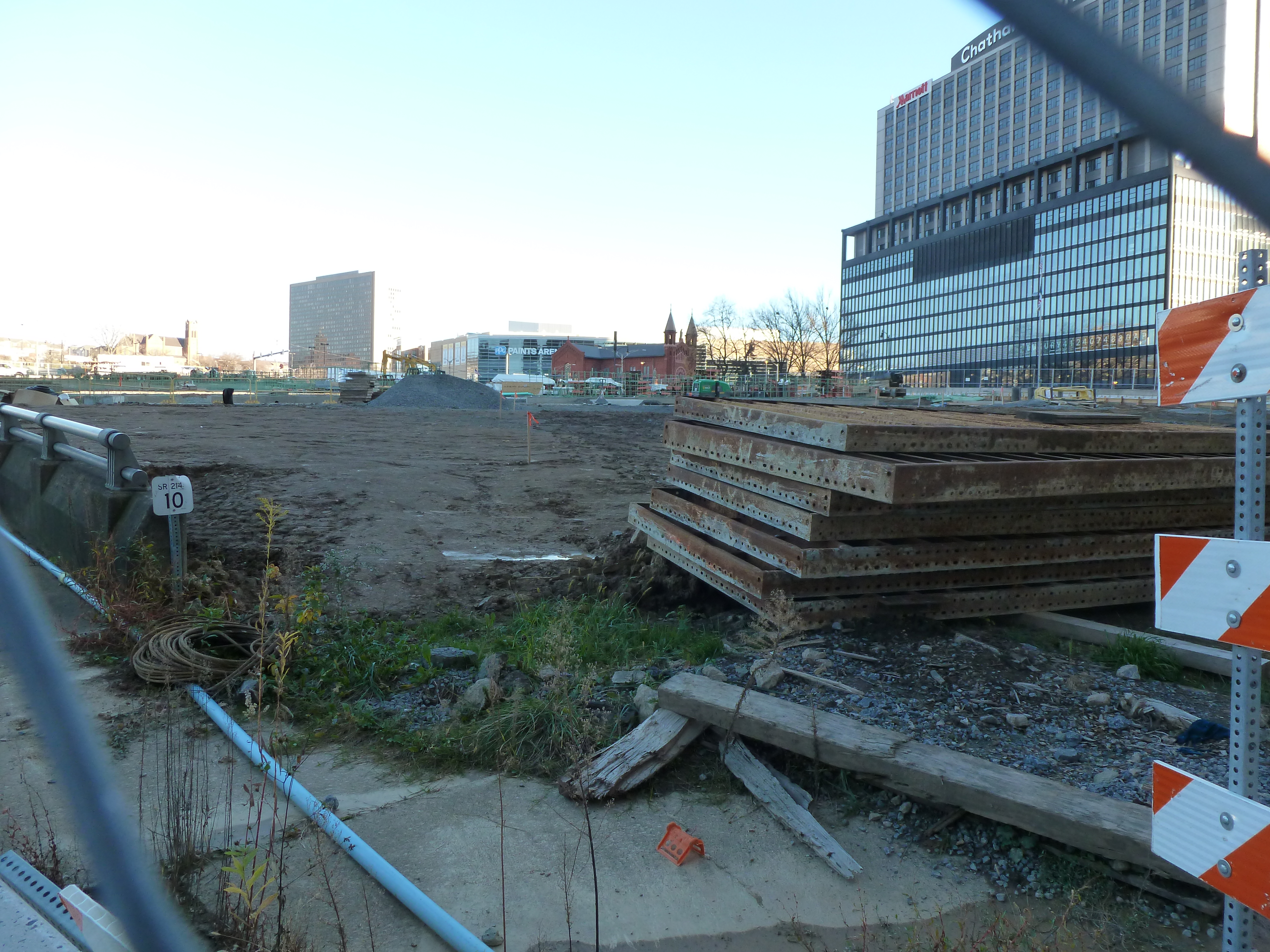
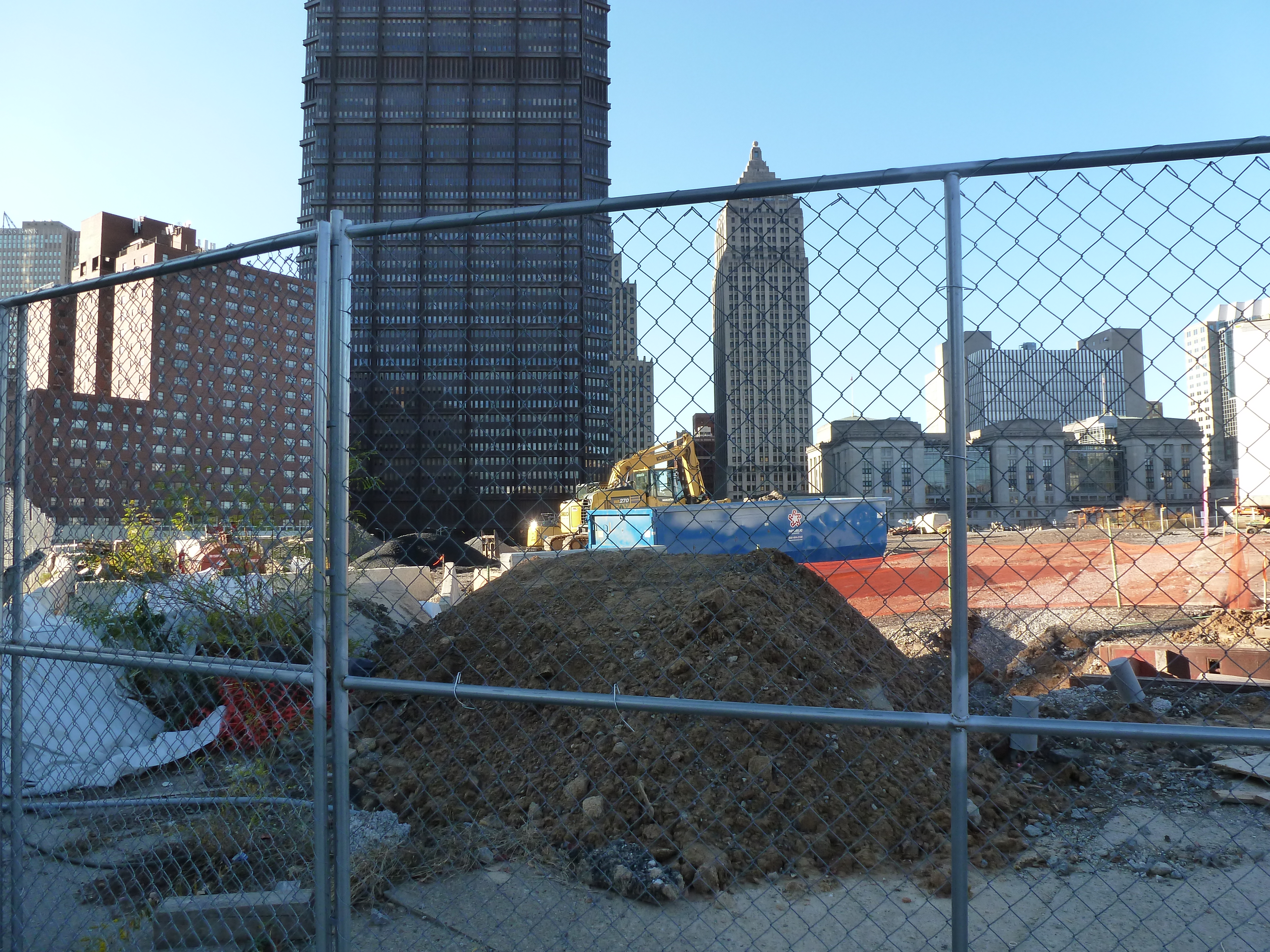




The CAP in the News:
Project on schedule despite pandemic (Tribune Review, July 29, 2020)
Project continues on schedule (WESA, October 5, 2020)
Previous Posts in the Series:
Keeping an Eye on the CAP: Jun. 2020
Keeping an Eye on Uptown: Nov. 2020
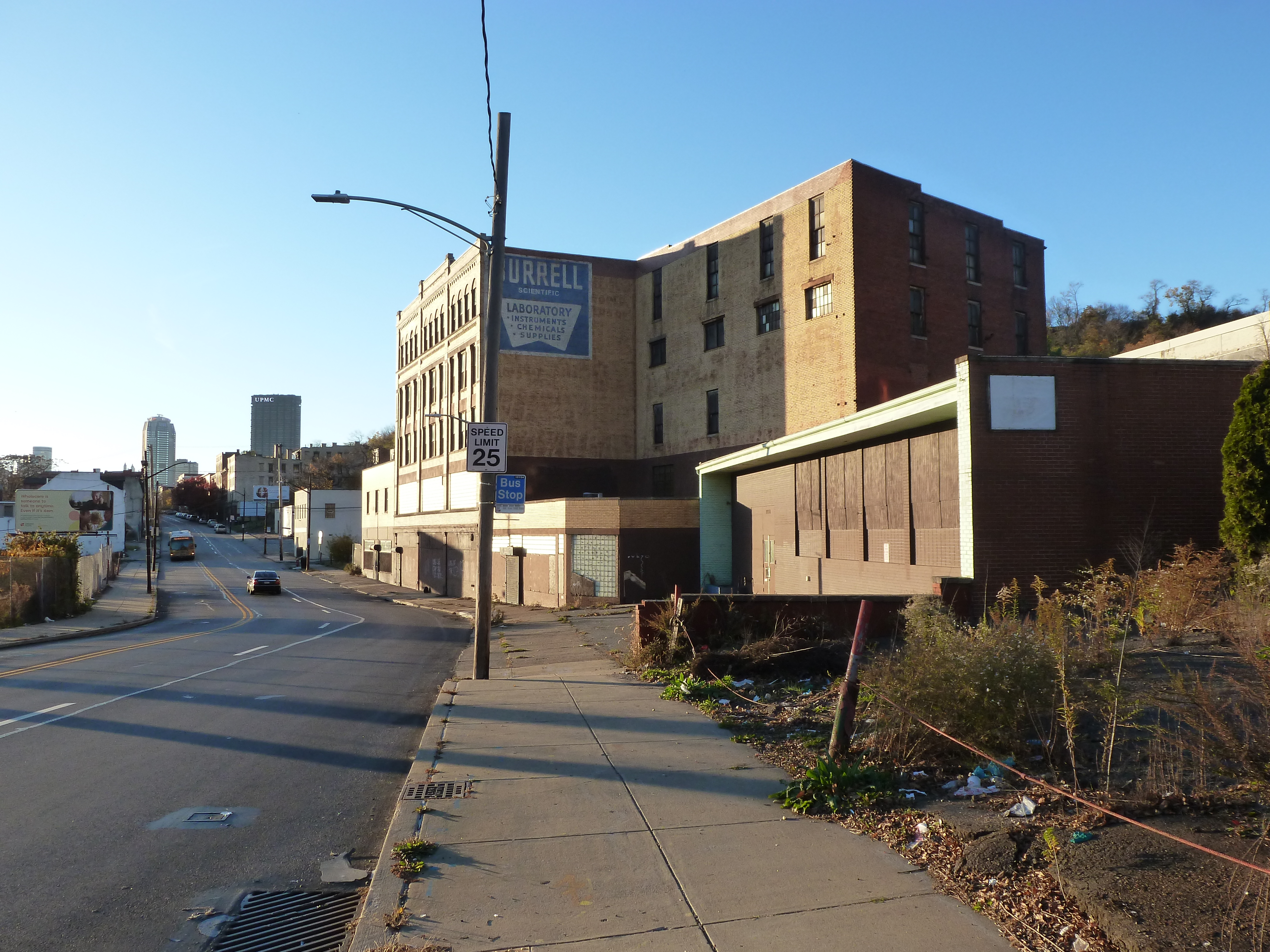
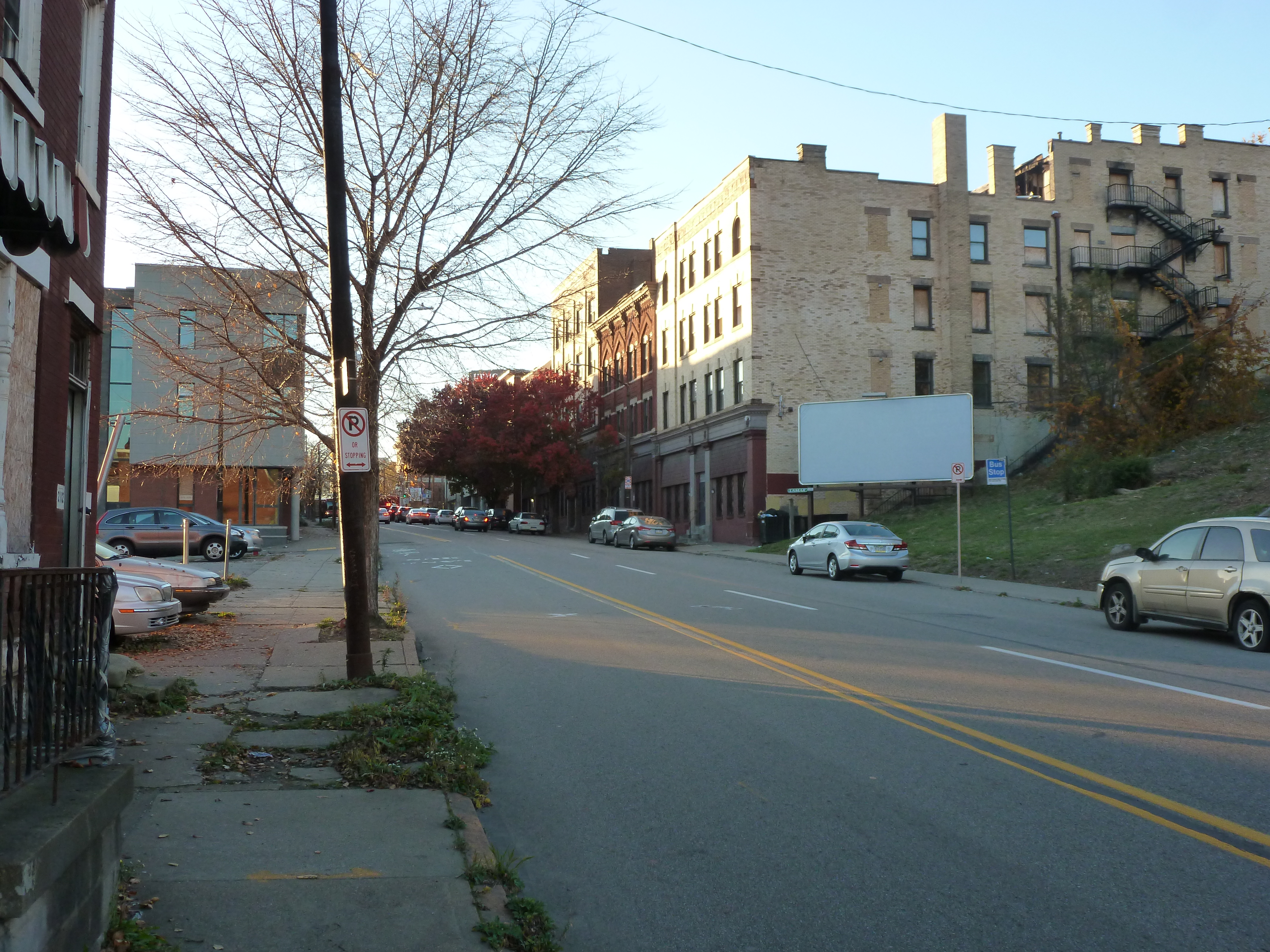
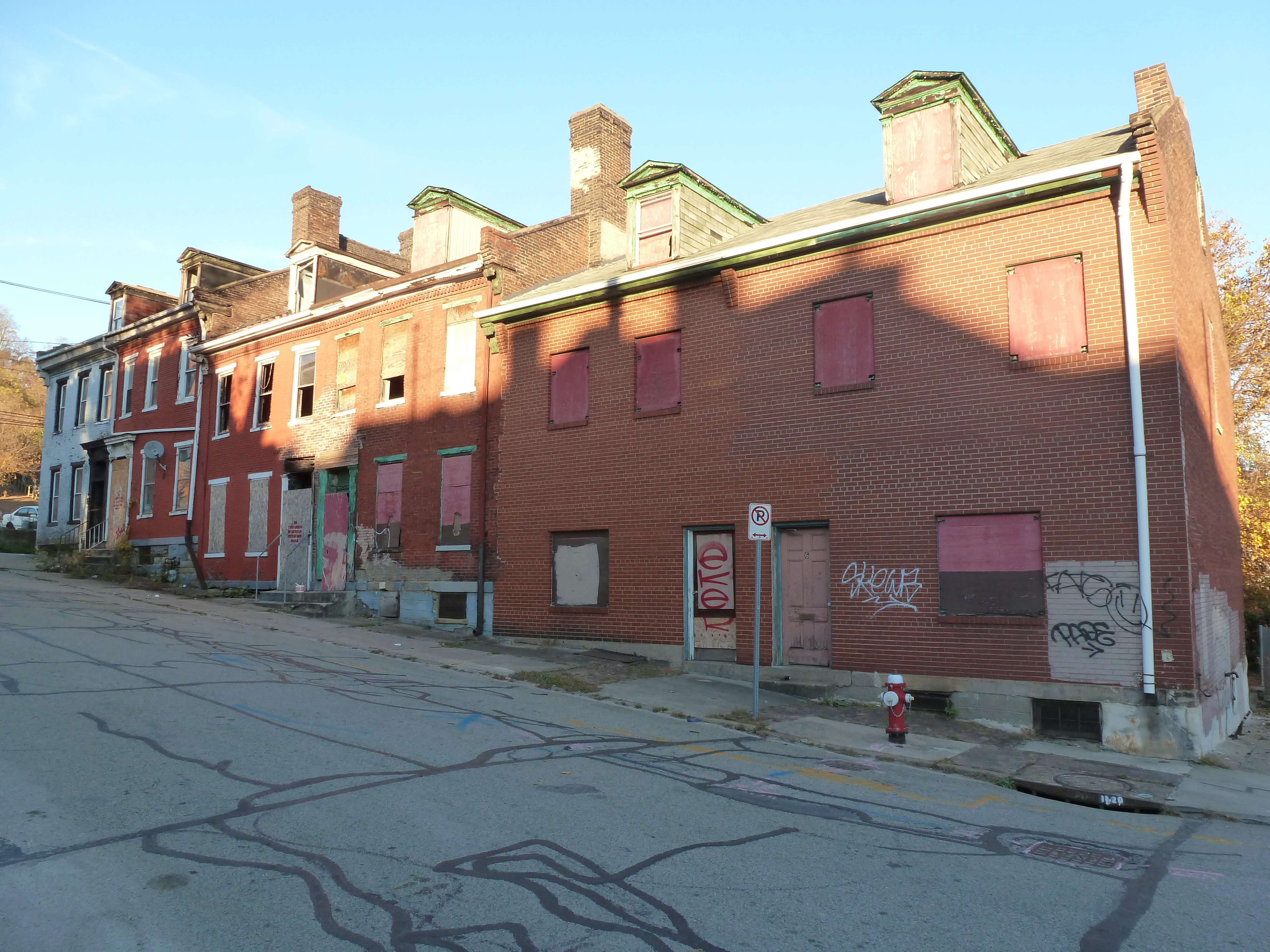
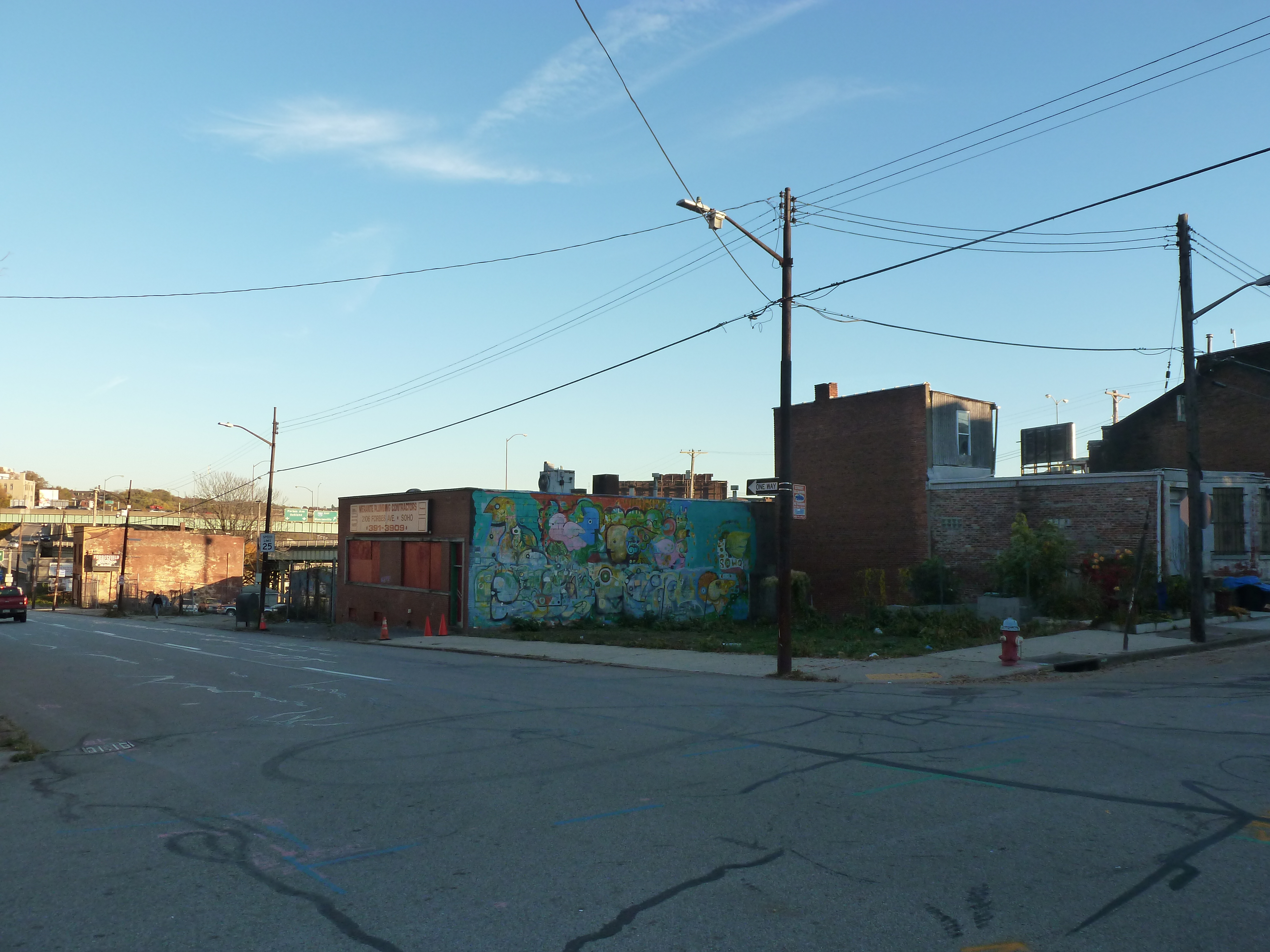
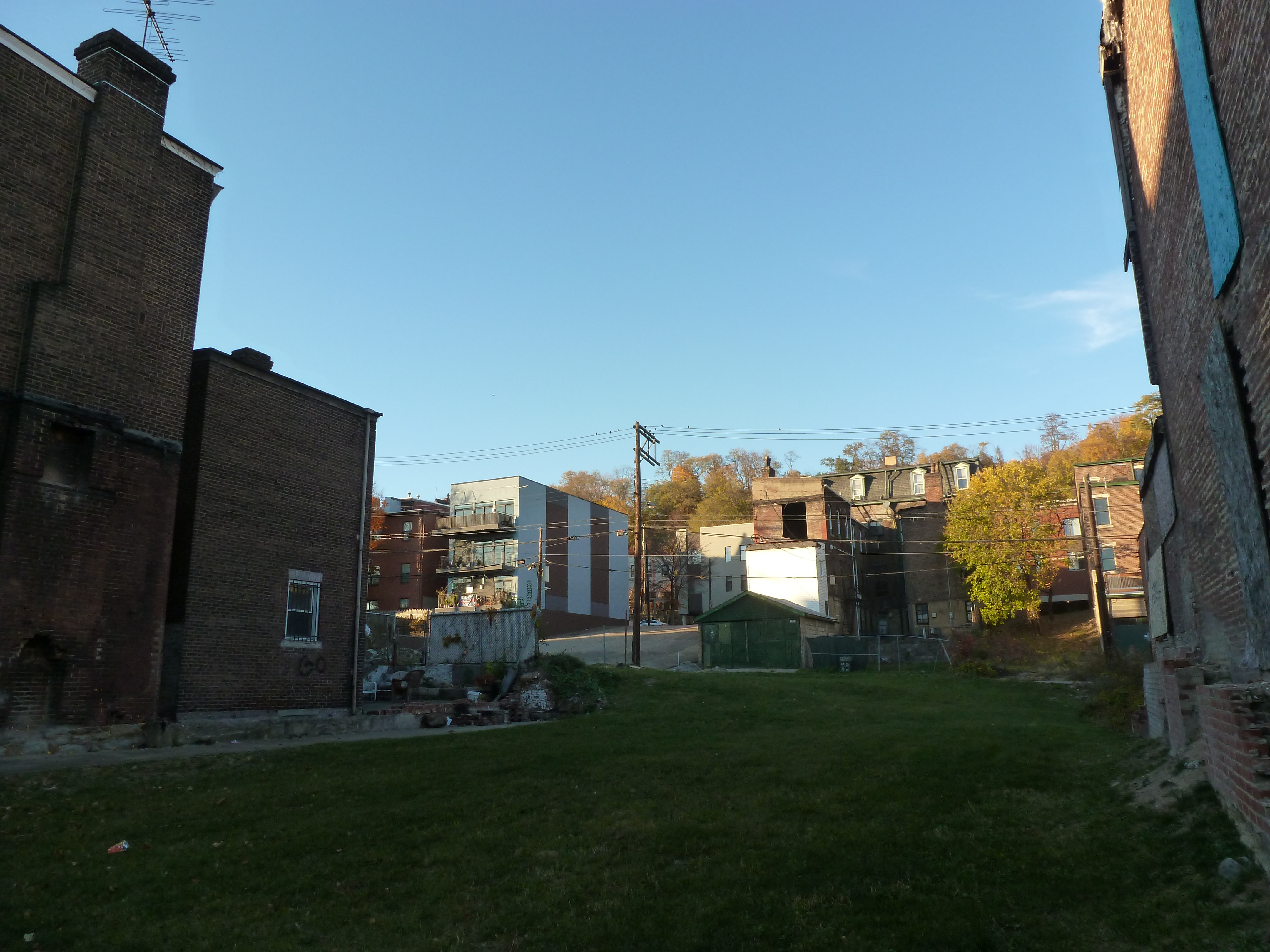
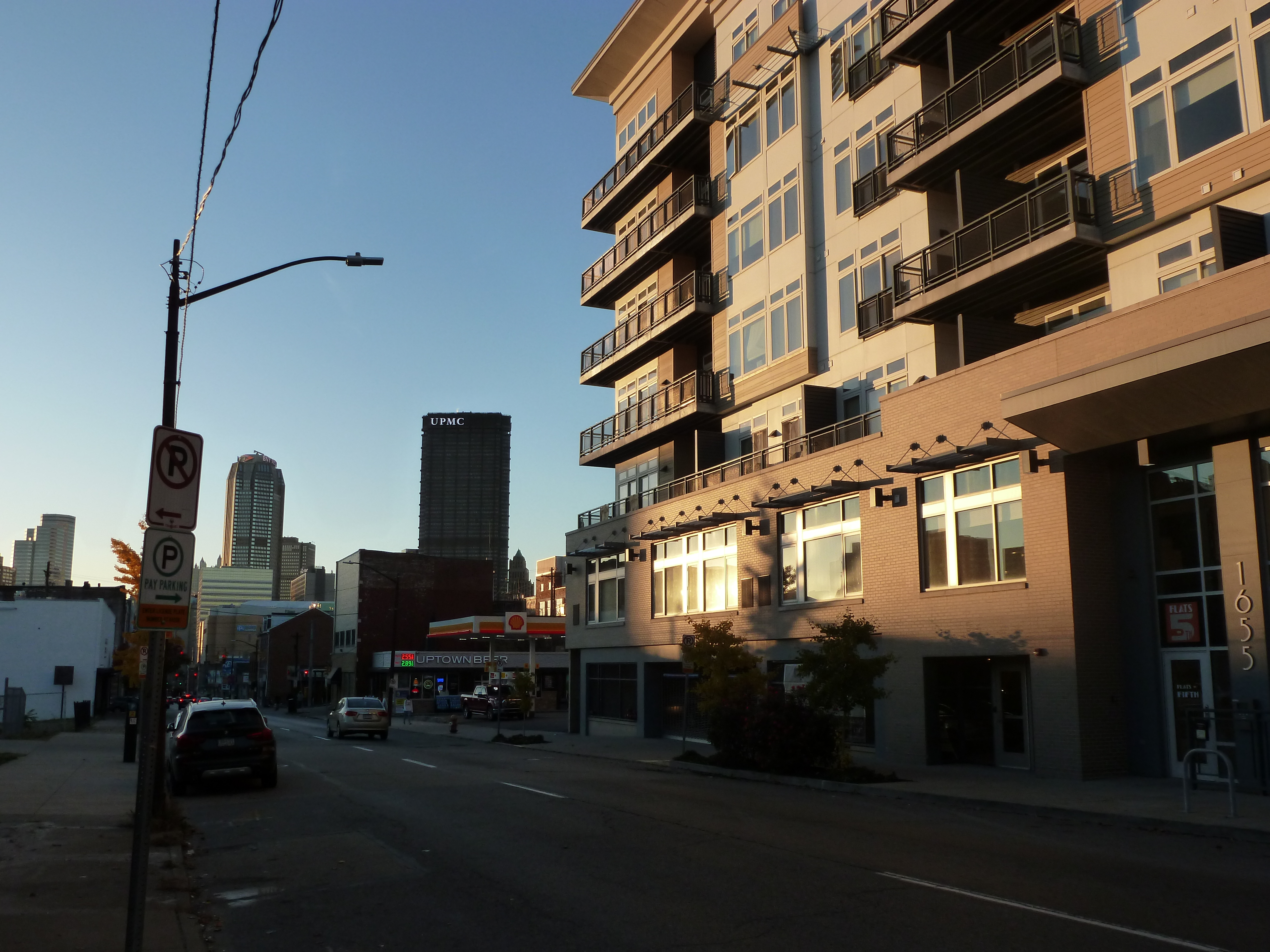
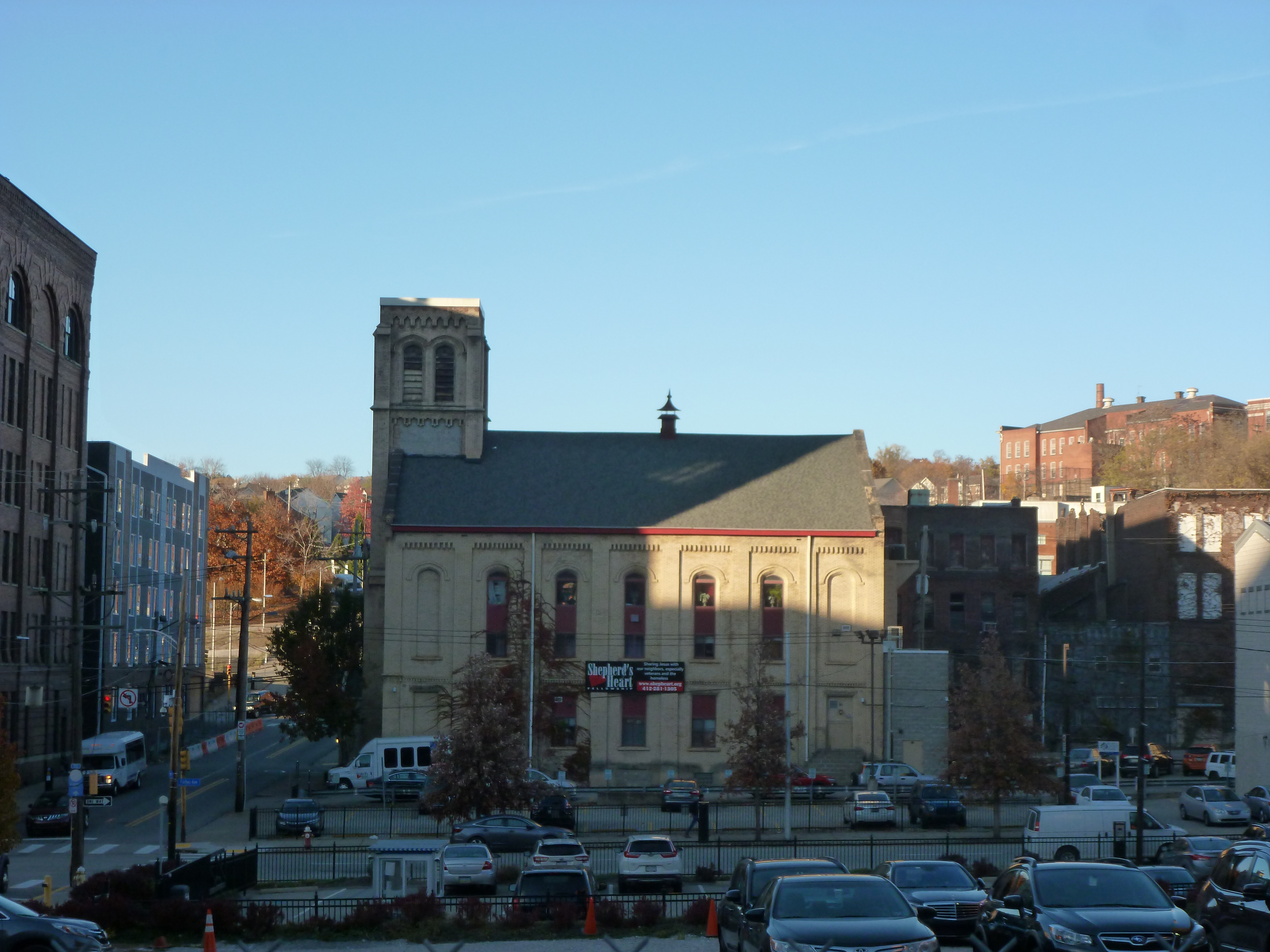
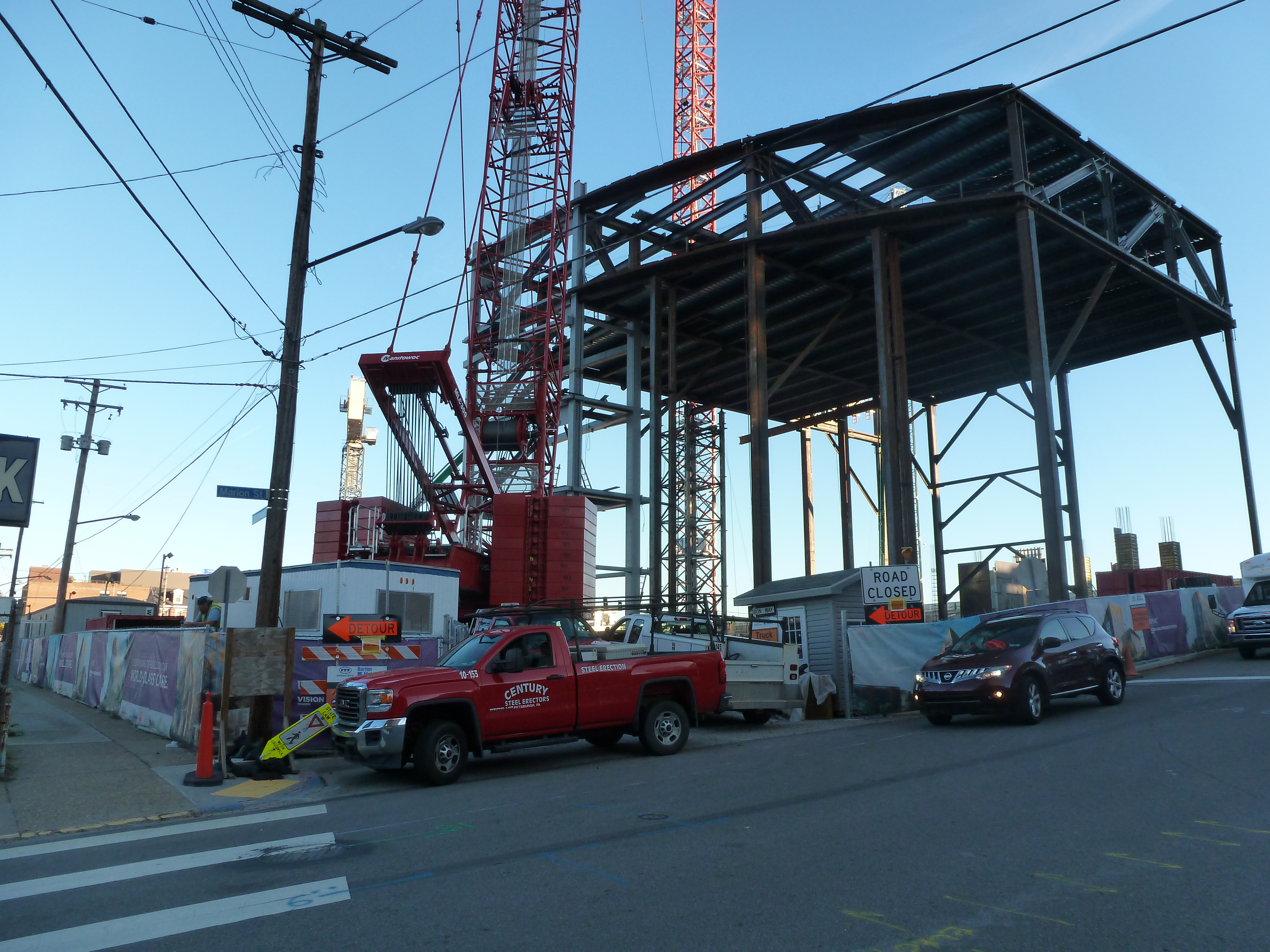
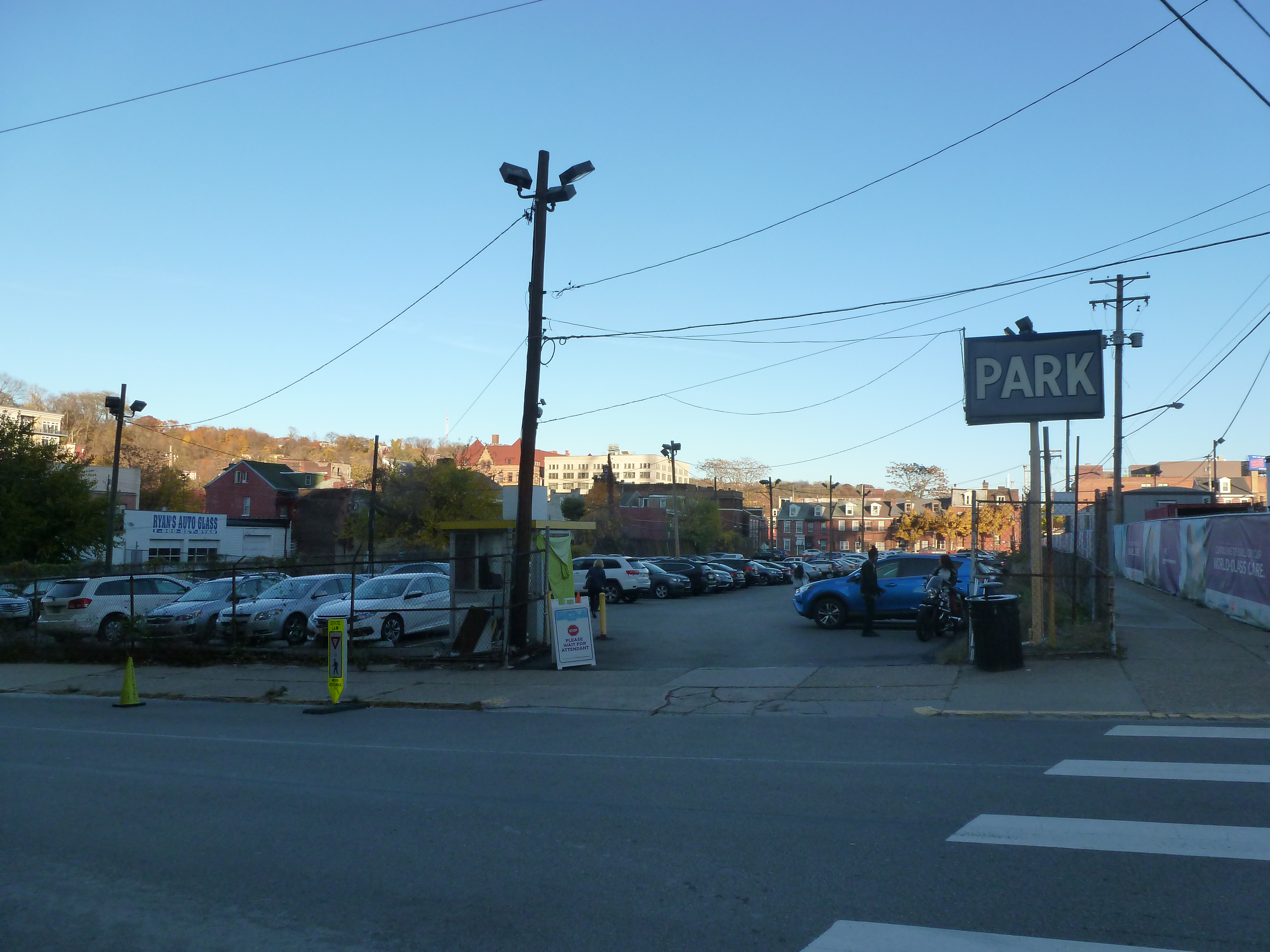
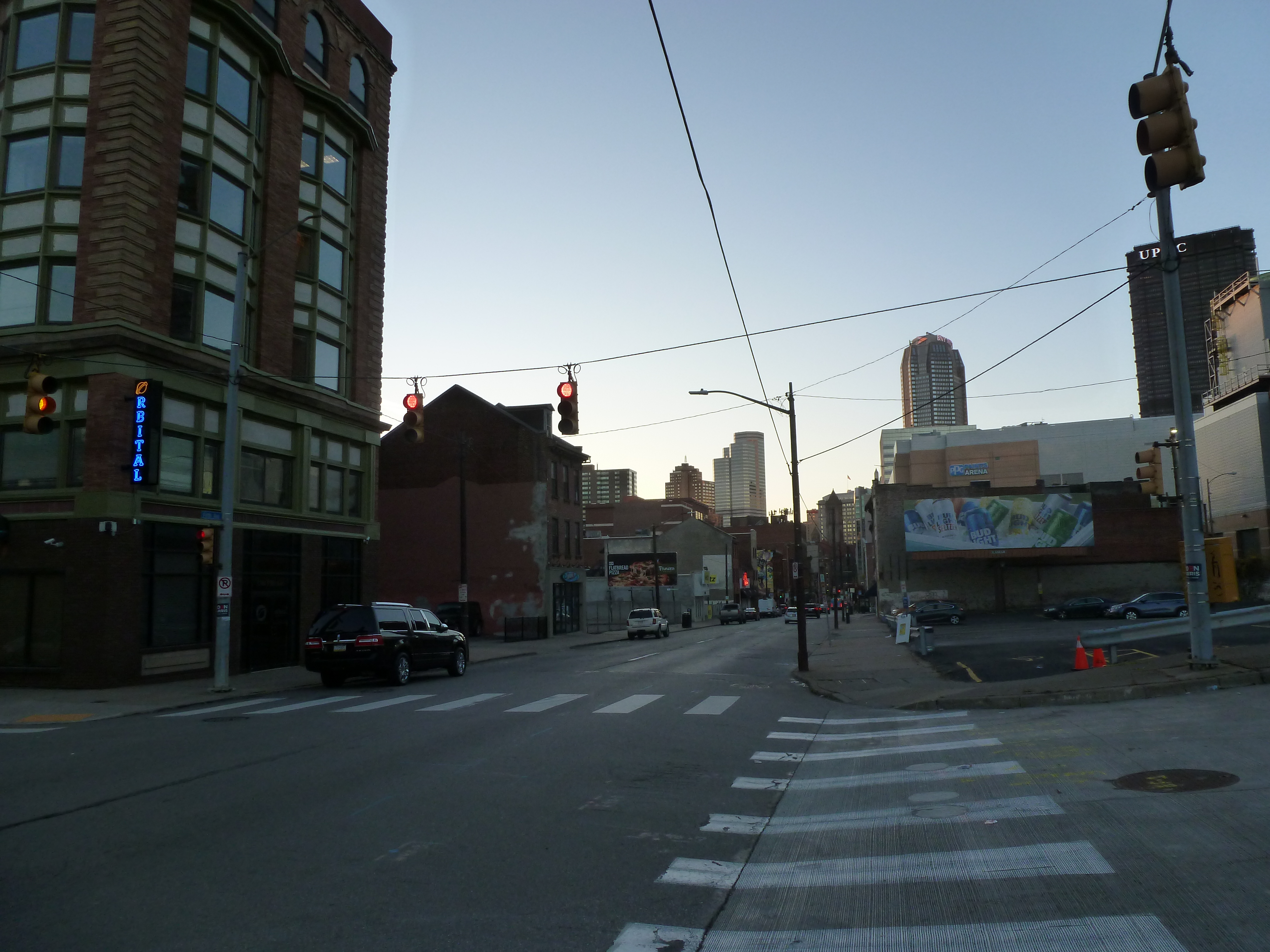






















Uptown in the News & on the Web:
President Trump tweets about BRT grant award (Post-Gazette, May 29, 2020)
Locust/Miltenberger Development Website
51-unit apartment proposed in 1700 block of Fifth Avenue (Pittsburgh Business Times, June 1, 2020)
