Tag Archives: Pittsburgh
Bridge Collapse: Eighteen Months Later
According to the Pittsburgh Business Times, the collapse of the Fern Hollow Bridge in Pittsburgh ranked 4th in the top stories of 2022. Ranked higher were the New Normal (#1), Economic Stressors (#2), and the Shutdown of Tech Startups (#3).
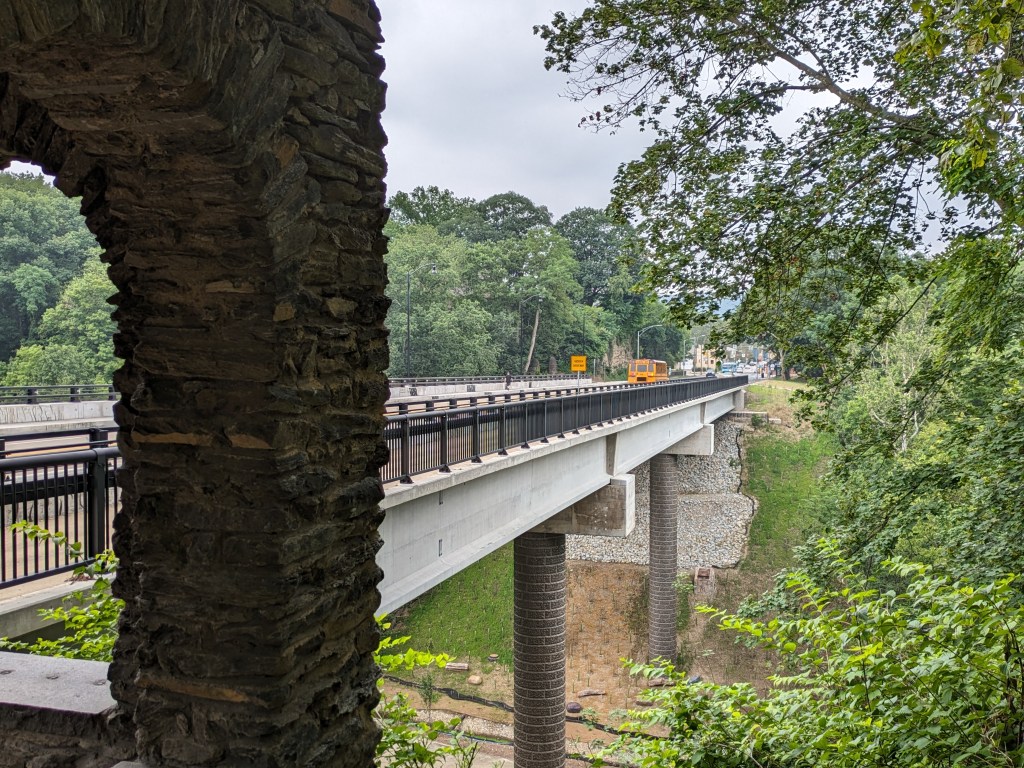
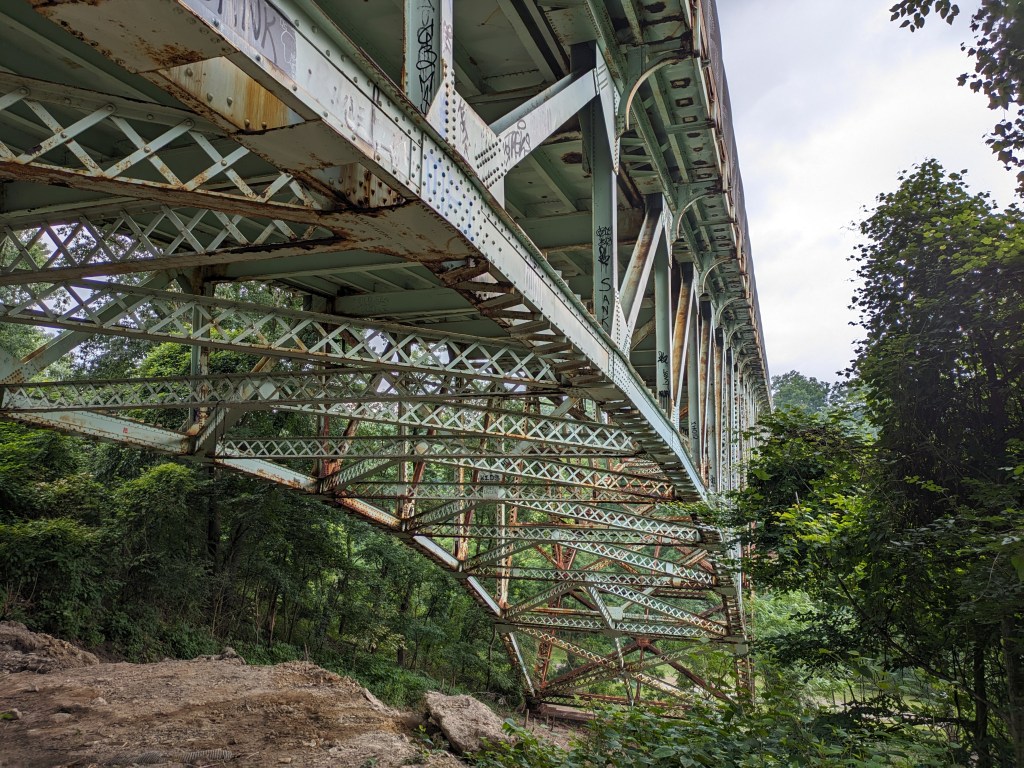
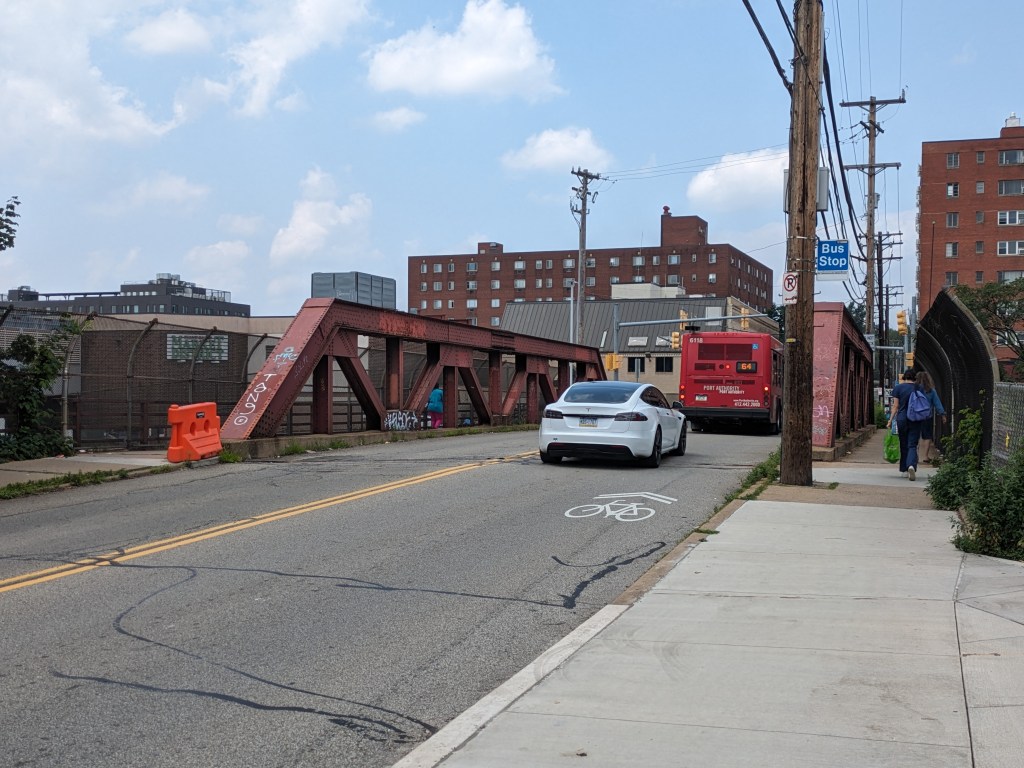
As the first bridge collapse in nearly 100 years within the city limits of Pittsburgh, this remains a top story on urbantraipsing. In the six months since our last look