$99.95 million awarded for BRT (Next Pittsburgh, June 2, 2020)
Funding awarded for proposed mixed-use with affordable housing project (Pittsburgh Business Times, August 18, 2020)
BRT service may start in 2023 (Pittsburgh Post-Gazette, September 21, 2020)
Solidarity murals coming to the city (Next Pittsburgh, September 27, 2020)
Gentrification concerns raised for proposed tech development (Pittsburgh Business Times, September 30, 2020)
Interview with developer of proposed Uptown mixed-use project (Pittsburgh Business Times, October 5, 2020)
Partner pulls out of Fifth and Dinwiddie project (Pittsburgh Business Times, October 26, 2020)
Planning Commission approves Uptown tech development (Public Source – Develop PGH Bulletins, October 27, 2020)
Commercial portion presented for Fifth and Dinwiddie project (Pittsburgh Business Times, November 10, 2020)
Previous posts in series:
Keeping an Eye on Uptown: May 2020
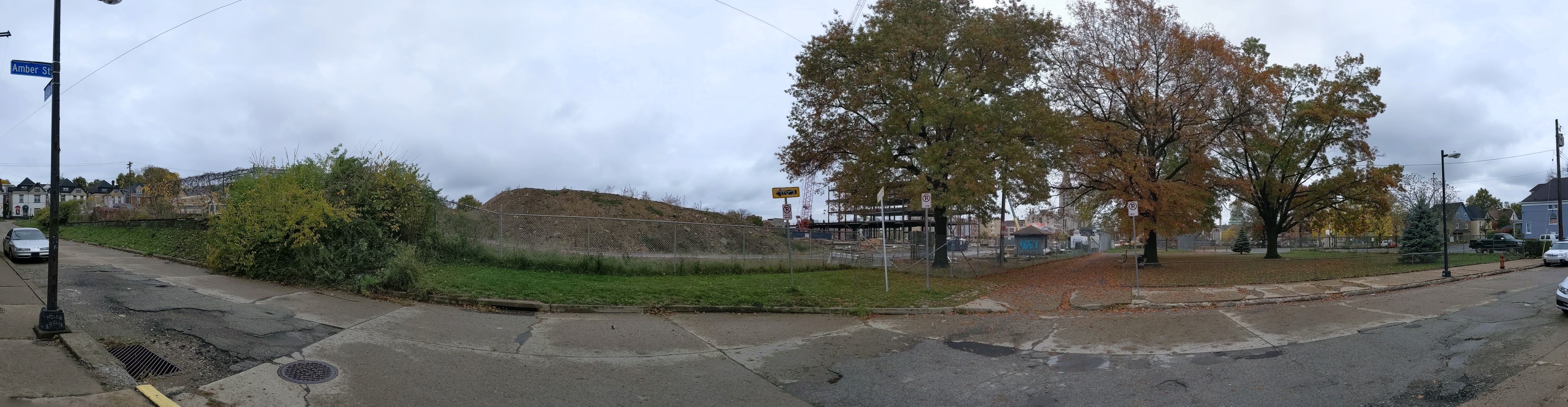
Keeping an Eye on Penn Plaza – Nov. 2020