at the bridge, there have been four important updates:
- The preliminary findings of the National Transportation Safety Board’s investigation into the collapse have been released
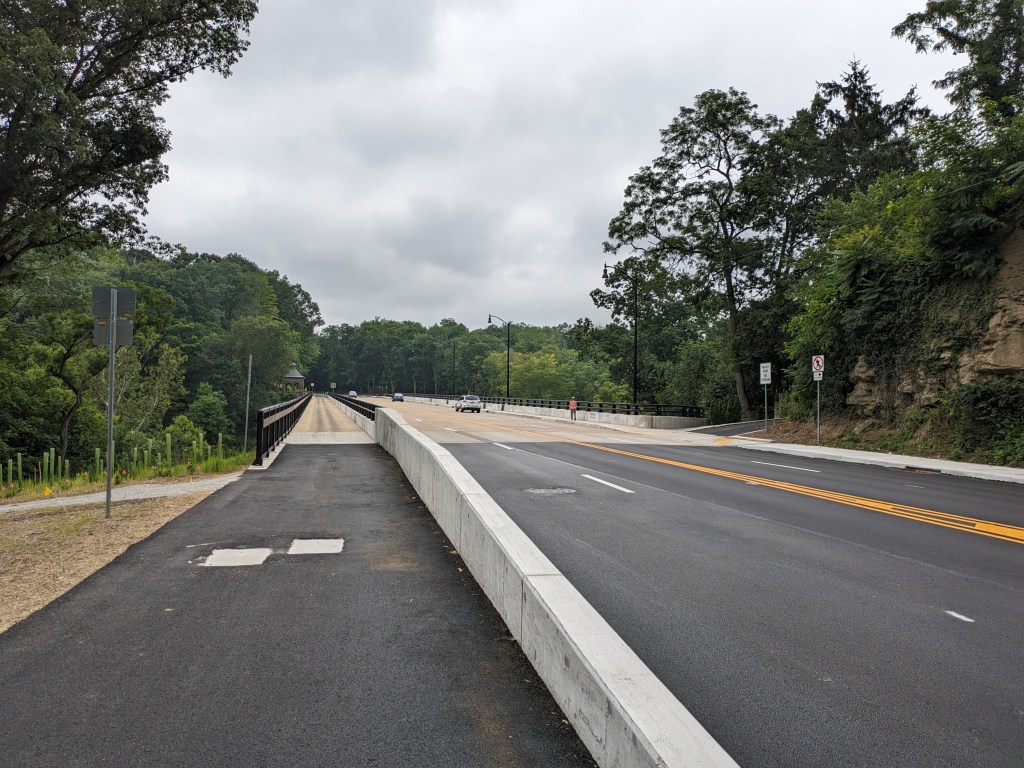
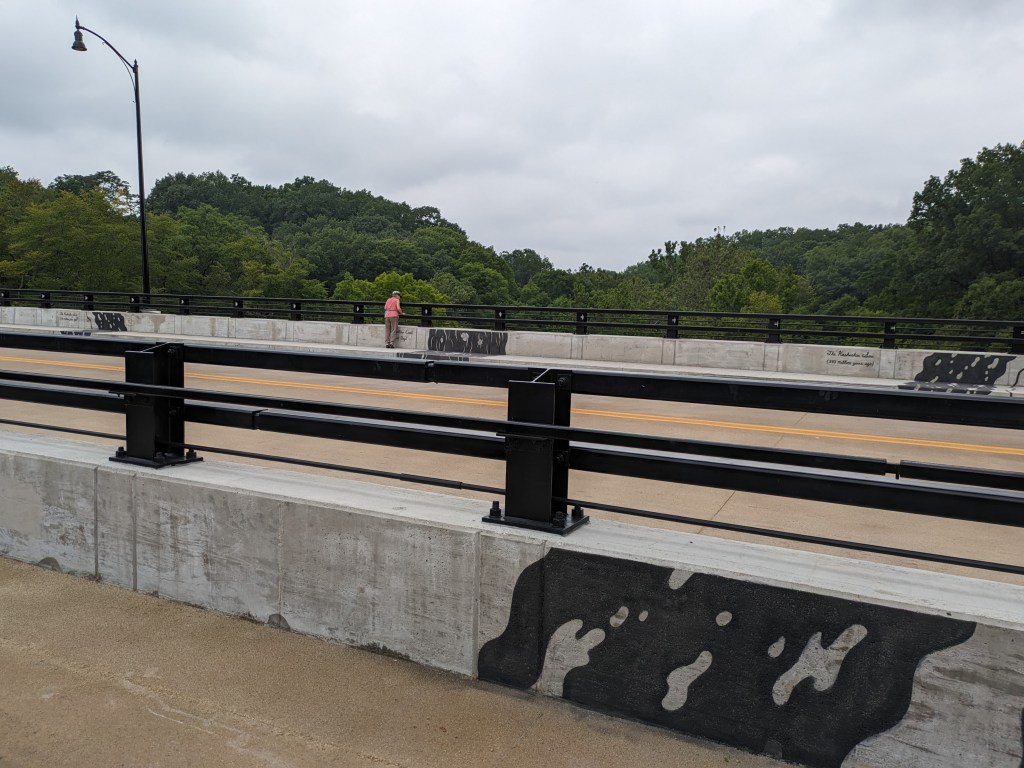
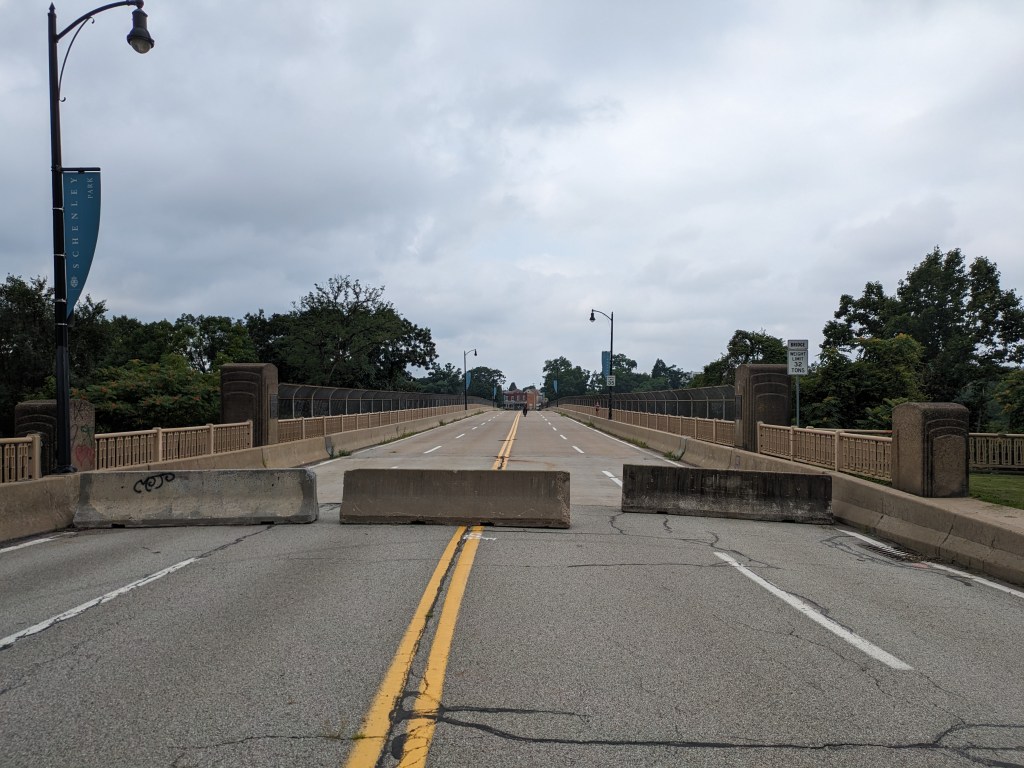