Everyday Art – Bethlehem
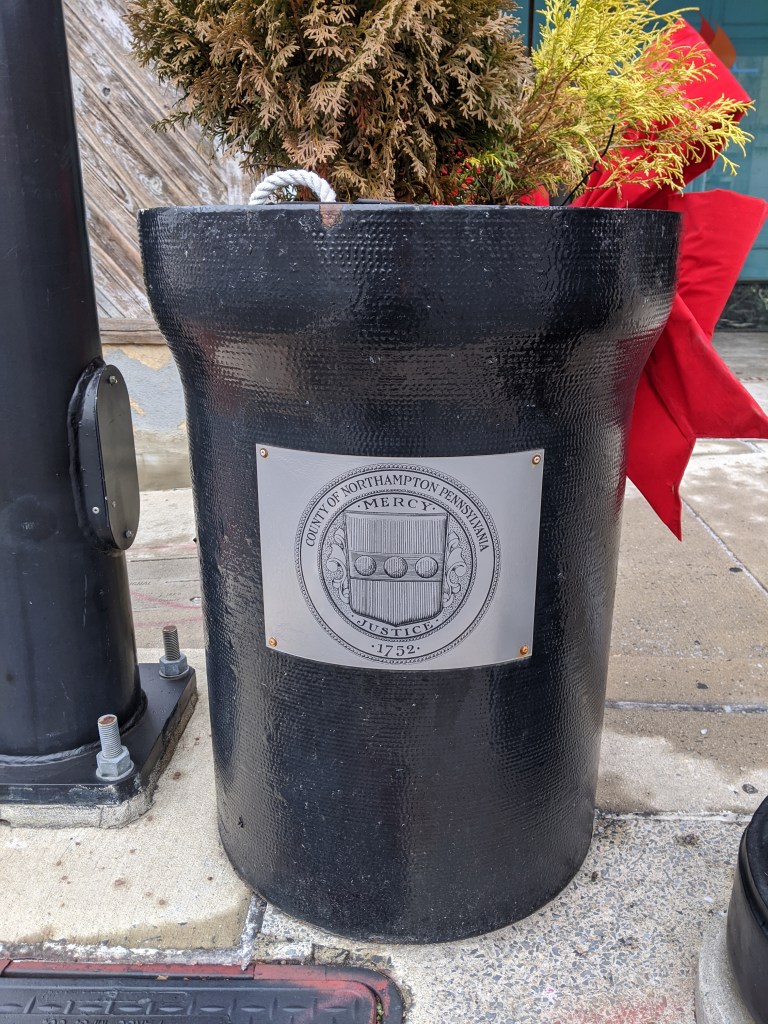
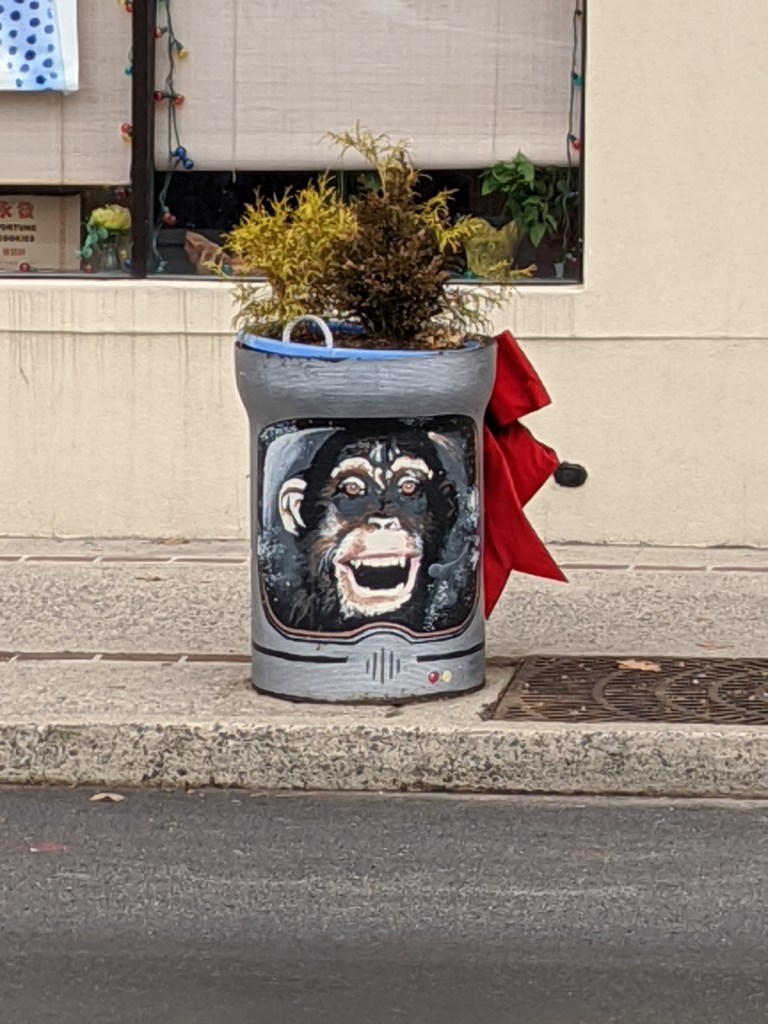
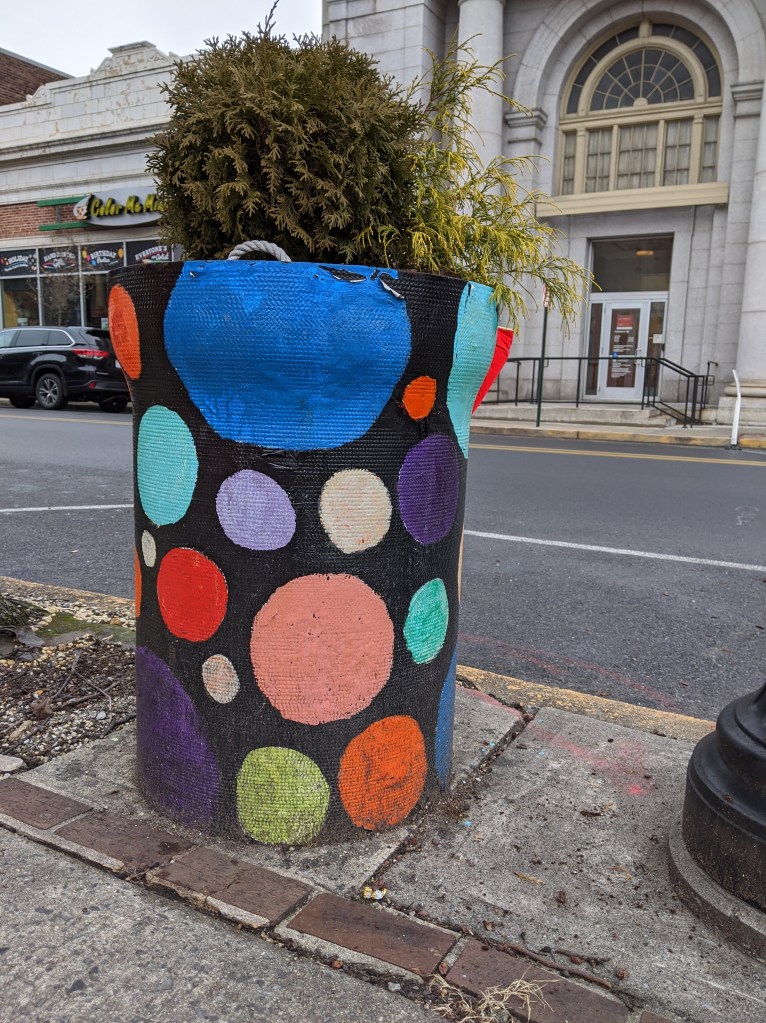
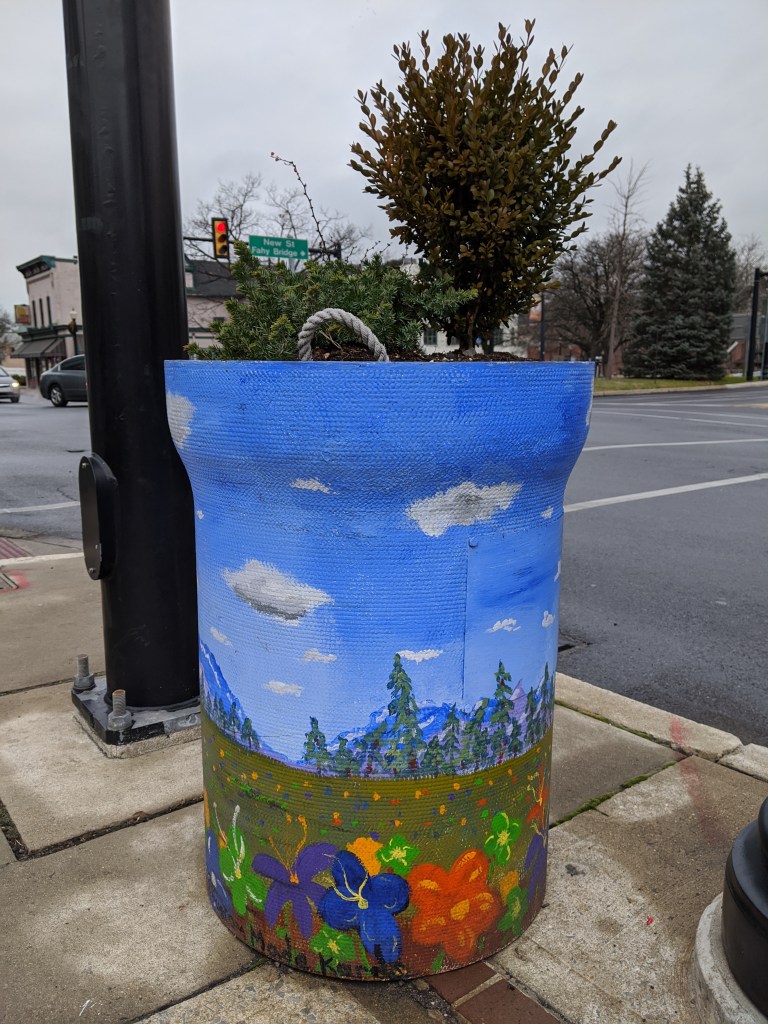
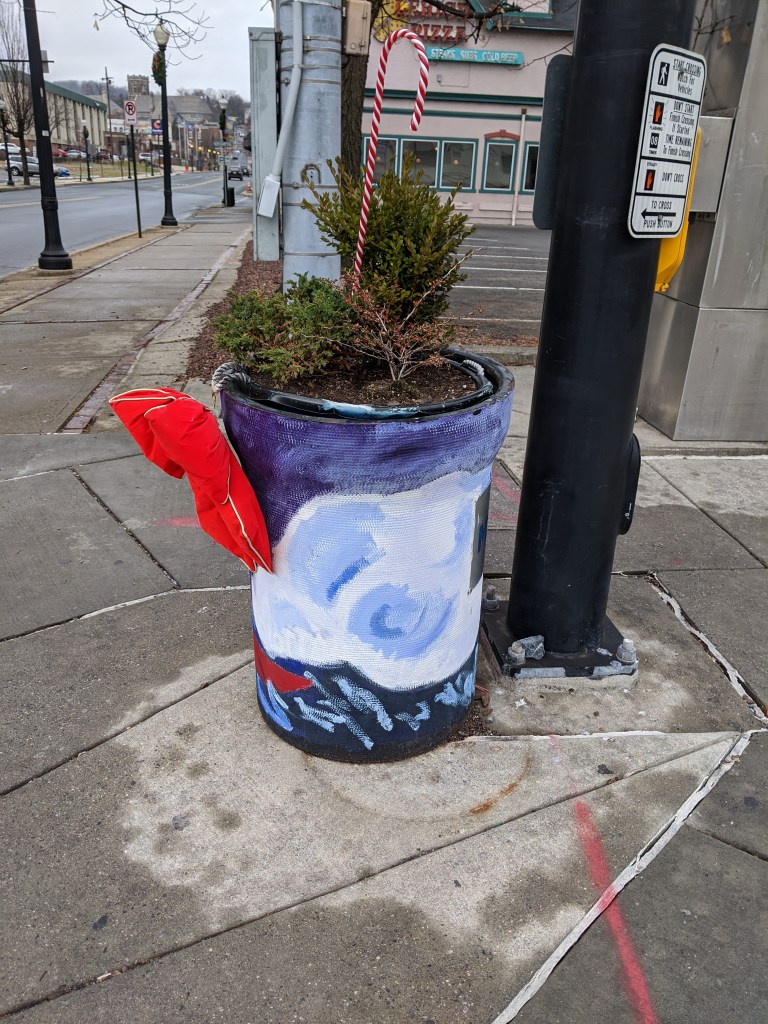
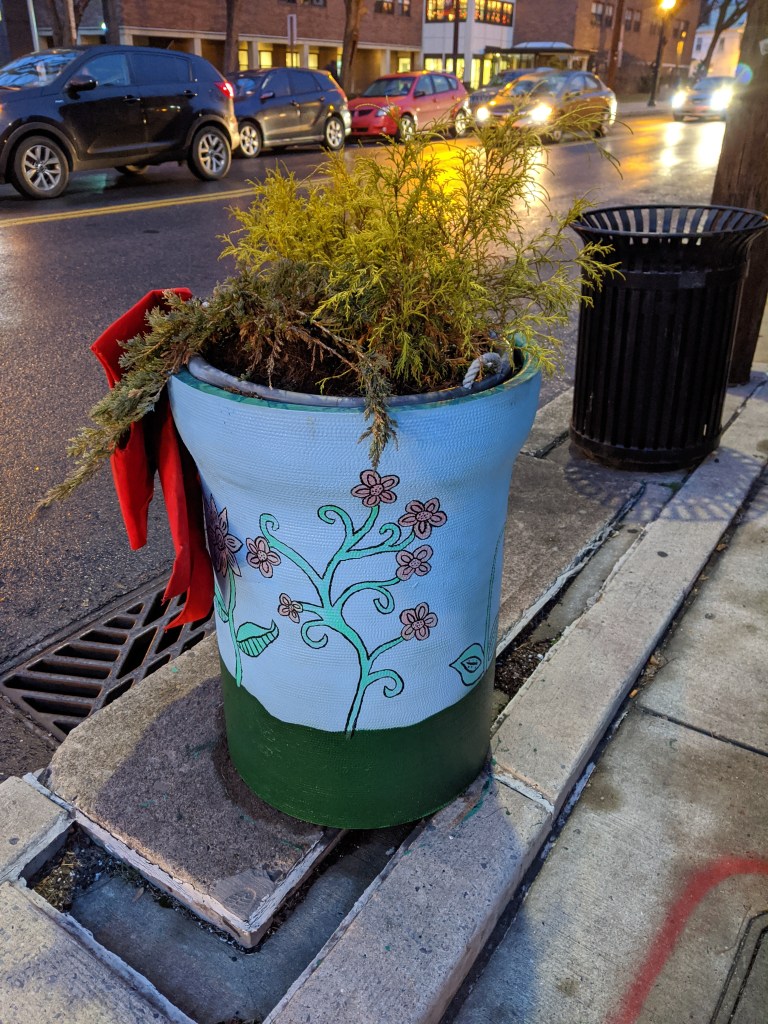
While looking for churches on Bethlehem’s South Side, I discovered fun, colorful planters lining the business district’s streets. I photographed 25 that were along my path, though there were many others if I had taken time to continue wandering.
The planters are a beautification project of Bethlehem’s South Side Arts District Main Street Program. Pittsburgh gets a shout-out as inspiration for the arts work of this organization, but I think they’ve surpassed Pittsburgh with this project. While Pittsburgh has various murals and hosted a dinosaur fiberglass fundraiser during that fad, it doesn’t have initiatives to turn everyday street objects into public art canvases. I’ve enjoy stumbling across these everyday artworks in Bethlehem and Harrisburg.
Keeping an Eye on Hazelwood (across the tracks): Sept. 2020
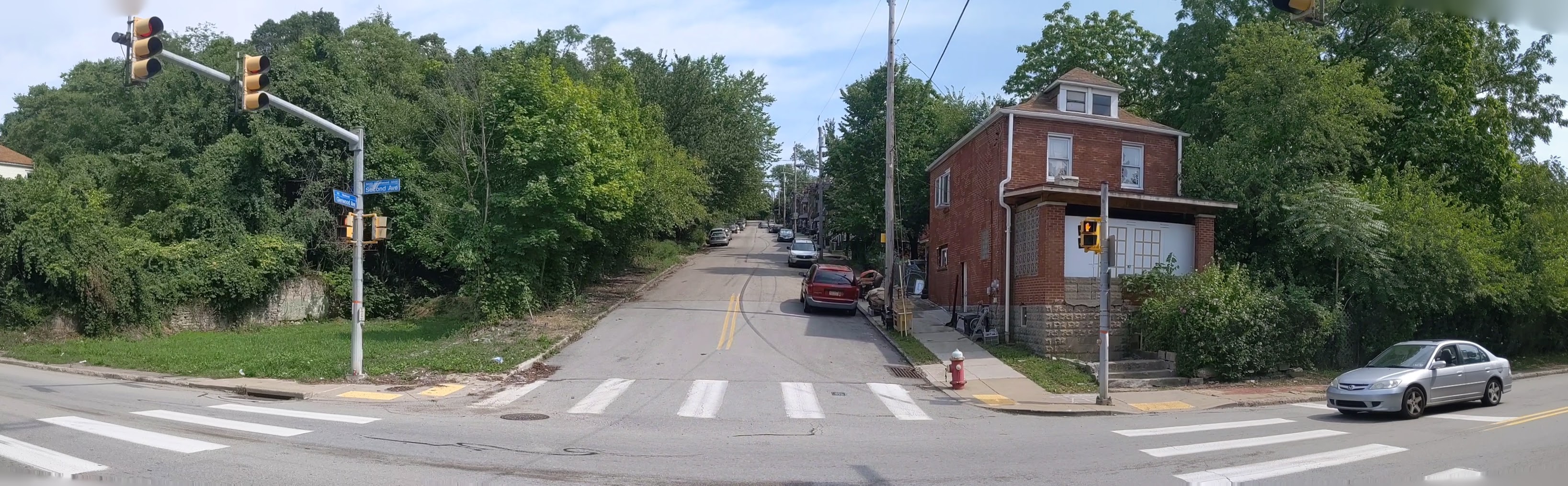
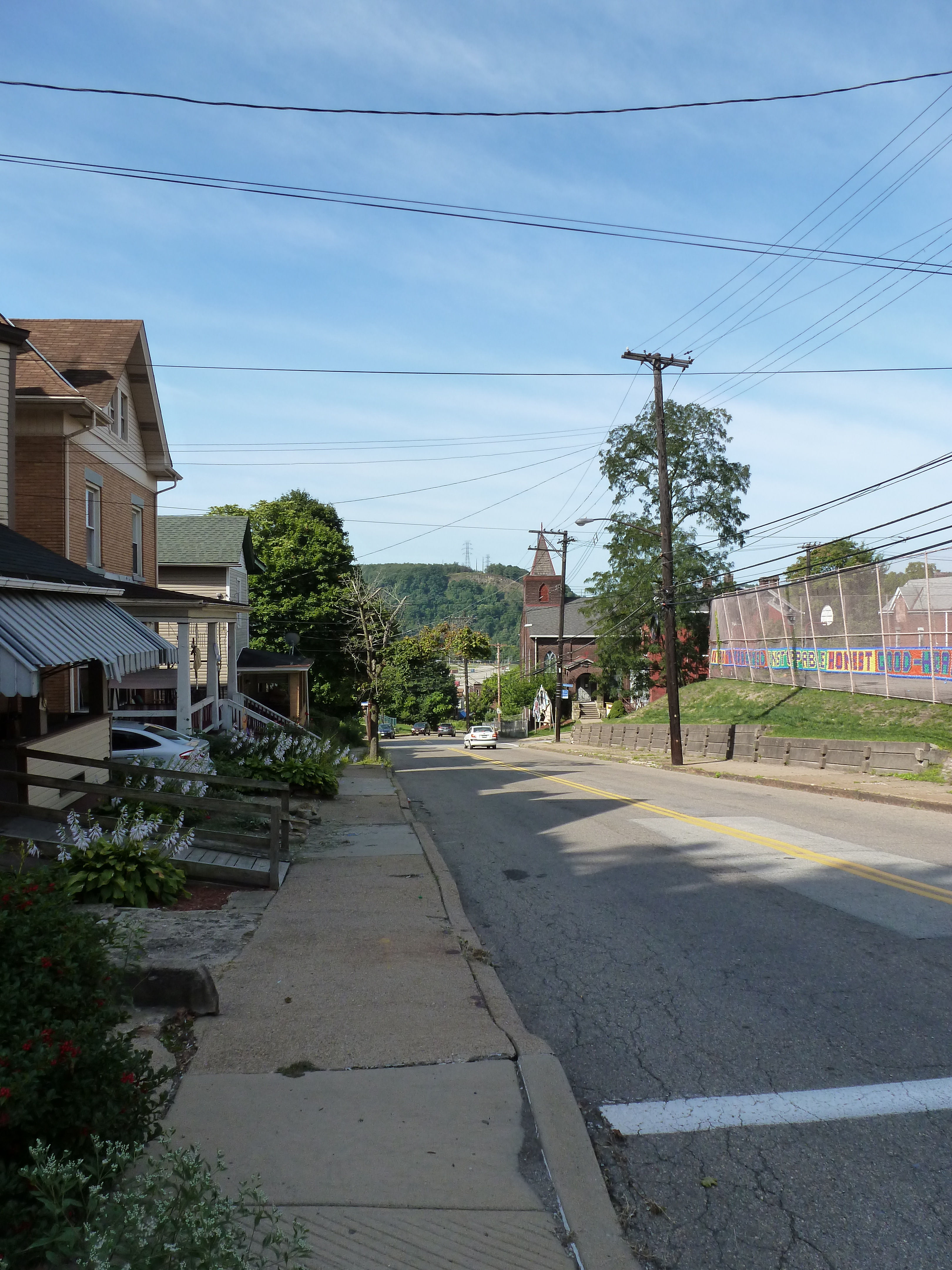
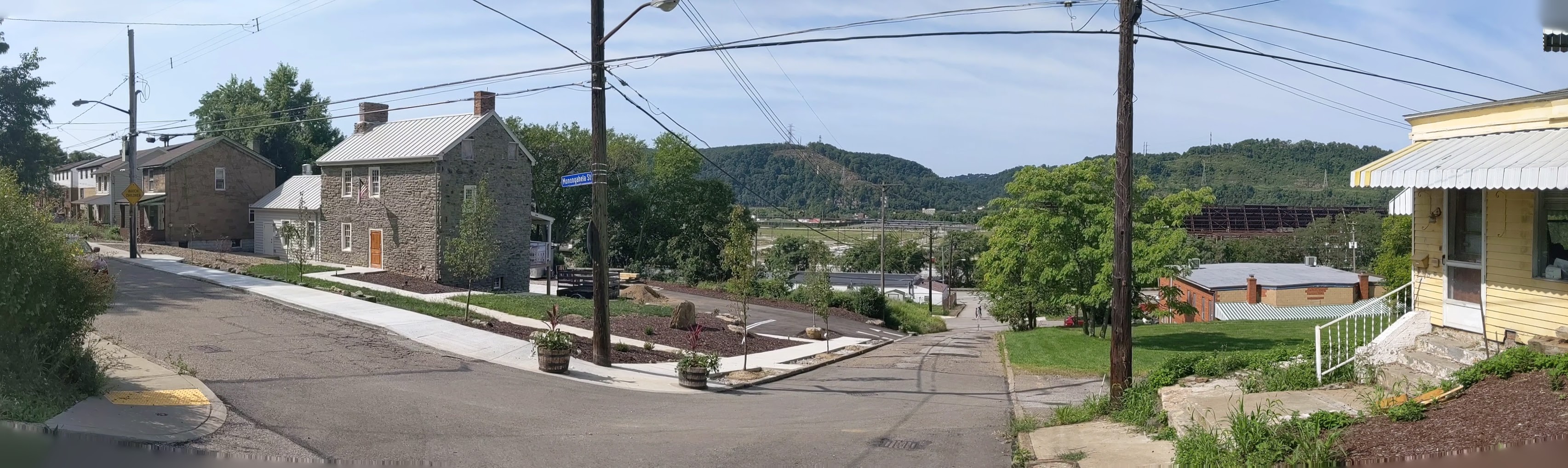
Hazelwood is a neighborhood divided in two by railroad tracks. On one side of the tracks are Hazelwood Green, a residential enclave, and some industrial and commercial uses. This is what is across the tracks:
Second Ave
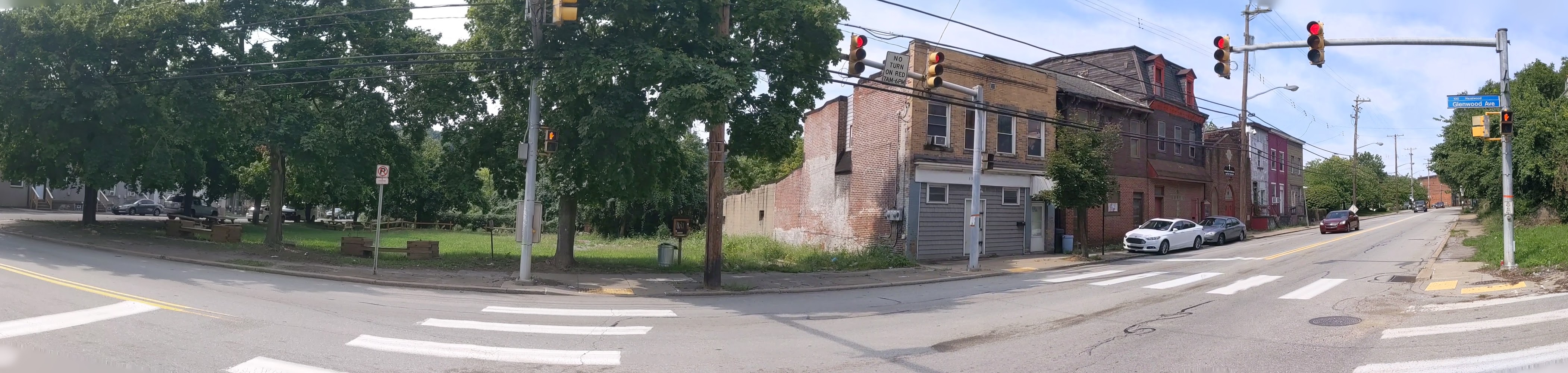
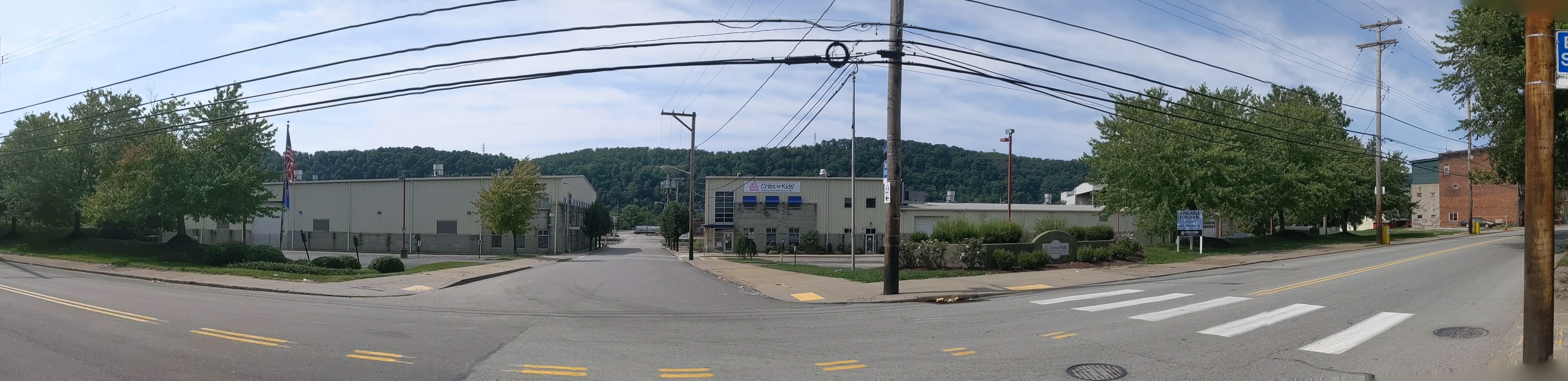
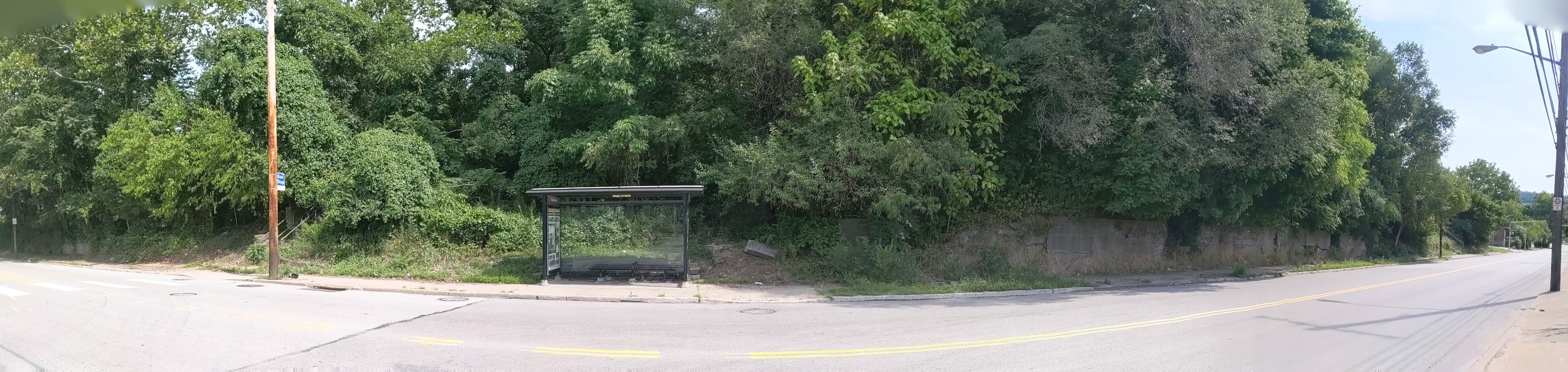
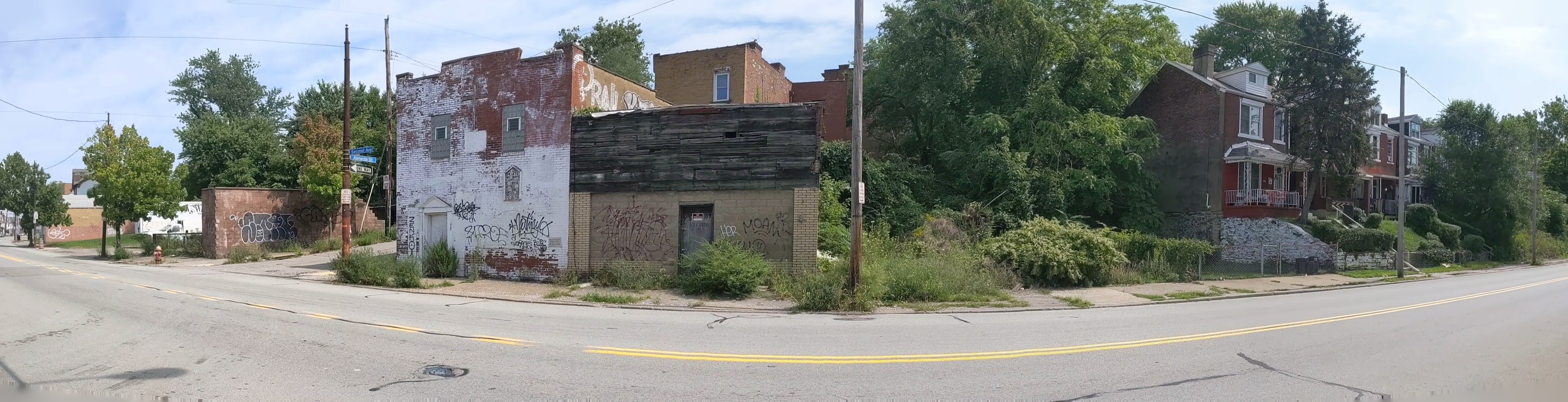
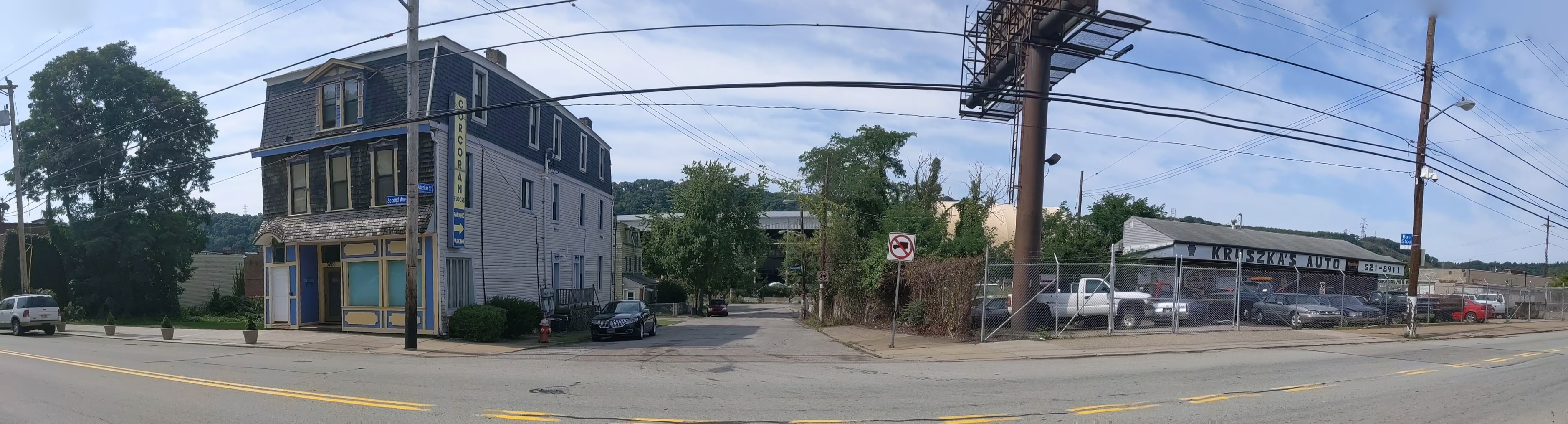
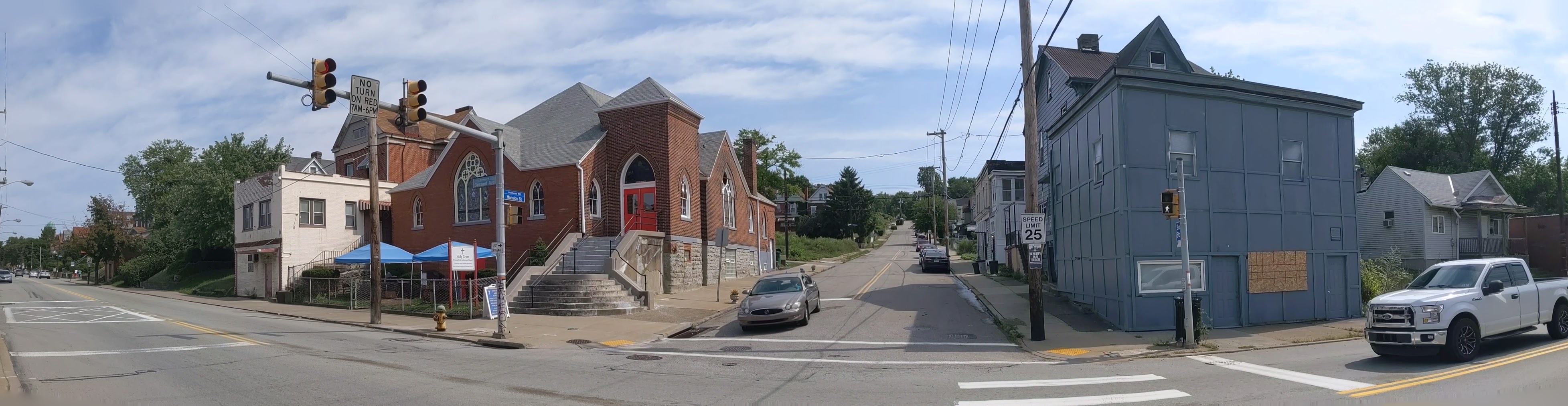
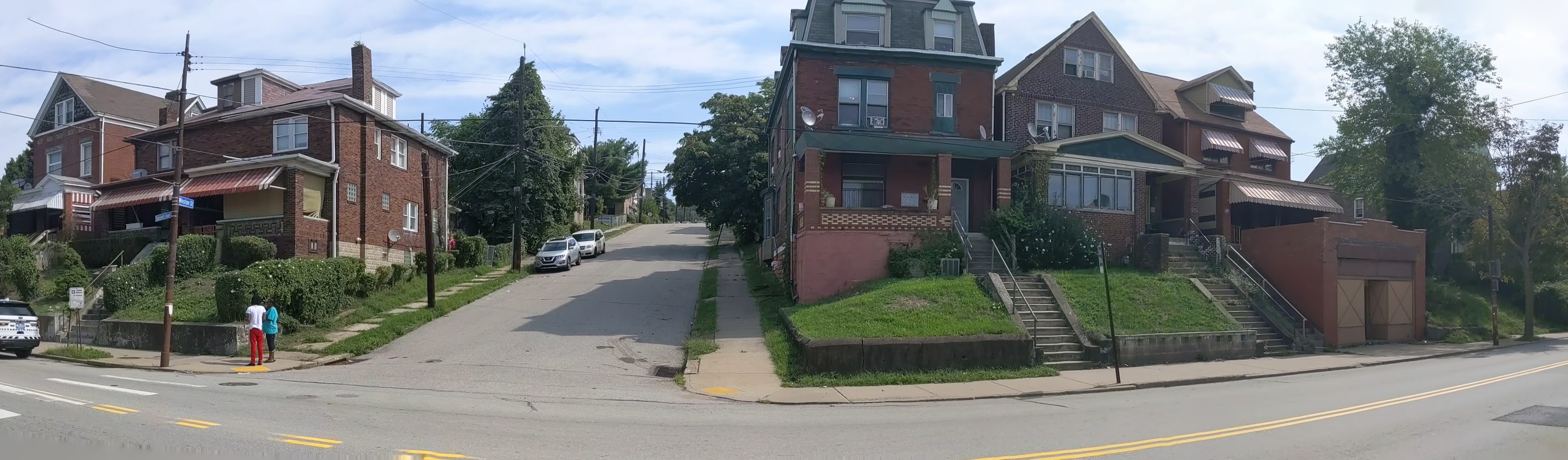
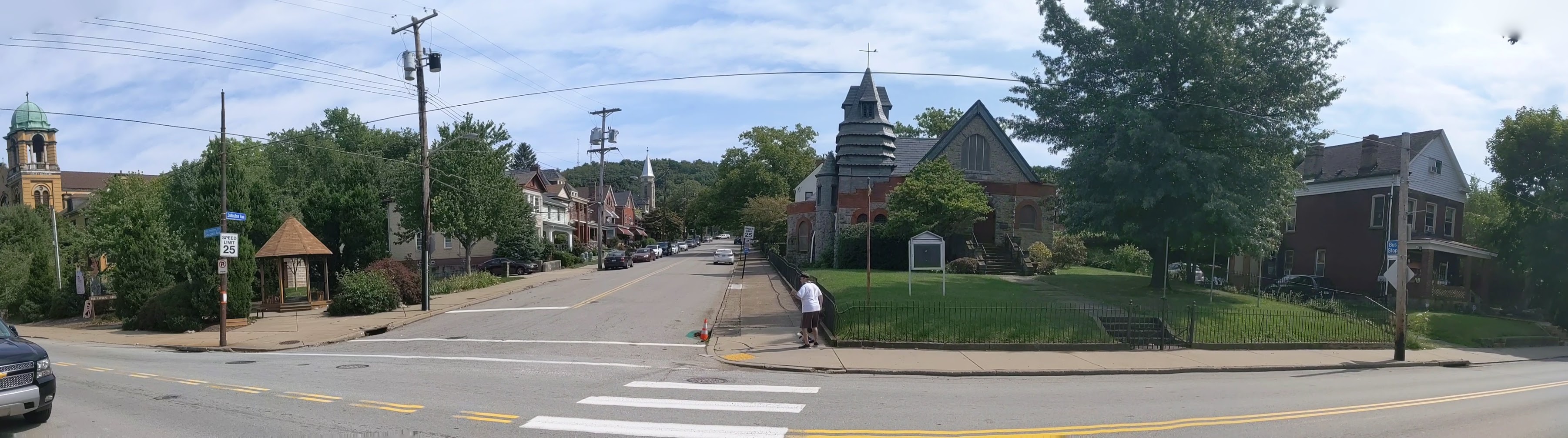
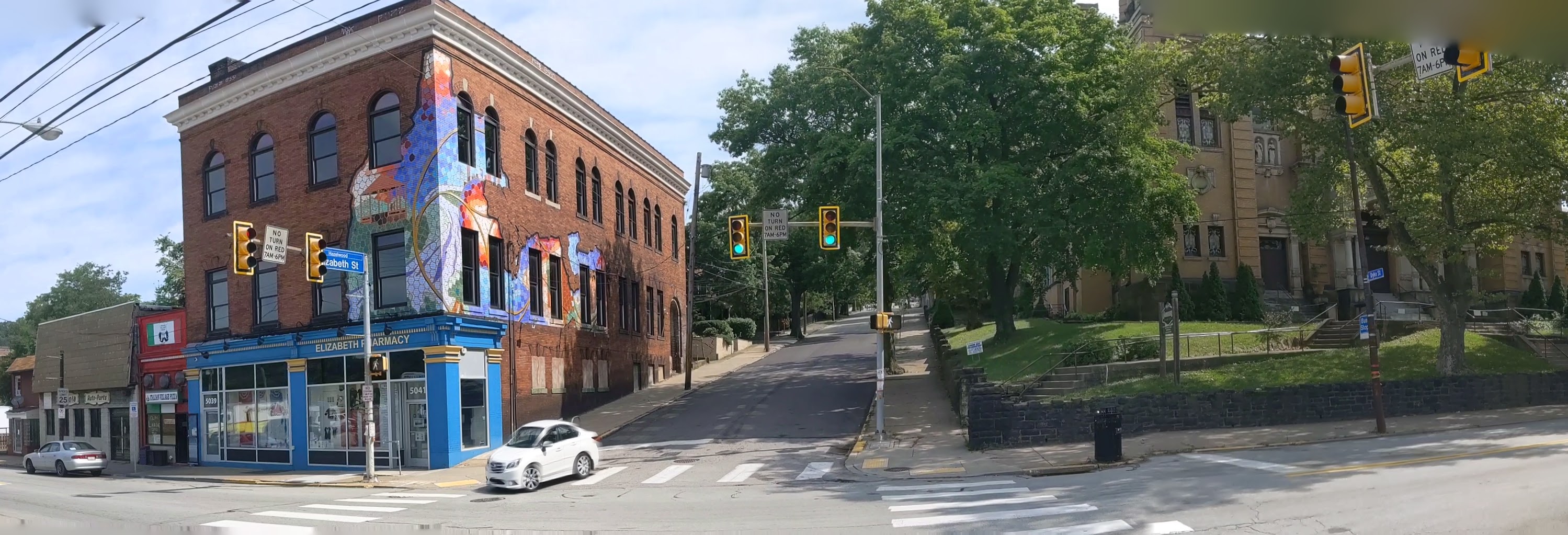
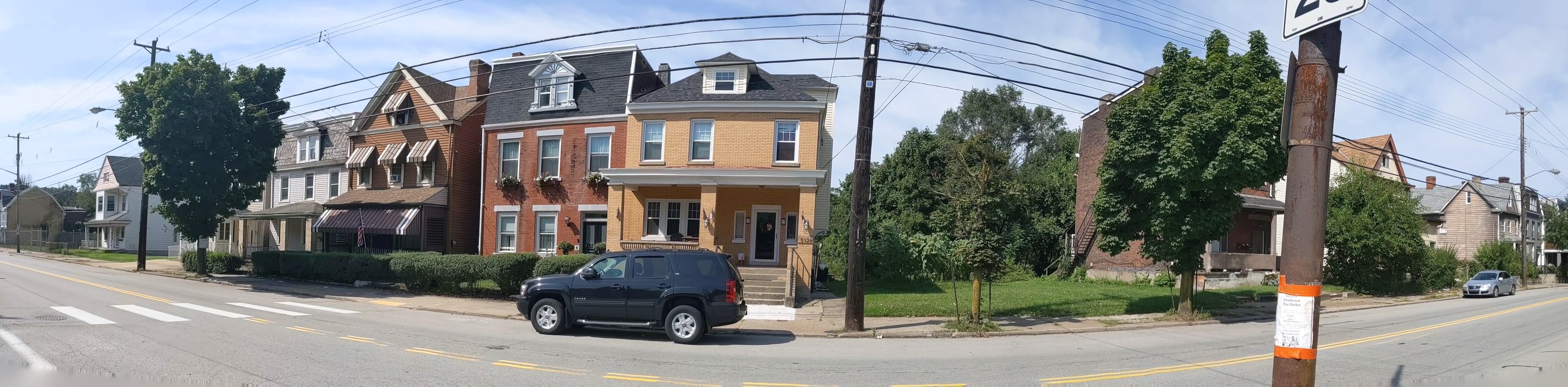
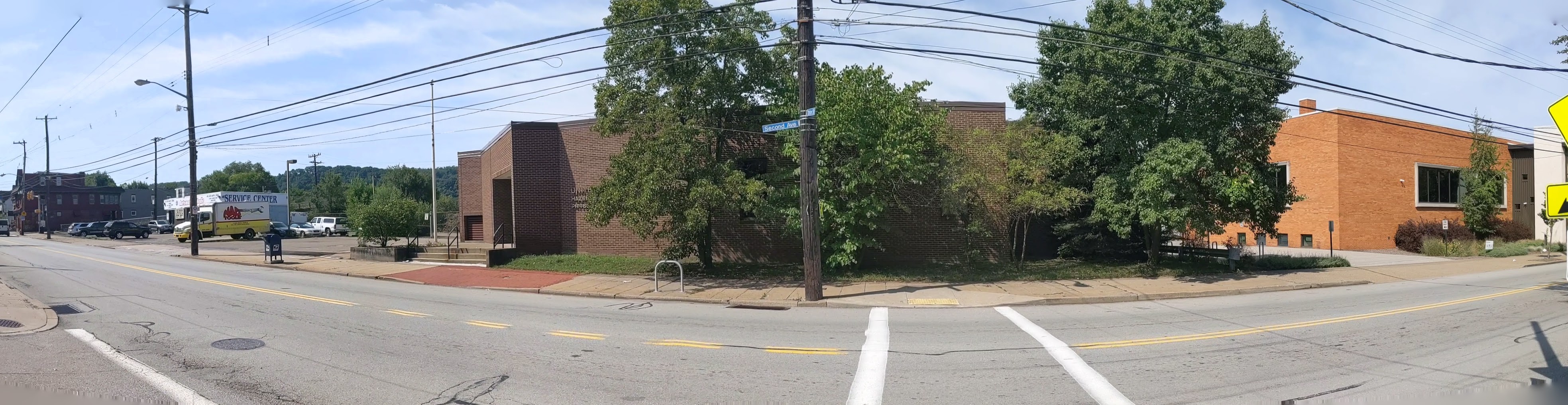
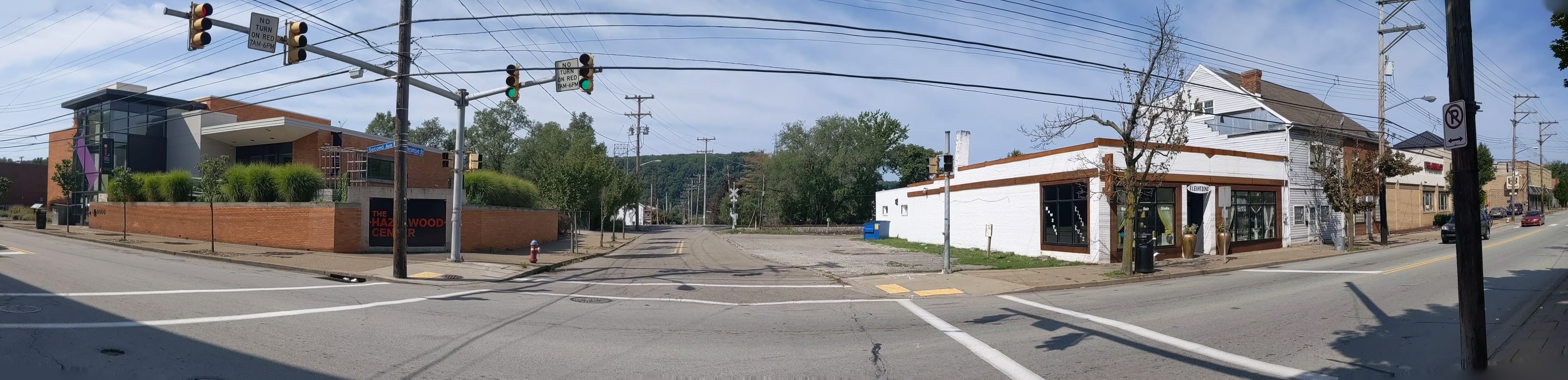
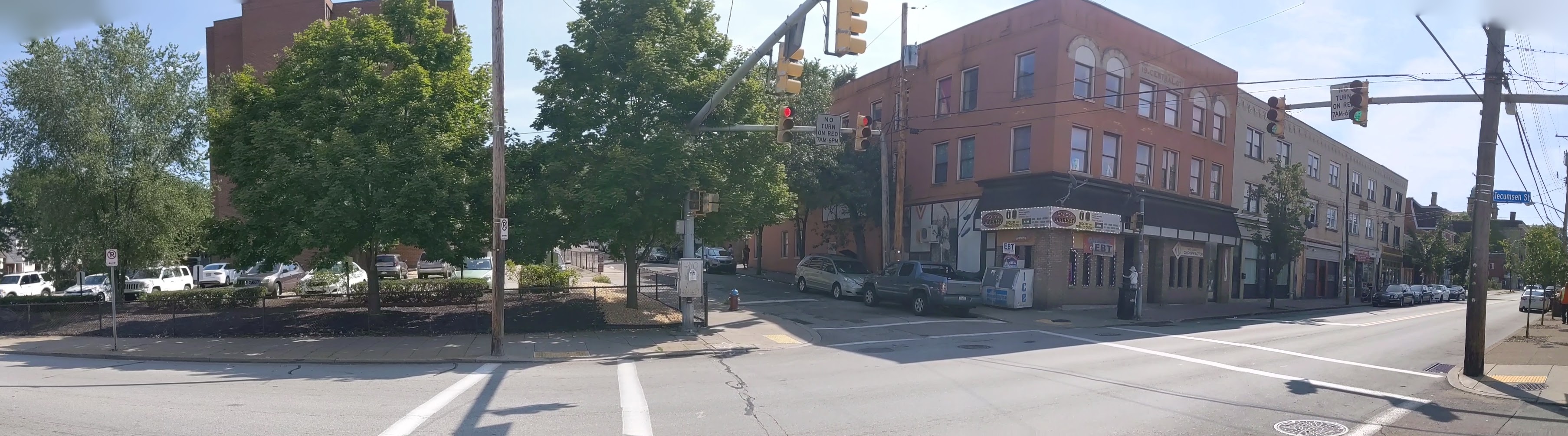
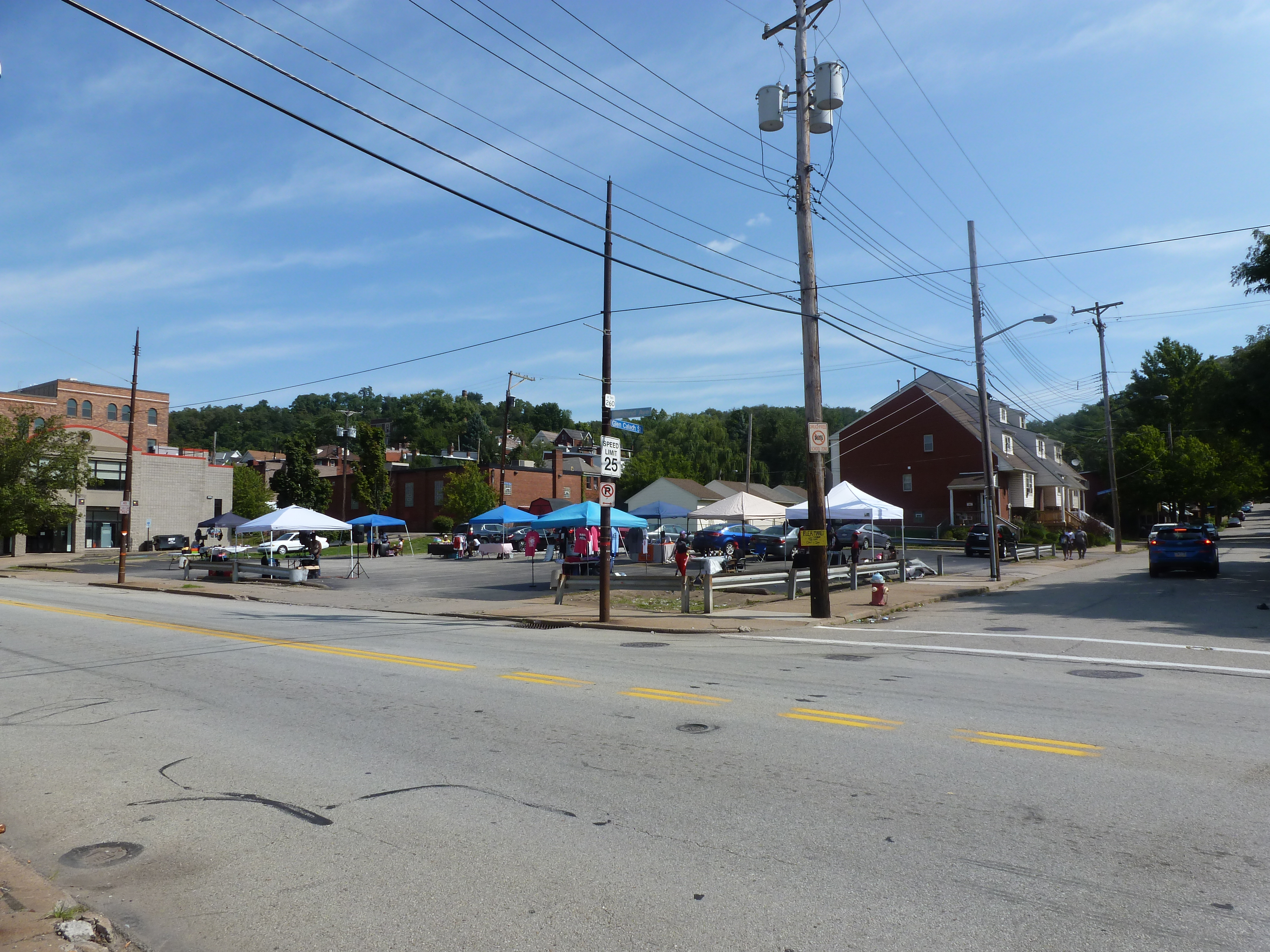
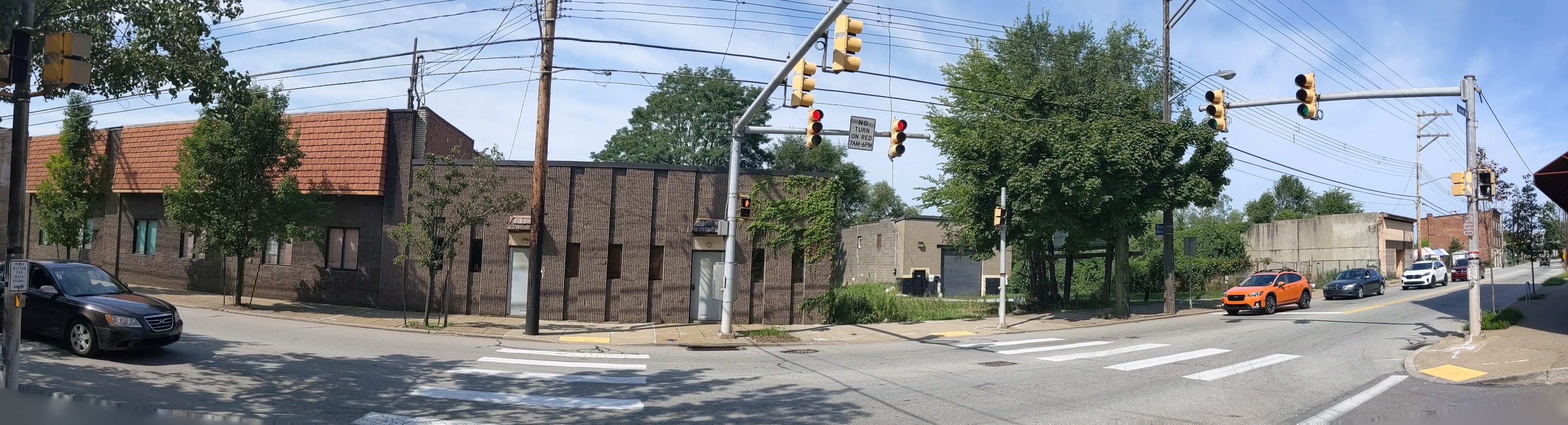
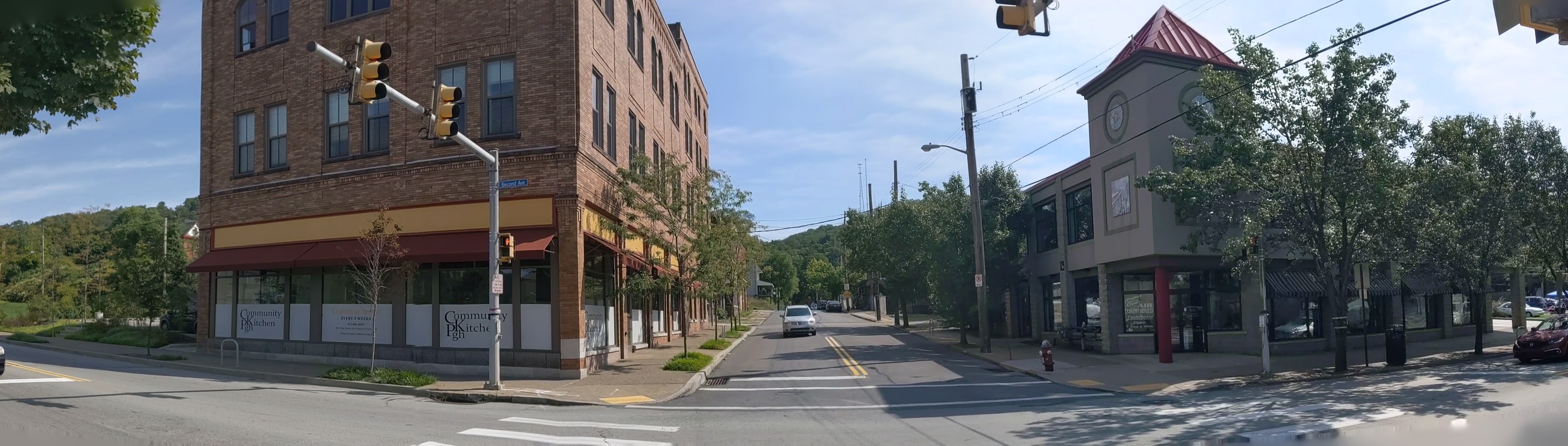
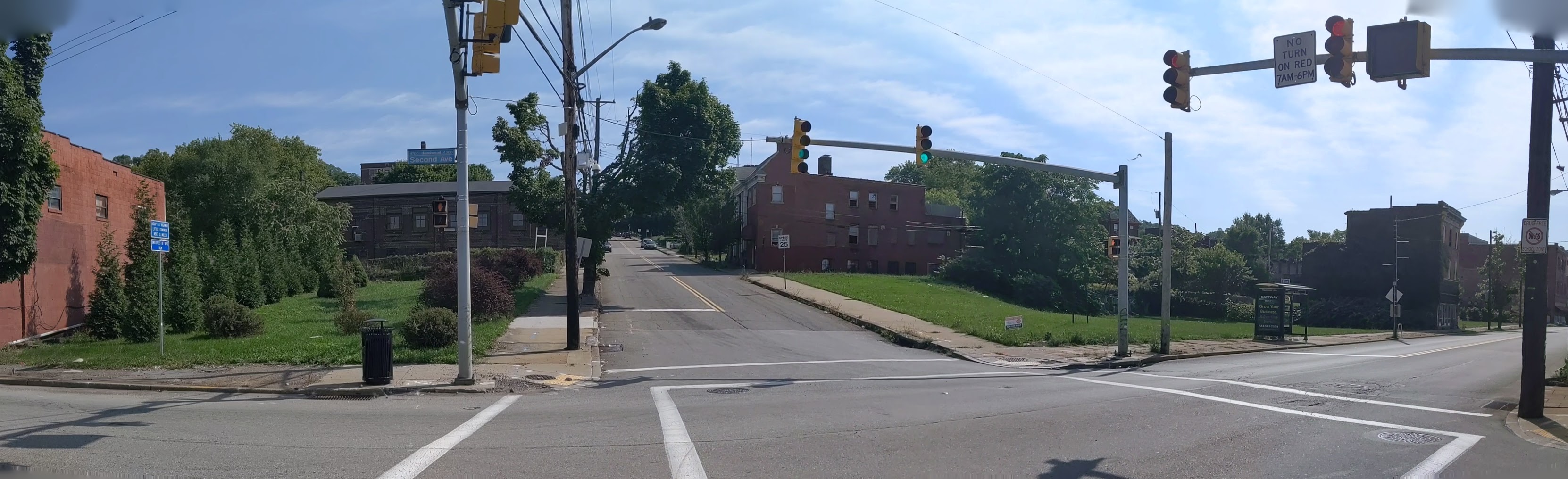
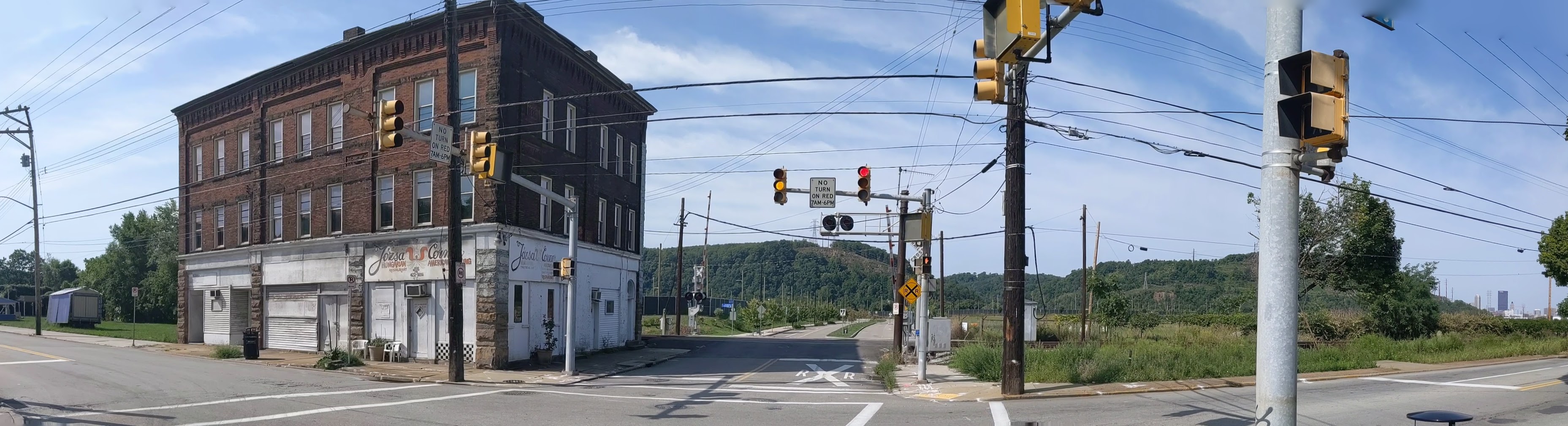
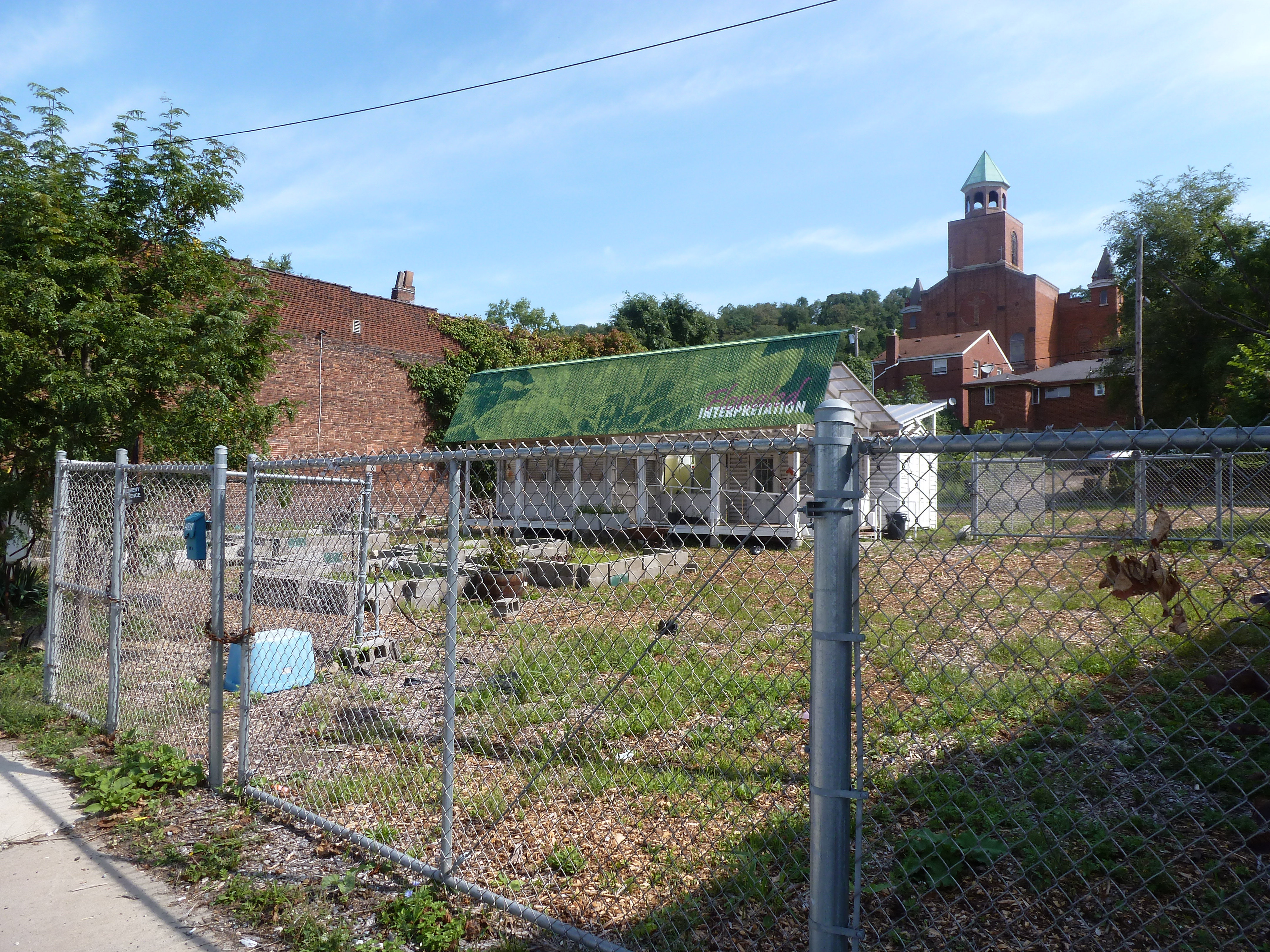
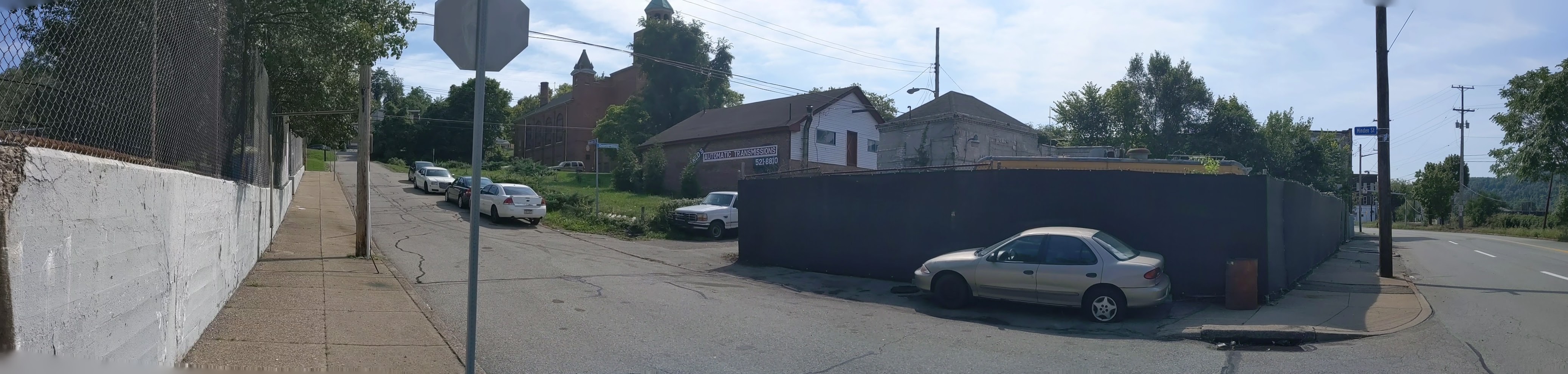
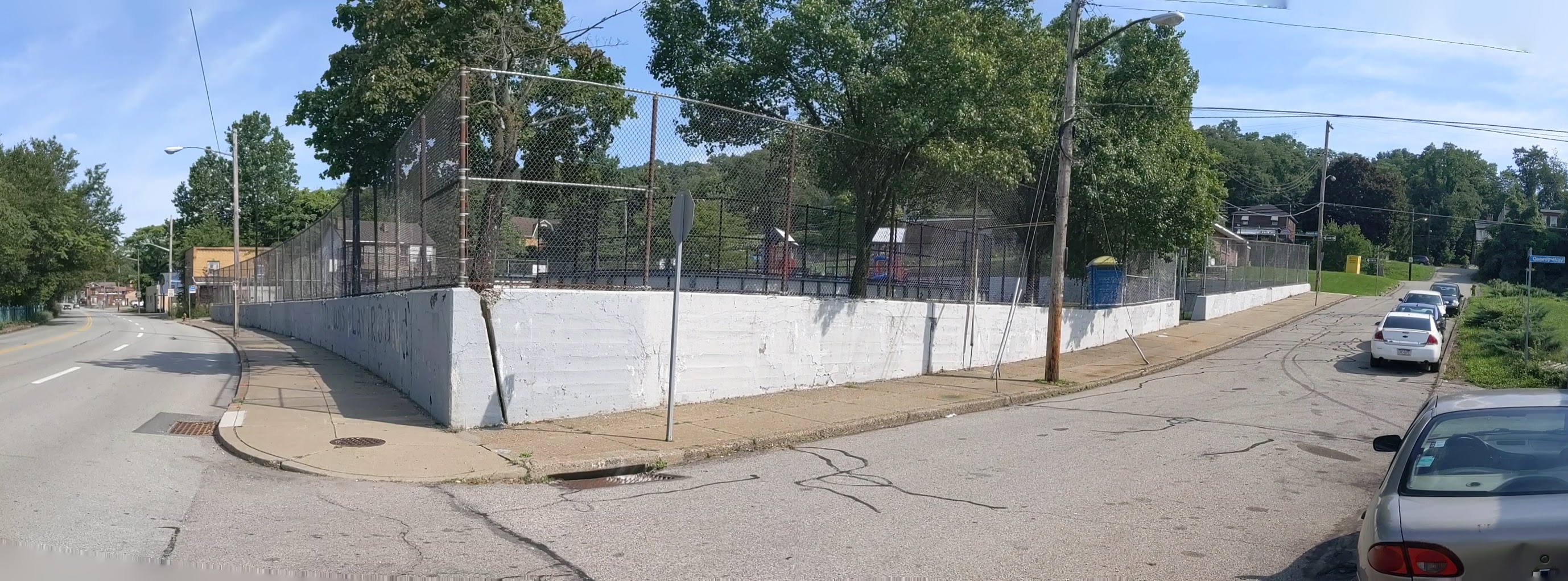
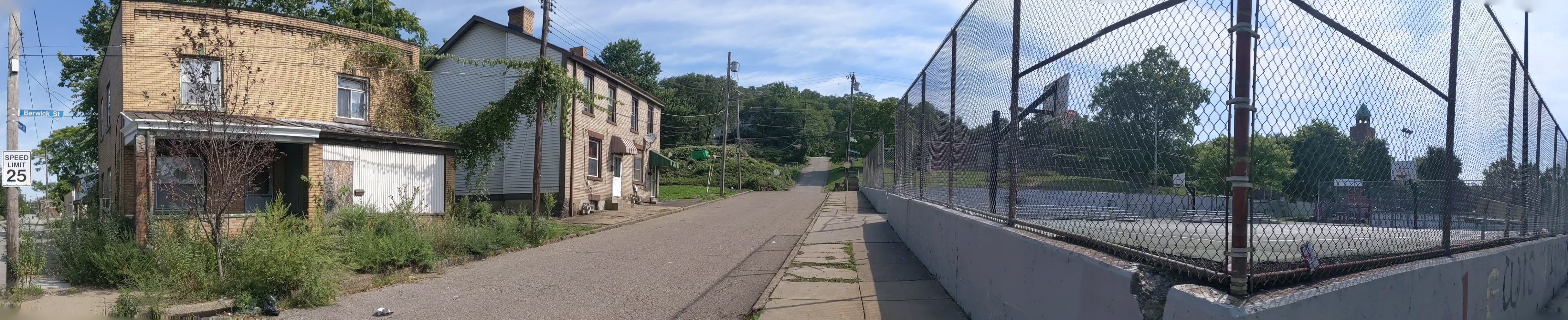
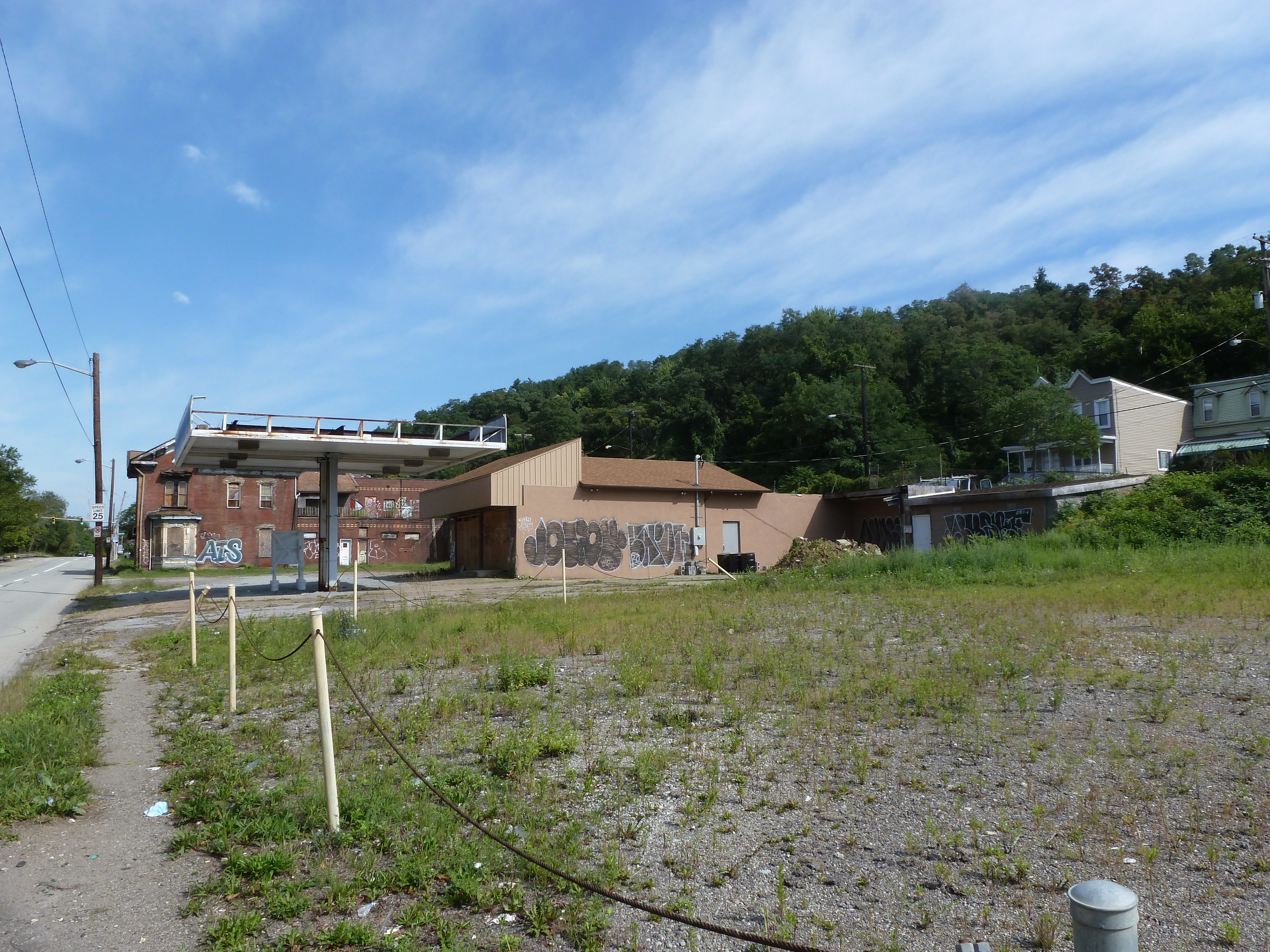
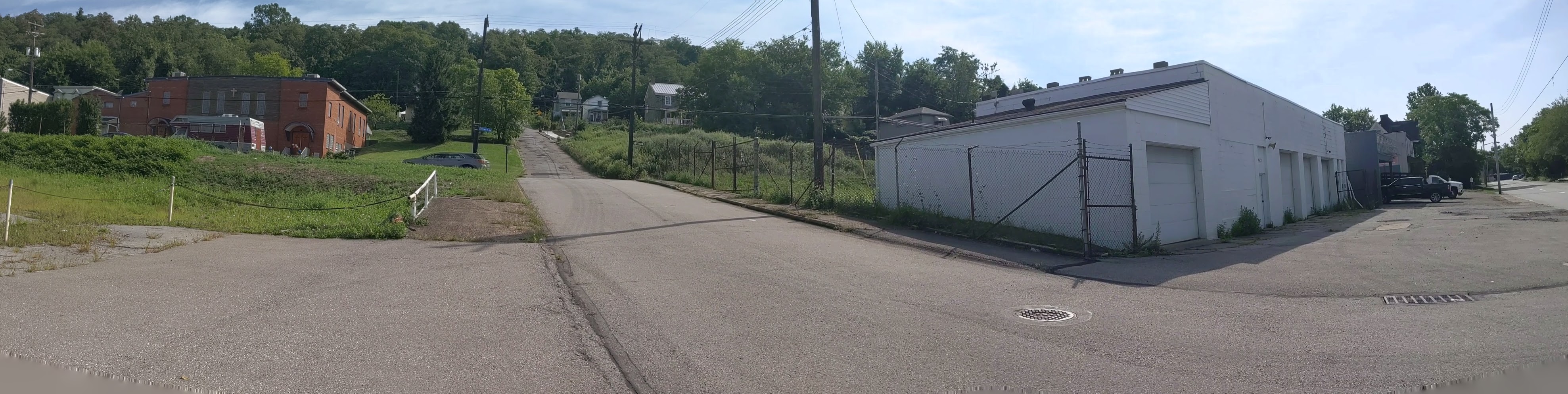
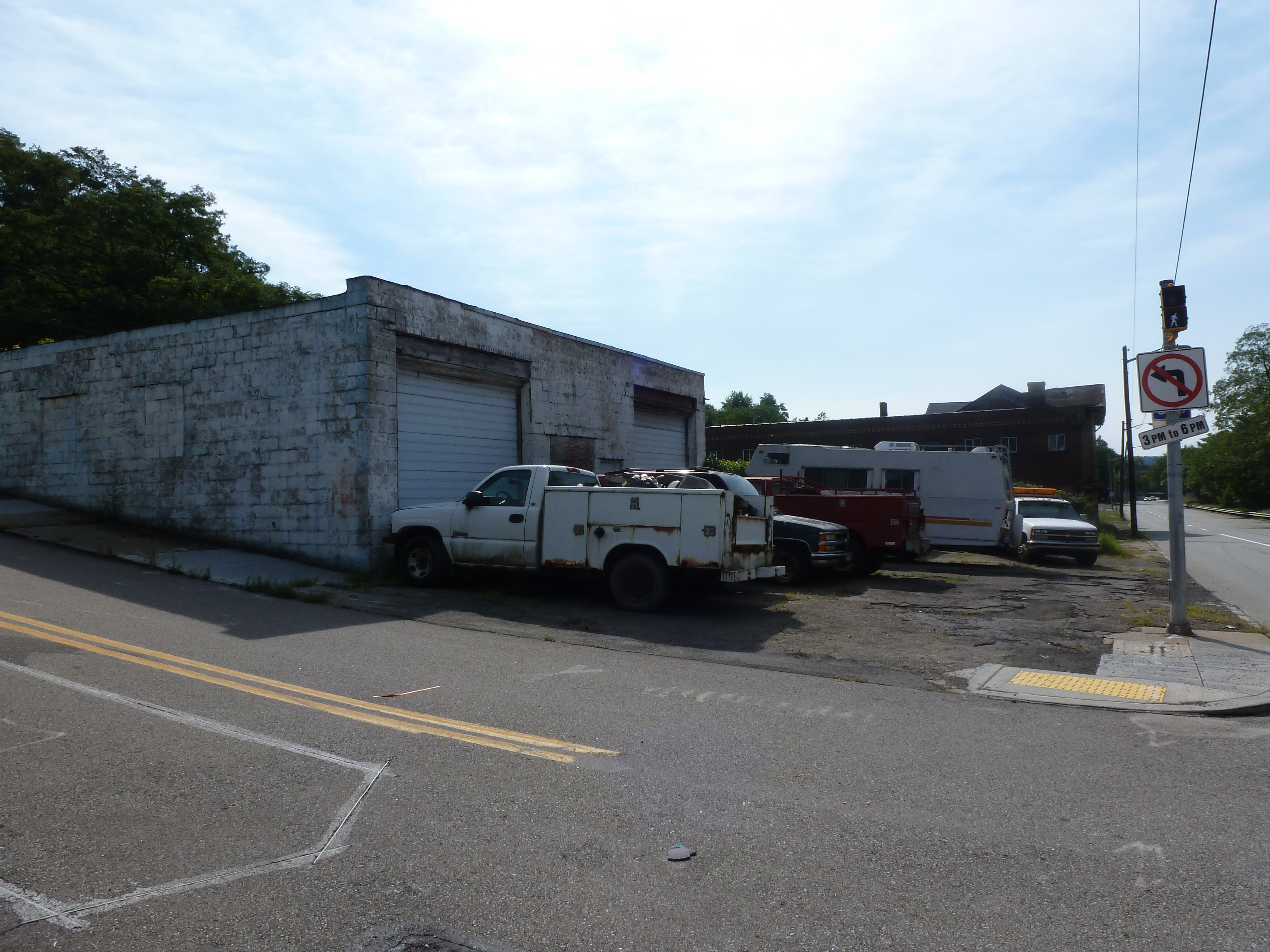
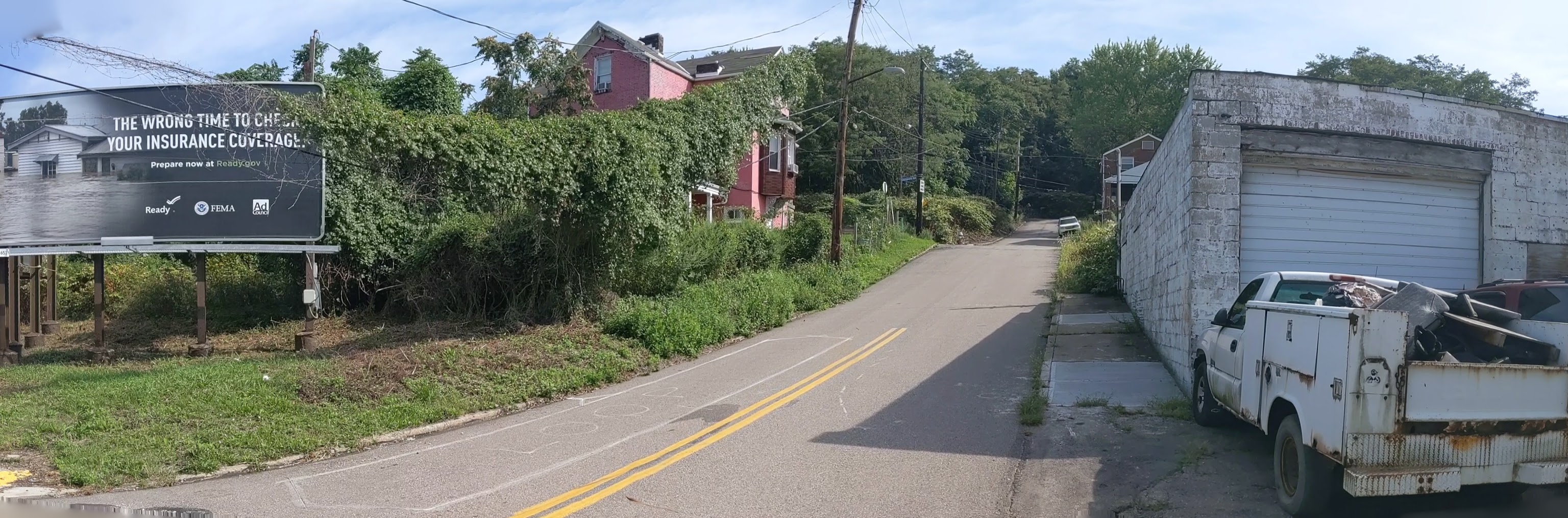































Hazelwood Ave
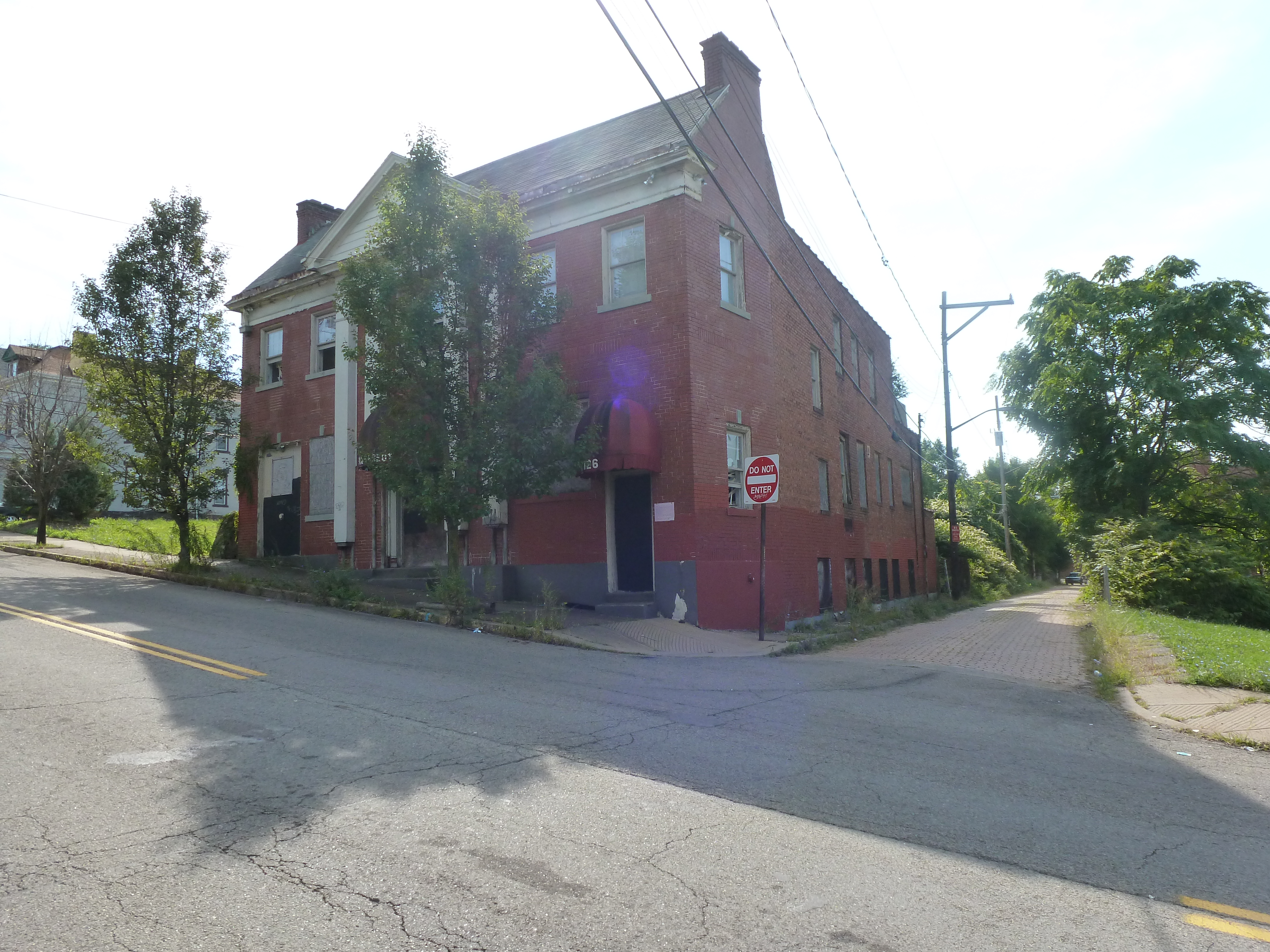
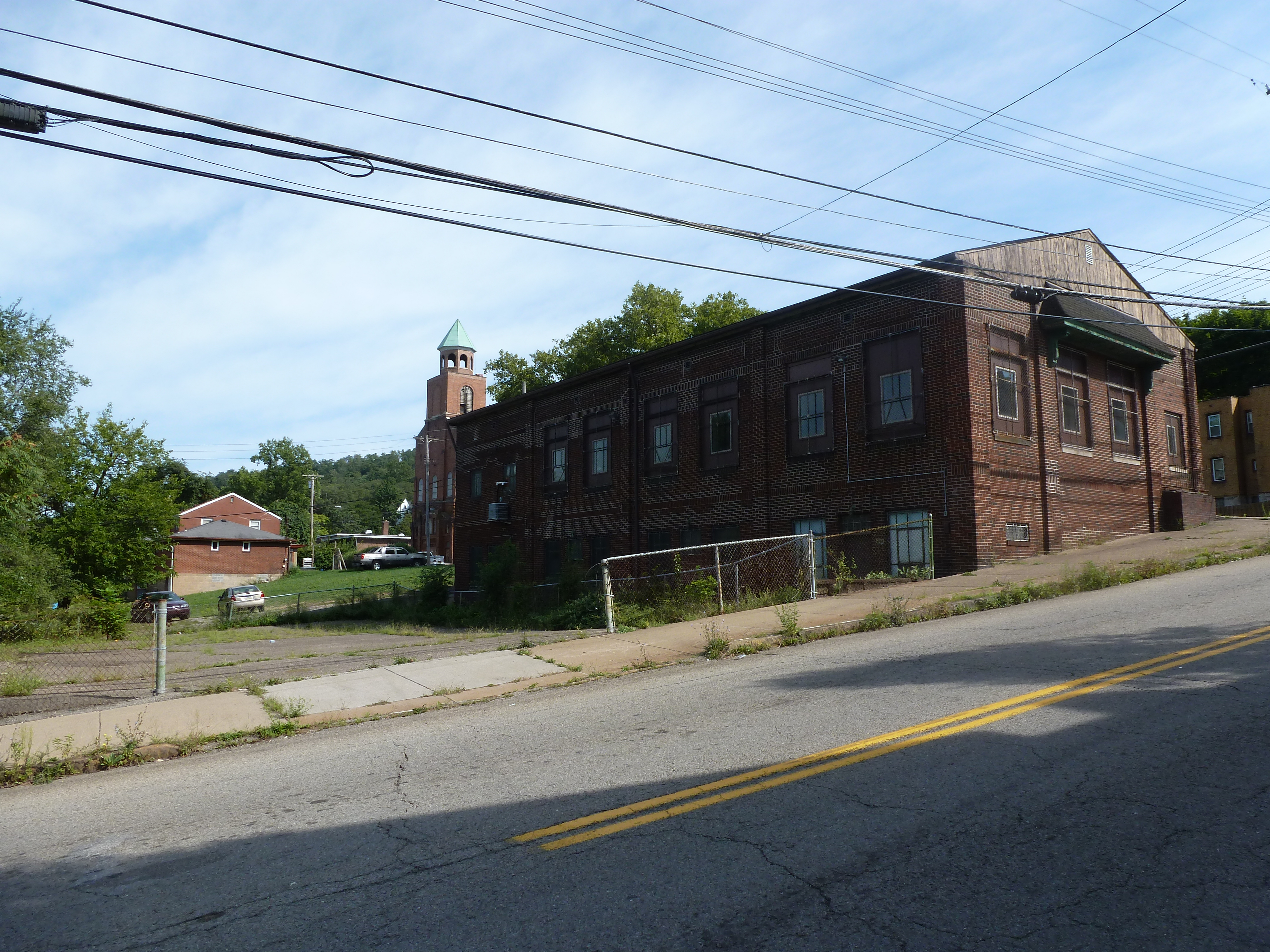
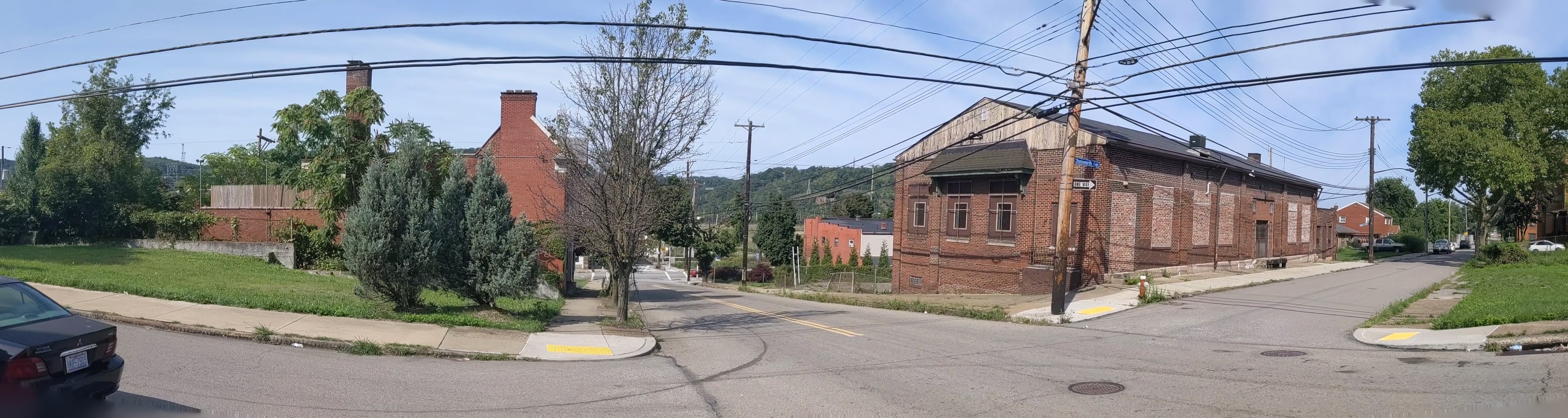
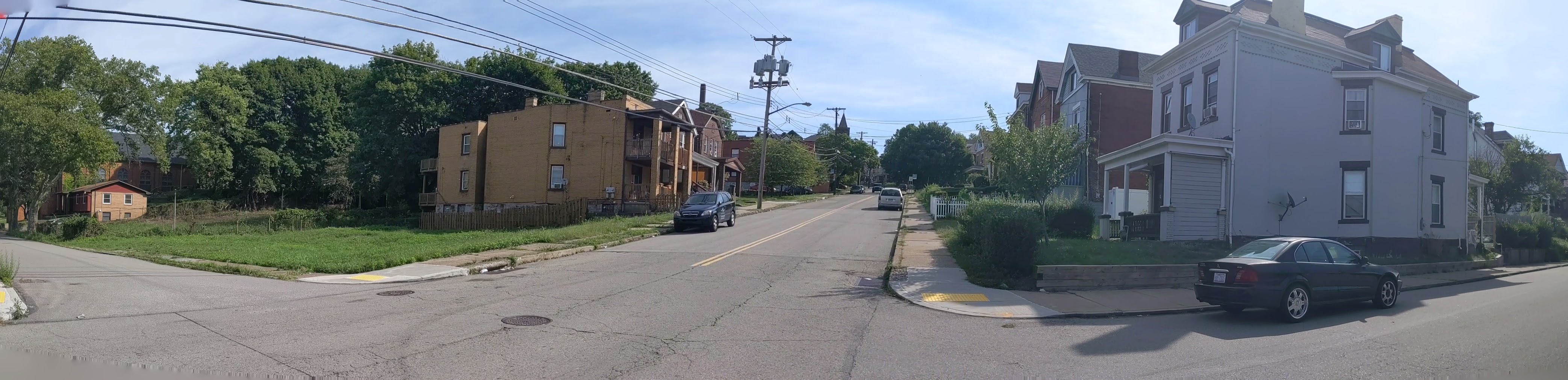
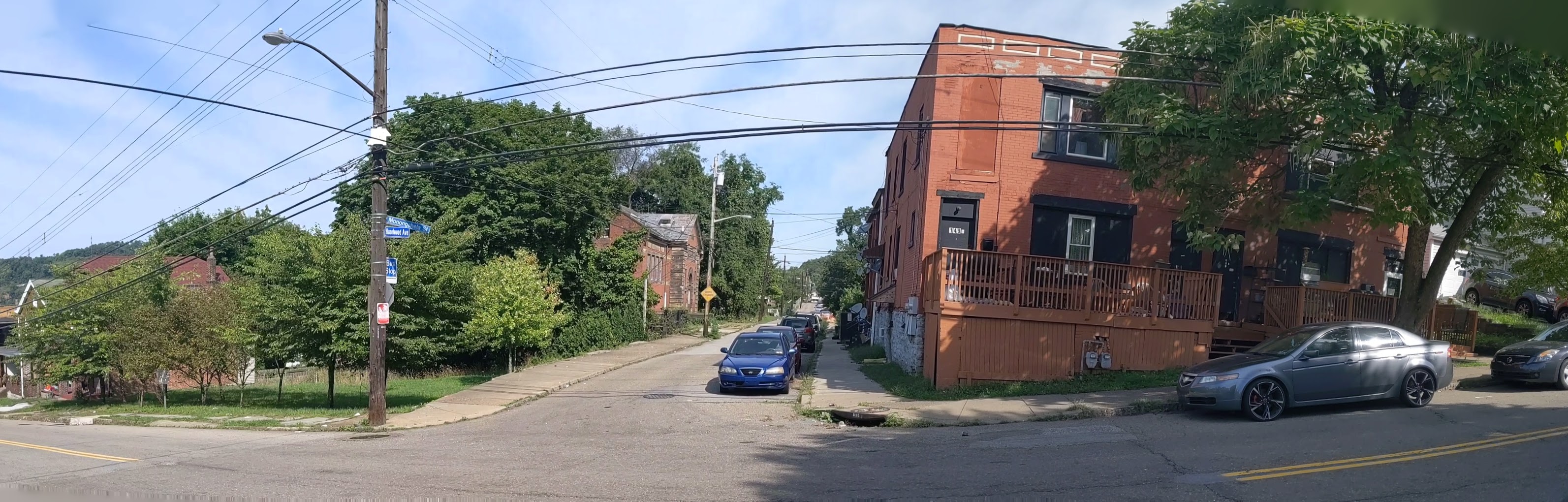
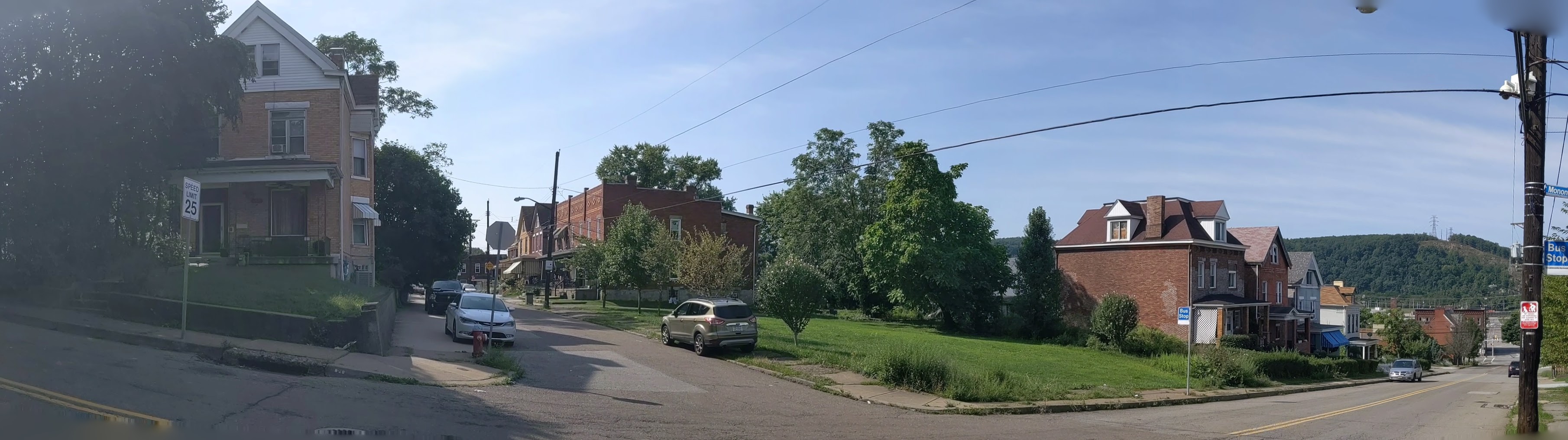
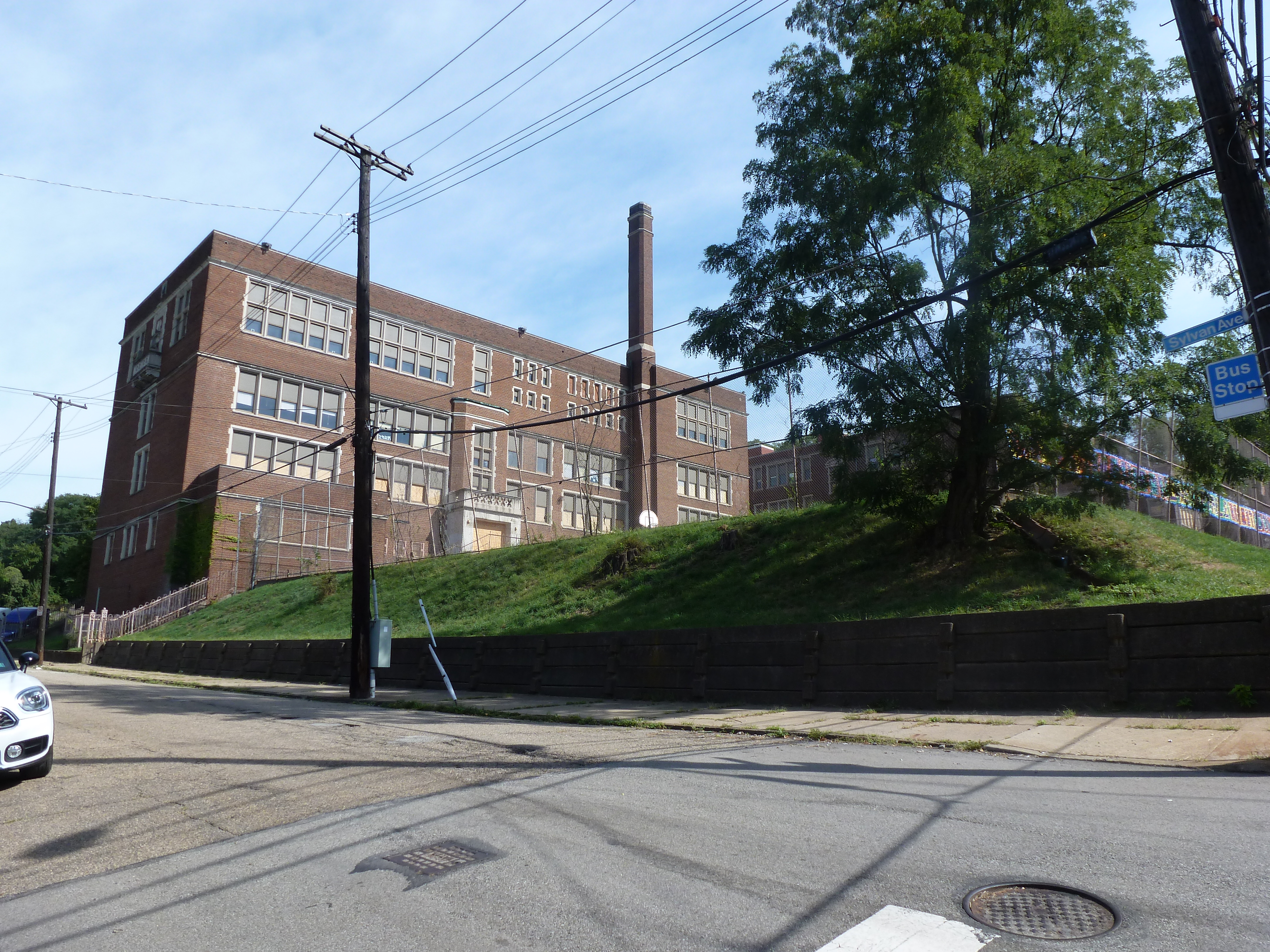
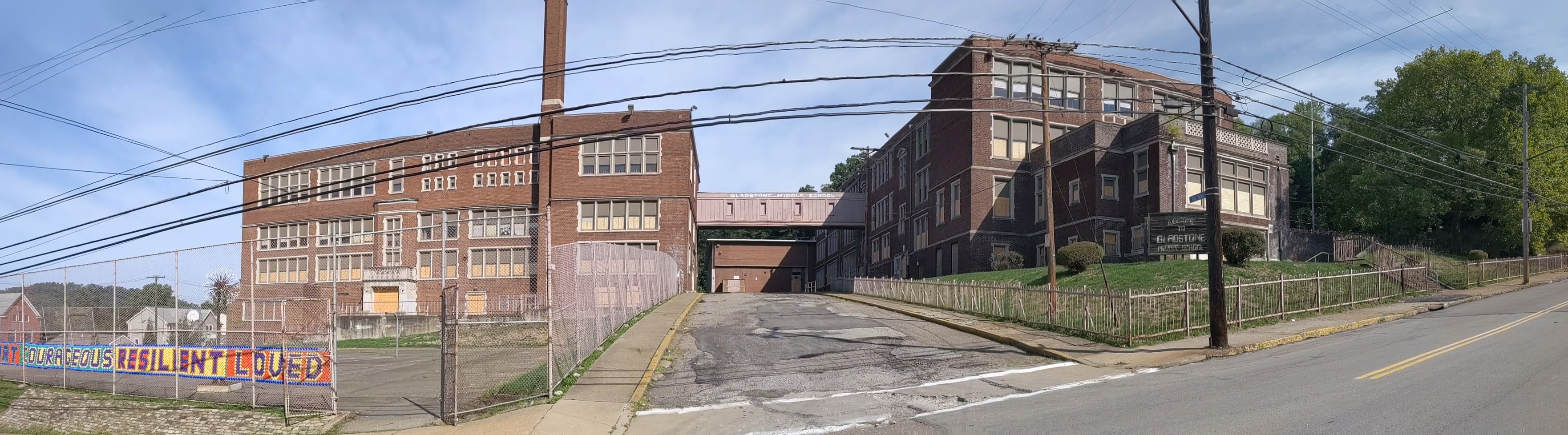










Other Sites


Hazelwood in the News:
New Businesses Revitalizing Second Ave (Next Pittsburgh, November 21, 2019)
URA Picks Community Builders for Affordable Housing Development on Second Ave (Pittsburgh Business Times, January 15, 2020)
Study Pushes Multi-modal Transit Improvements to Hazelwood’s 2nd Avenue (Post-Gazette, February 10, 2020)