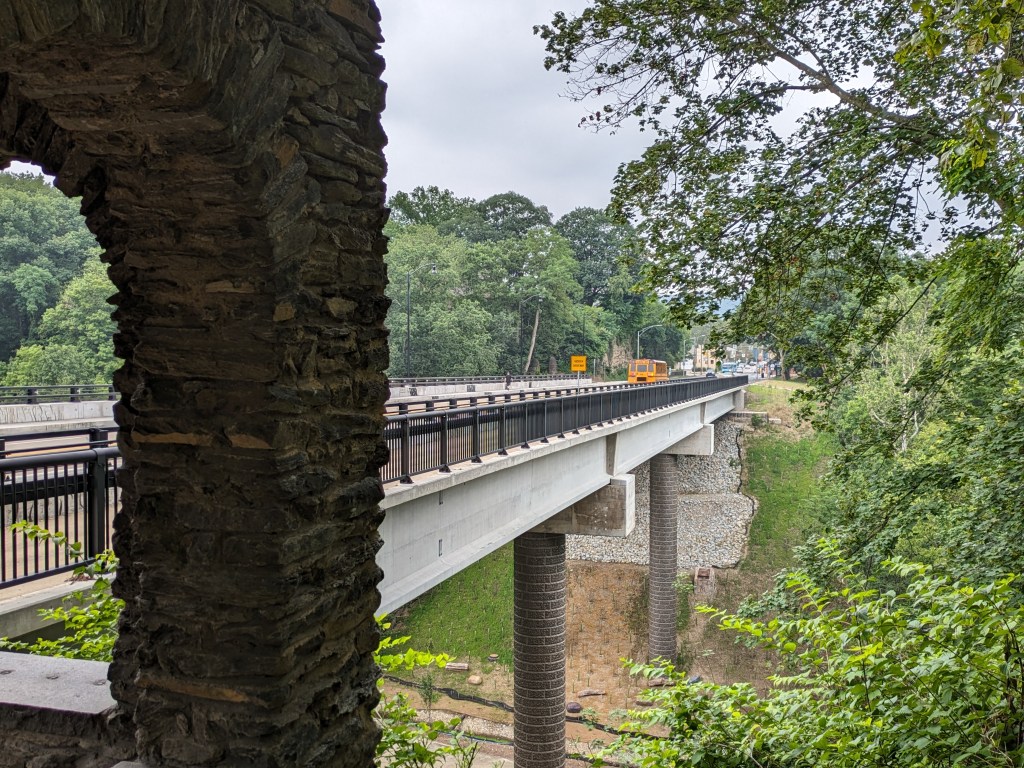
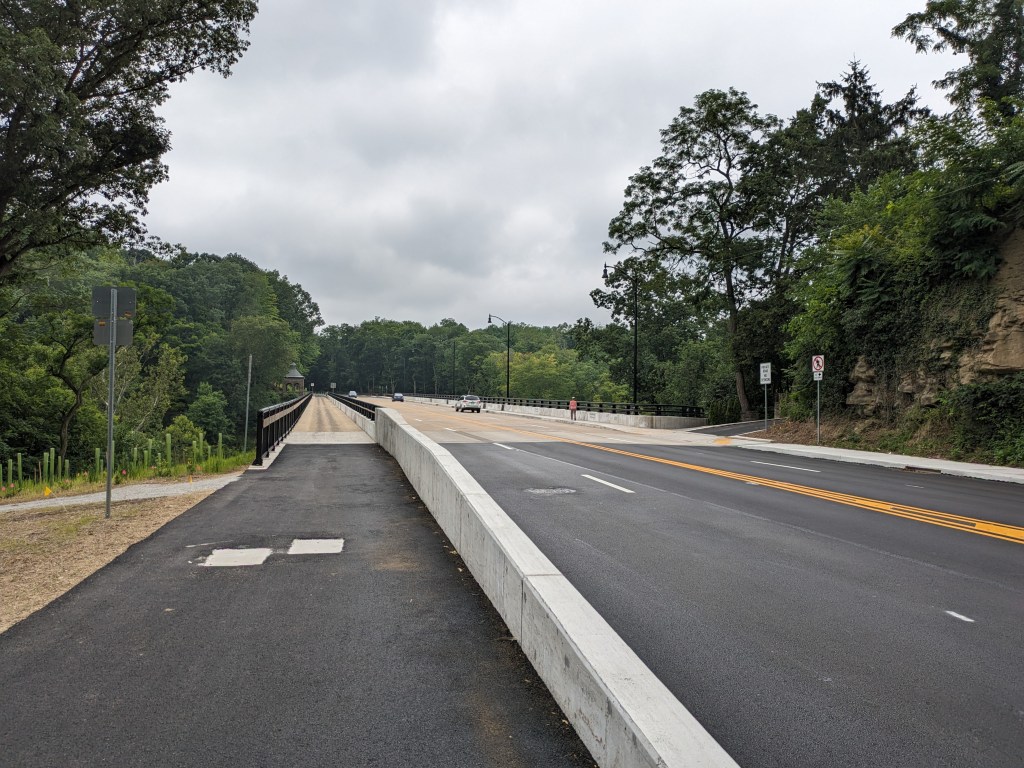
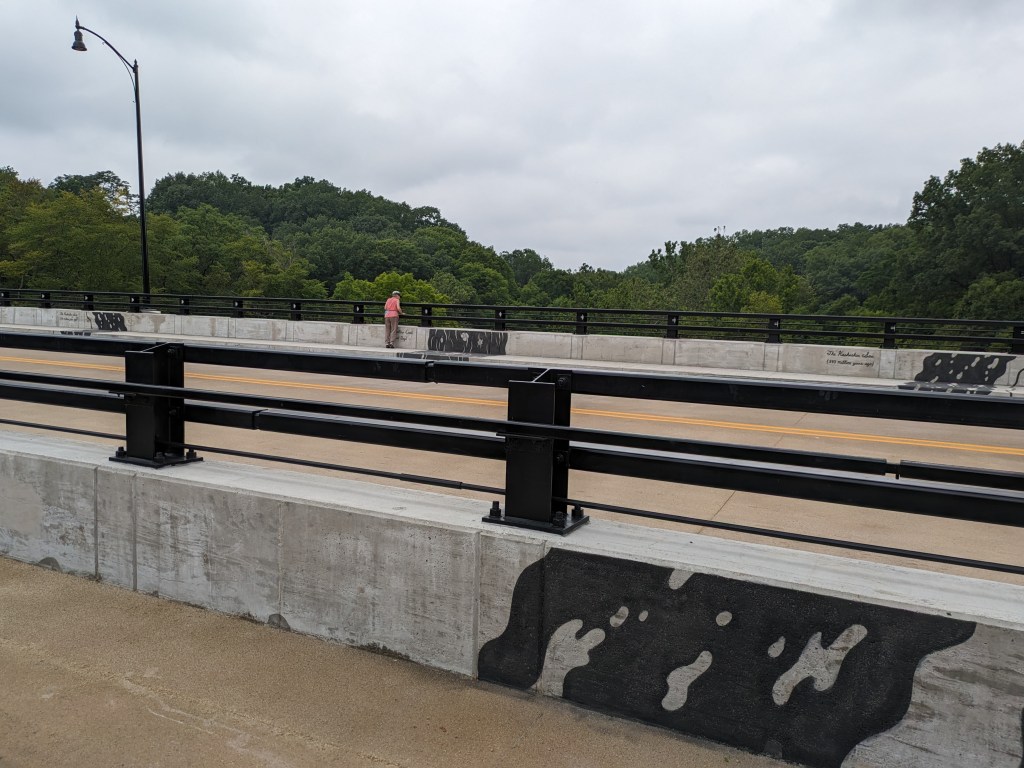
- The bridge is now fully open to vehicular, bicycle, and pedestrian traffic
- The two art installations have been installed
- My feet are back to being fully functional
Update 1: Unsurprisingly, the NTSB’s investigation found that a decade of ignoring the calls for maintenance in the annual bridge inspection resulted in the deterioration of the steel structure of the bridge. The findings reference the inspections of bridges of similar construction in Pennsylvania following the collapse of the Fern Hollow Bridge. It noted that while those bridges have also experienced deferred maintenance, none of them are exhibiting deterioration as bad as Fern Hollow’s. The report did express concern that the status of similar bridges outside of Pennsylvania is unknown.
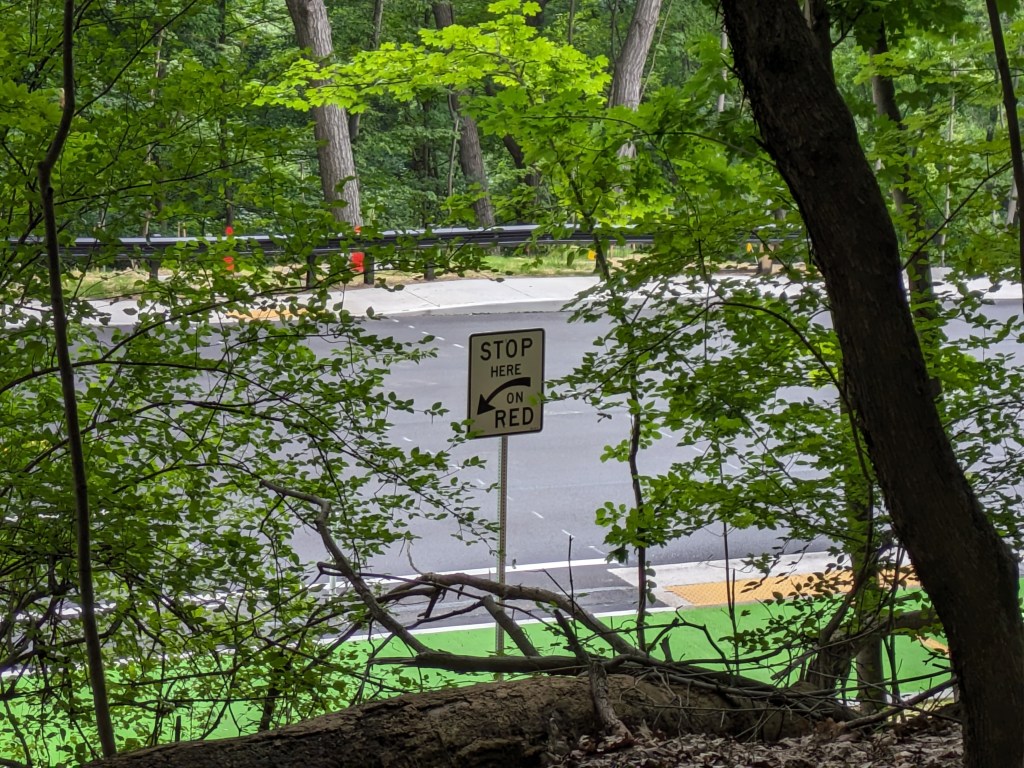
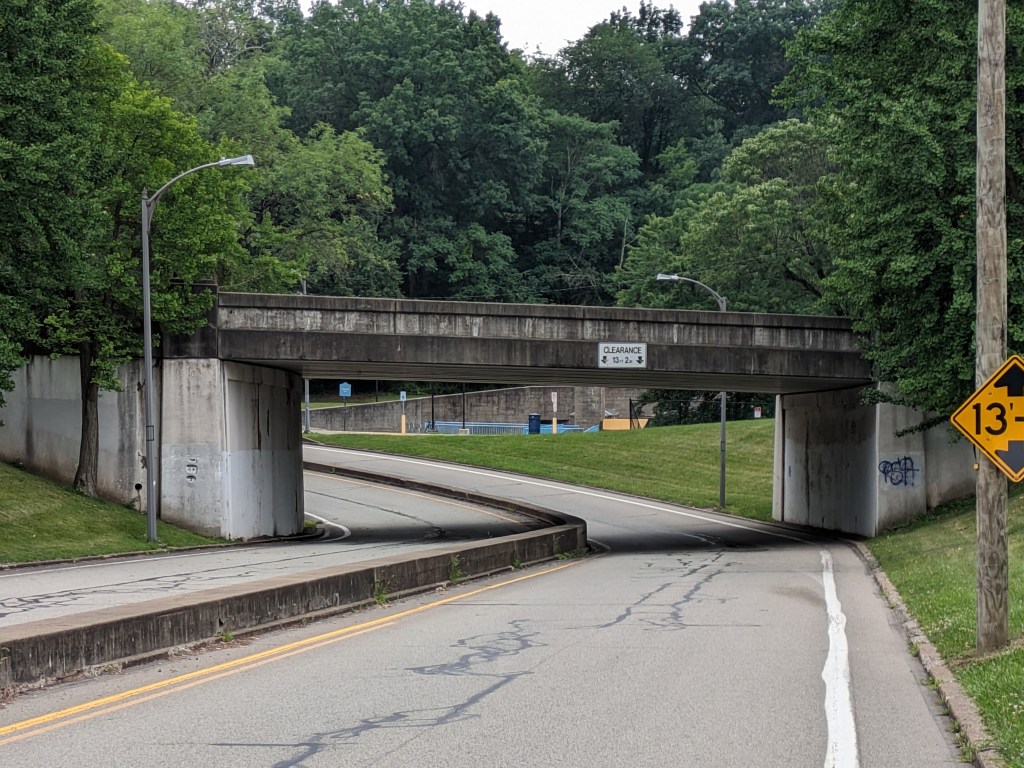