Report Says Traditional Buses Better for Hazelwood than Autonomous Shuttles (City Paper, April 21, 2020)
Restaurants Reopen – Diners Return (Post-Gazette, June 28, 2020)
66 New Homes Proposed (Pittsburgh Business Times, September 10, 2020)
Previous posts in series:
Keeping an Eye on Hazelwood (across the tracks): Apr. 2020
Keeping an Eye on Hazelwood: Introduction
Keeping an Eye on Penn Plaza – Aug. 2020
I regret not starting this series on the former Penn Plaza site sooner. I missed opportunities to photograph the former apartments in their neglected, partially occupied state and the demolition of the buildings. Starting with the project several months into construction is a case of better late than never and provides an opportunity to watch how the promise to rebuild the neighborhood park becomes fulfilled.
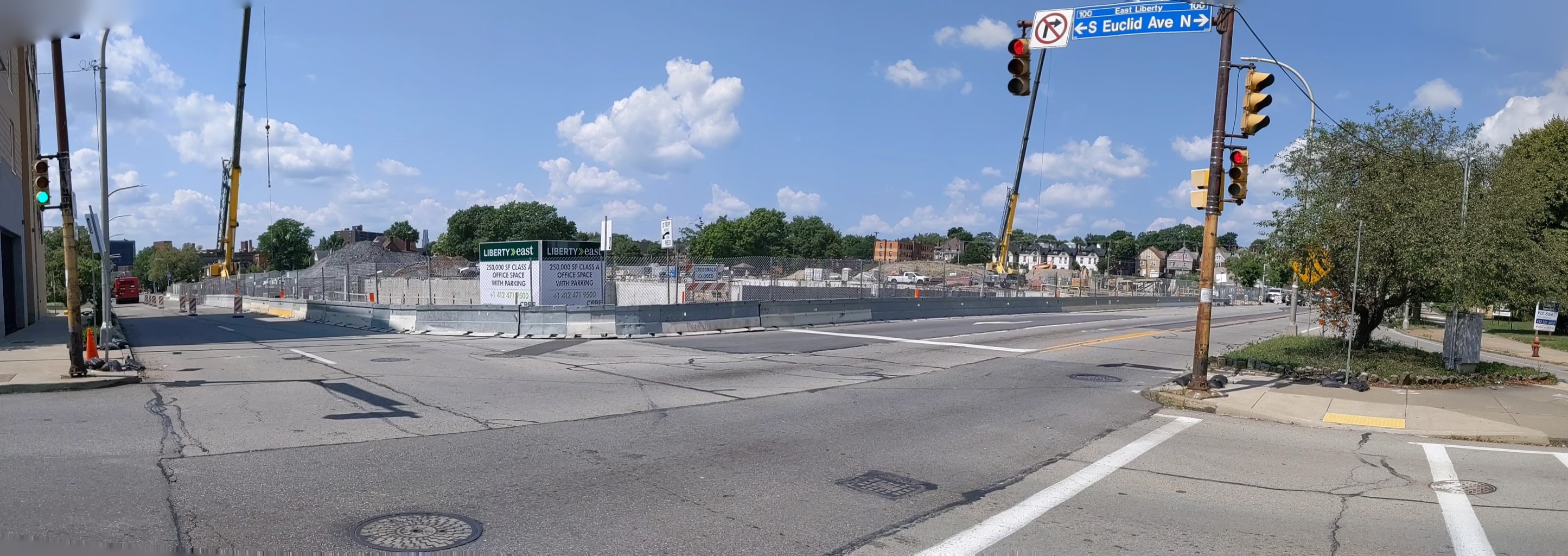
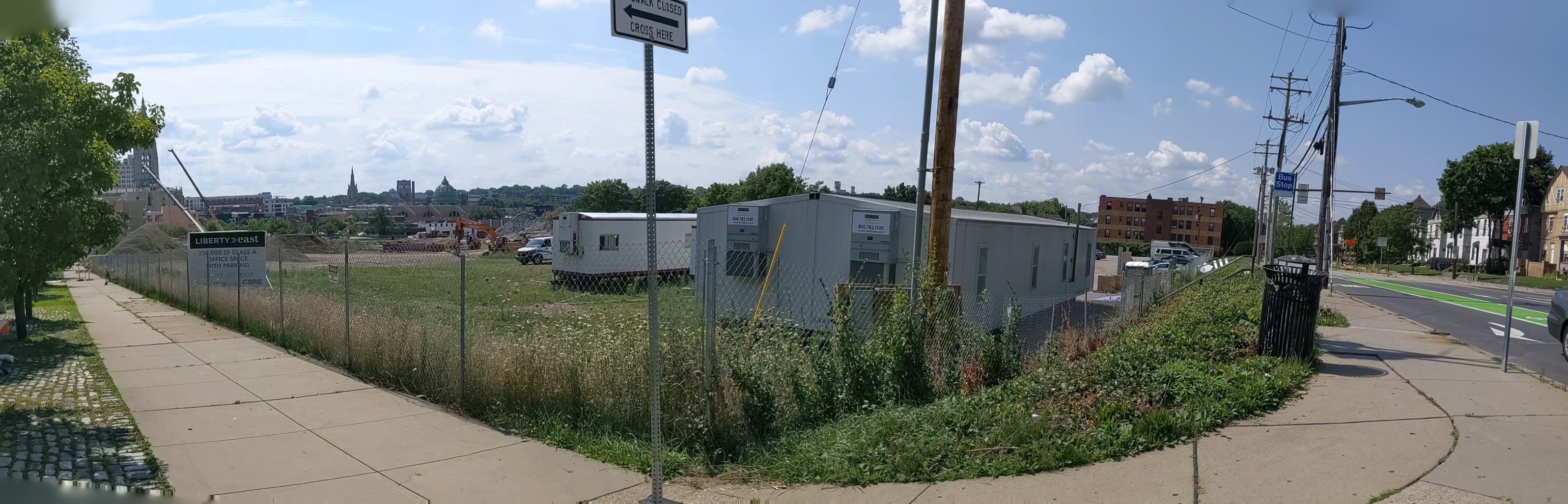
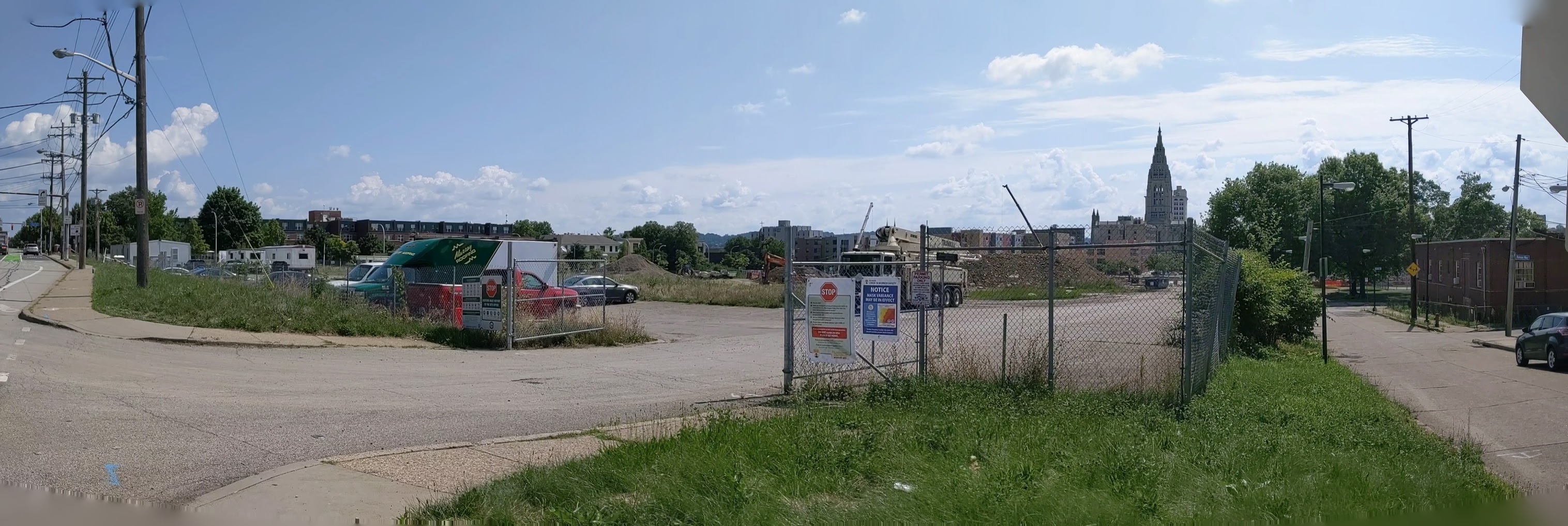
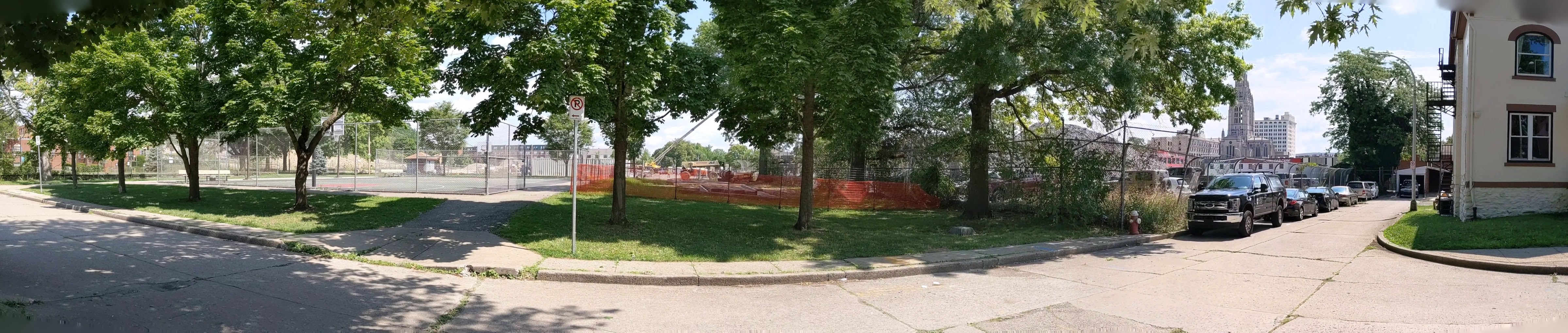
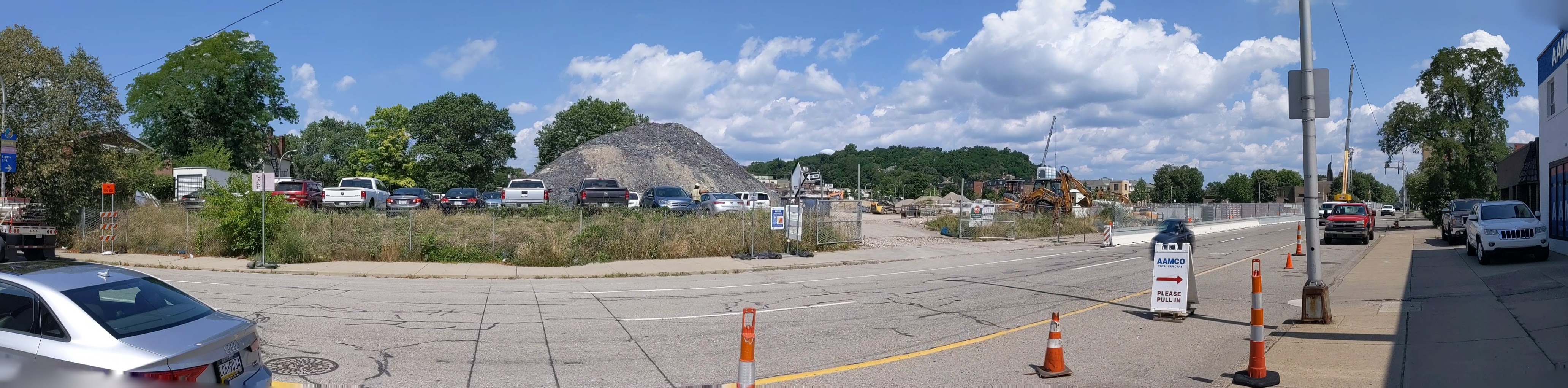








Penn Plaza in the News
Evictions 2015-2019:
Evictions Highlight Lack of Affordable Housing (City Paper, July 22, 2015)
Residents Meet About Eviction Notices (New Pittsburgh Courier, July 23, 2015)
Evictions Set Standard for Future (WESA, February 29, 2016)
Owners and Displaced Tenants Work out Deal (WTAE, February 29, 2016)
Final Residents Move Out (WESA, March 31, 2017)
Mass Evictions (Downstream, February 15, 2018)
Protesters Call for Action Years After Evictions (KDKA, July 28, 2018)
Dark Stain on the City (Pittsburgh Current, July 30, 2018)
Defining Community (Public Source, September 27, 2019)
Negotiations 2017-2019:
Penn Plaza Support and Action Blog
City, Community, Developer Reach Agreement (WESA, October 27, 2017)
Final Go-Ahead Approved (Post-Gazette, February 12, 2019)
City Seeks Land Swap (WESA, October 4, 2019)
Controversy Continues with Land Swap Proposal (Tribune Review, October 15, 2019)
City Fails to Keep Promises (WESA, October 23, 2019)
City Falling Short on Guarantees (Post-Gazette, October 28, 2019)
Residents Concerned About Park Reconfiguration (Tribune Review, October 28, 2019)
Construction 2019-current:
City Council Clears the Way (WESA, October 29, 2019)
Construction Starts (Pittsburgh Business Times, October 30, 2019)
Groundbreaking Announced for December 2019 (Next Pittsburgh, October 30, 2019)
Keeping an Eye on Hazelwood Green: Aug. 2020
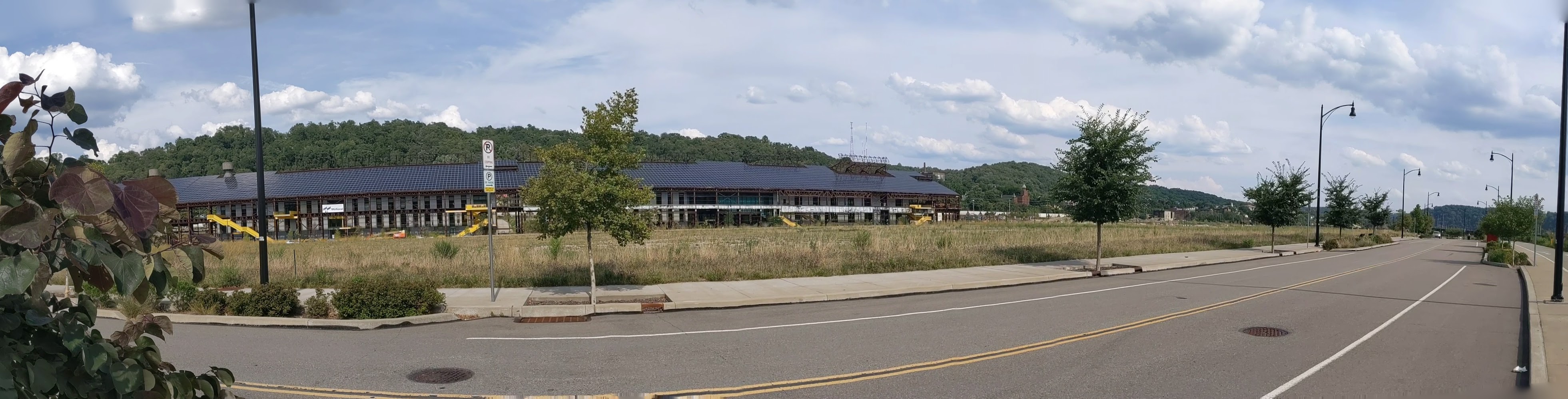
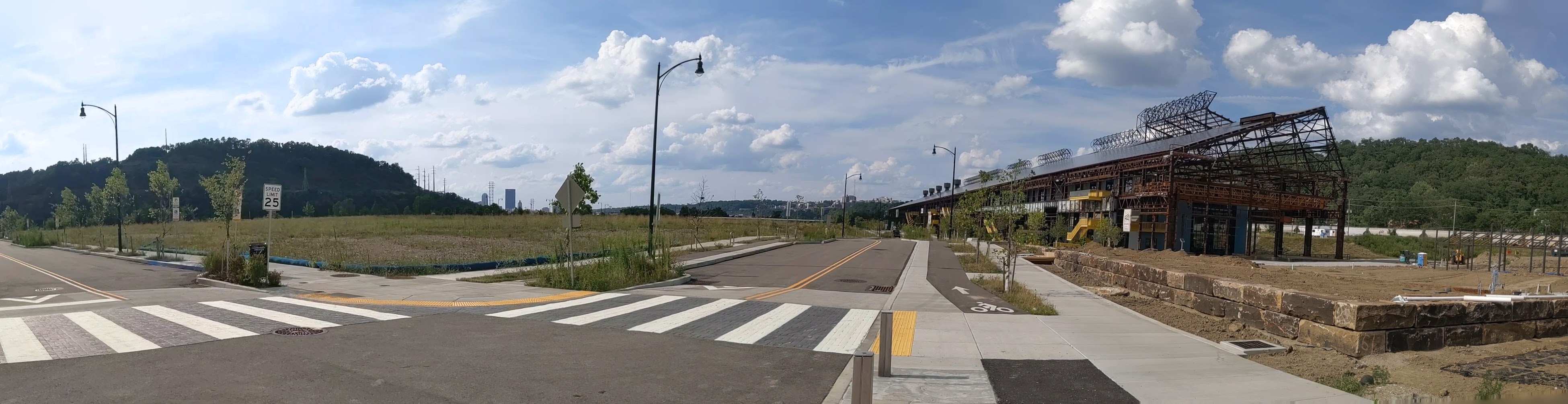
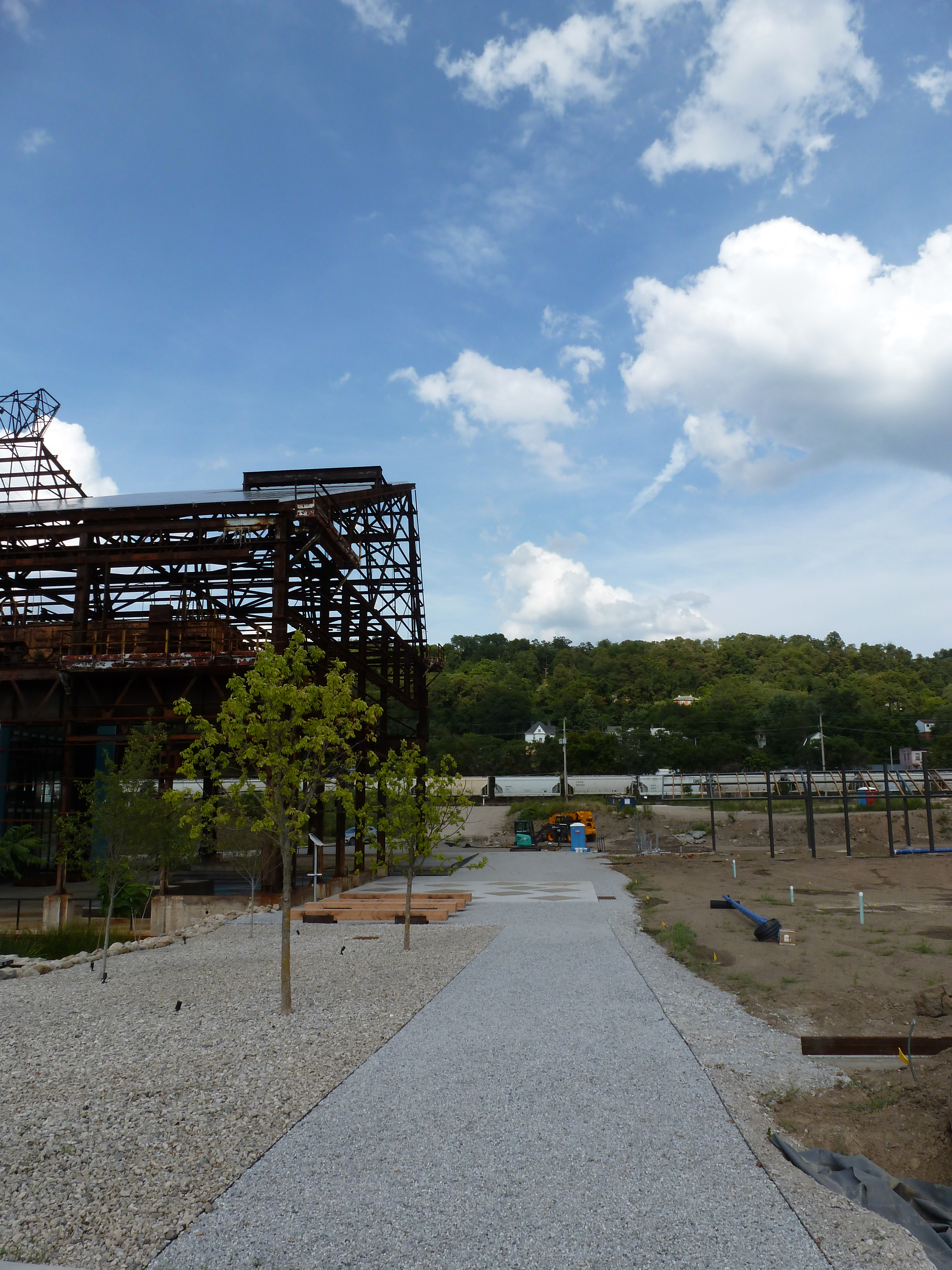
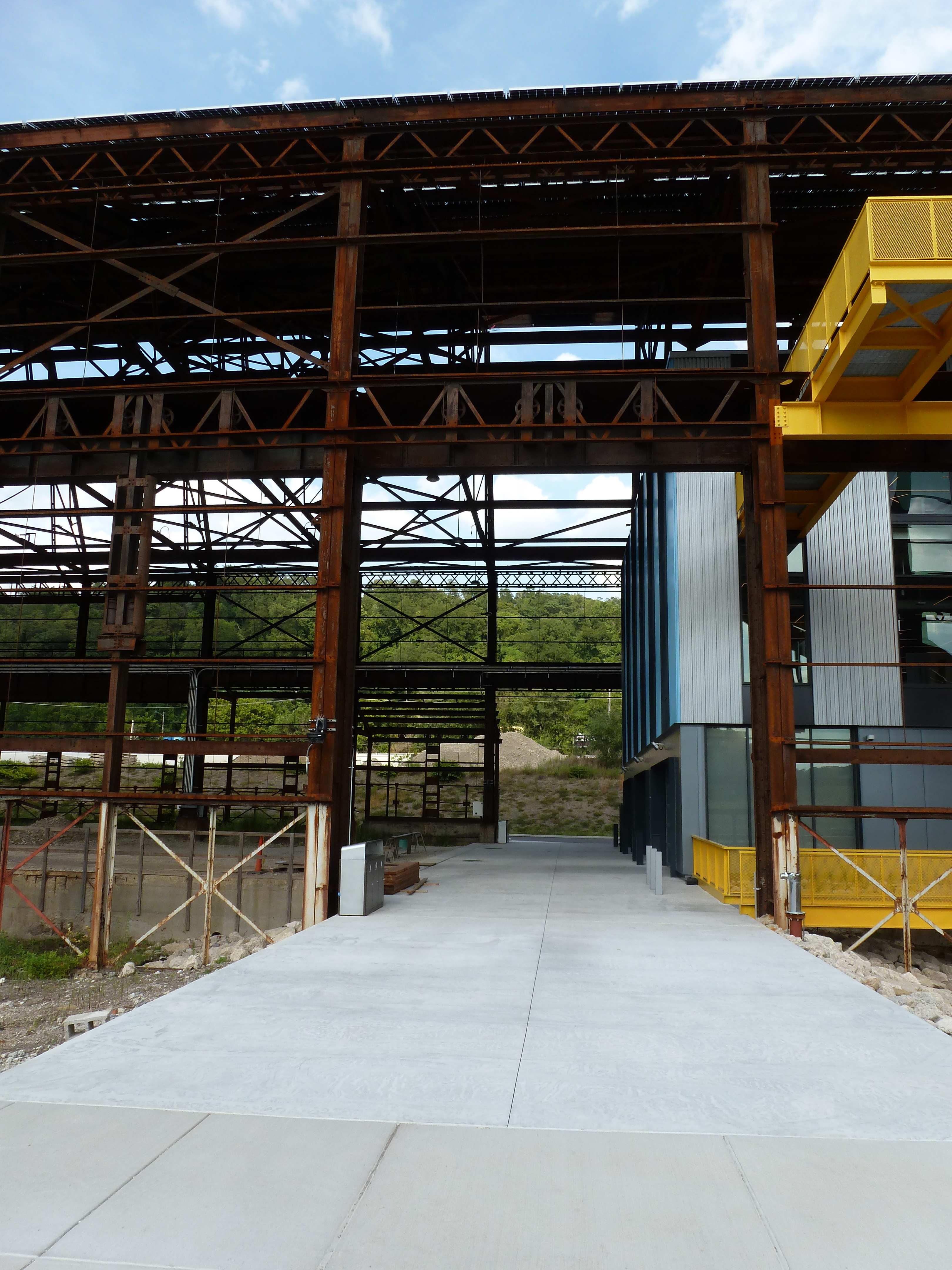
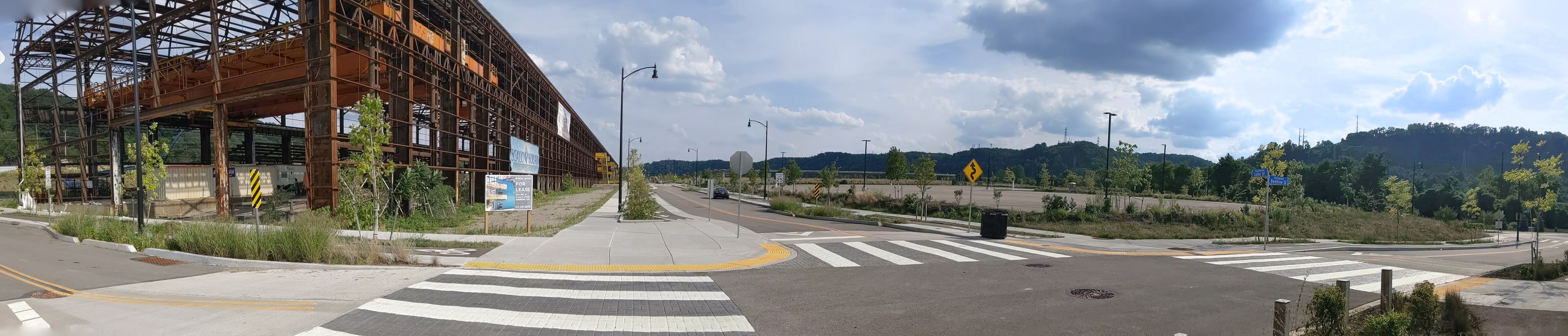





































Hazelwood Green in the News:
Roundhouse Renovation Next For Hazelwood Green (Next Pittsburgh, January 26, 2020)
Locomotive Roundhouse to Host Co-working Space (Pittsburgh Post-Gazette, January 28, 2020)
Tenant Landed for Roundhouse (Pittsburgh Business Times, February 25, 2020)
From Blight to Tech Node? (CoStar, June 3, 2020)
Largest Solar Installation (Next Pittsburgh, June 29, 2020)
Hazelwood Green – Mill 19 Building A Named 2020 Best Project (ENR MidAtlantic, July 29, 2020)
Largest Solar Installation Completed (Solar Power World, August 13, 2020)
Drive-In Arts Festival at Hazelwood Green (Twitter, August 13, 2020)
Previous posts in series:
What is a Bridge? Bethlehem Edition II

Looking back at the original intent of the Hill-to-Hill Bridge and comparing it to its use today, I find myself asking a new question: what is the purpose of a bridge? The word bridge is often used metaphorically to describe something that brings two things together. At the same time, there is a running joke in Pittsburgh (the City of Bridges) that if it involves crossing a bridge, people would rather stay home. This conflict of ideas between a bridge as a connector and a bridge as a divider is illustrated by the Hill-to-Hill Bridge.
The Hill-to-Hill Bridge started out as a connector. A Y at the north end linked West Bethlehem and Bethlehem to the main span which connected to South Bethlehem. The ramps in-between connected the neighborhoods to the businesses on the flats by the water.* Over time, the priority on connection disappeared as the bridge was modified. Of the seven original approaches, three were demolished, one was permanently closed to through traffic, and one was changed to one-way traffic.
The explanations I came across for alterations to the bridge seem reasonable, but they do not tell the whole story.
- Reason #1: Industry changed and shut down in Bethlehem as with other Rust Belt cities. Some of the business destinations connected to the bridge were among those that closed, removing the need for the connection.
- Reason #2: Cars became bigger, faster, and more numerous, making it harder to navigate the tight turns on some of the approaches.
The story that is overlooked by these explanations is that in the 1960s a new highway was built from the north directly tying into the bridge. The introduction of high-speed traffic to the bridge, or to any roadway, certainly makes it less safe for local traffic.
As a result of the addition of the highway, instead of connecting the neighborhoods of West Bethlehem, Bethlehem, and South Bethlehem, the bridge funnels traffic directly toward the former steel mill, Lehigh University, and other points south. In fact, the residents of West Bethlehem are practically excluded from using the bridge to get anywhere, as the western ramp is closed to through traffic (though open to parking). To use the Hill-to-Hill Bridge to reach South Bethlehem, a resident of West Bethlehem would have to drive north several blocks to get on the highway going south. Alternately, a resident could go south by taking Spring Street, a road parallel to the western and eastern wings of the bridge, (by)passing under the main span, then skirting around the hill of historic downtown, and taking the Fahy Bridge instead.
People living and working in the historic downtown area (the Bethlehem neighborhood) are also now limited in their use of the bridge. If coming across the bridge from the south, they can take the eastern viaduct to enter the historic downtown, but to leave the area by way of the Hill-to-Hill Bridge, they would have to drive north to the same highway access point as the residents of West Bethlehem. They could alternately take the Fahy Bridge for a more direct route south.
Use of the bridge is a little easier as a pedestrian, though it is still the most challenging for residents of West Bethlehem. For pedestrians to access the bridge from the west, they would have to use the sidewalks on Spring Street, walk under the main span, and climb a towering staircase up to the sidewalks on the bridge. If they are not able to use the stairs, they could keep going on Spring Street up the hill to the eastern end of the viaduct. Once on the bridge, both the historic downtown and south side are accessible. Given the history of the bridge, I imagine that there once was a time when there were crosswalks at the intersection of the main span and the east and west spurs so that pedestrians had full use of the structure just as drivers would have had.
The shift in the bridge’s focus from local to regional traffic seems like a classic case of the Urban Renewal efforts of the 1950s and 1960s. The discussion among planners and officials in recent years is how do they undo or erase the mistakes of Urban Renewal. Pittsburgh is trying to reconnect the local by returning some one-way roads to two-way traffic and by building a cap over the highway that divided downtown and the Hill District. As I watch these developments in Pittsburgh, I wonder if there are ways to return the Hill-to-Hill Bridge to a focus on the local.
For example: The highway has to end at some point, which is currently at the southern end of the bridge. What if it were moved to the north end of the bridge? If a traffic light were introduced there, the western branch could be reopened to through traffic and the eastern branch could be restored to two-way traffic. Pedestrians would also be able to then use all the remaining approaches. Thus, West Bethlehem, Bethlehem, and South Bethlehem would be reconnected for the enjoyment of pedestrians and drivers.
This suggestion is based upon the assumption that the local community would want to be better connected by way of this bridge. Perhaps the question that should come before “what is the purpose of a bridge?” is “who gets to decide the purpose of a bridge?”
*By prioritizing connections, Clarence W Hudson, the bridge’s designer, was forced to develop a one-of-a-kind truss design to accommodate the railroad tracks beneath the bridge and the connections coming into the bridge. There is no record of this truss design being used on any other bridge.