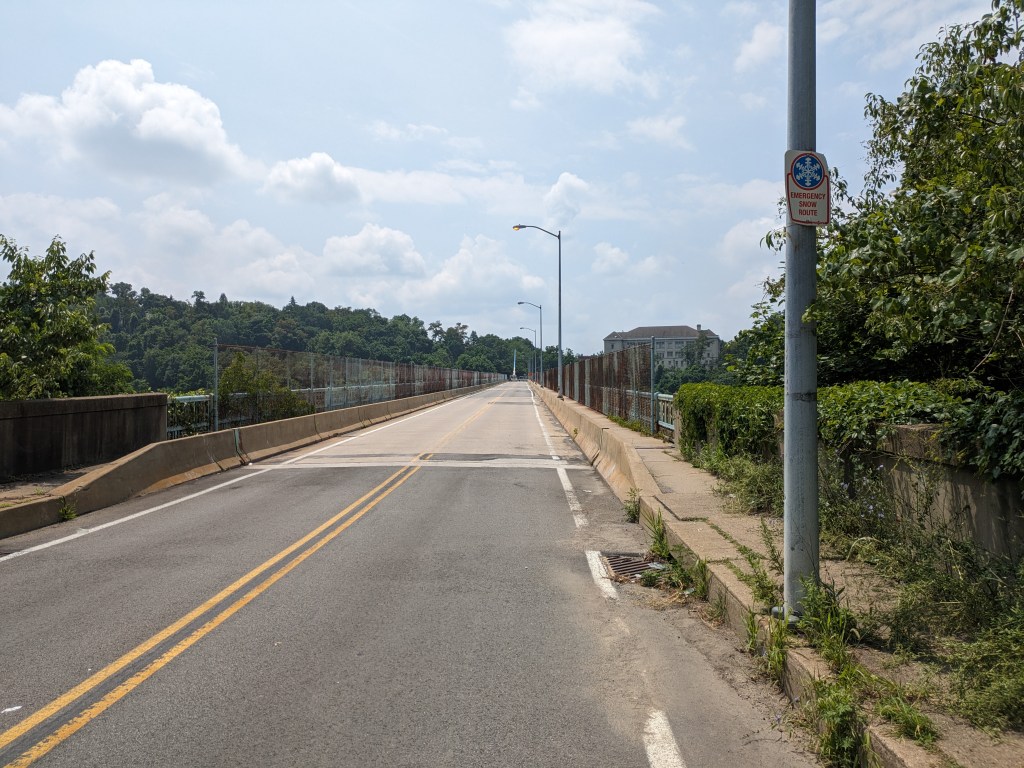
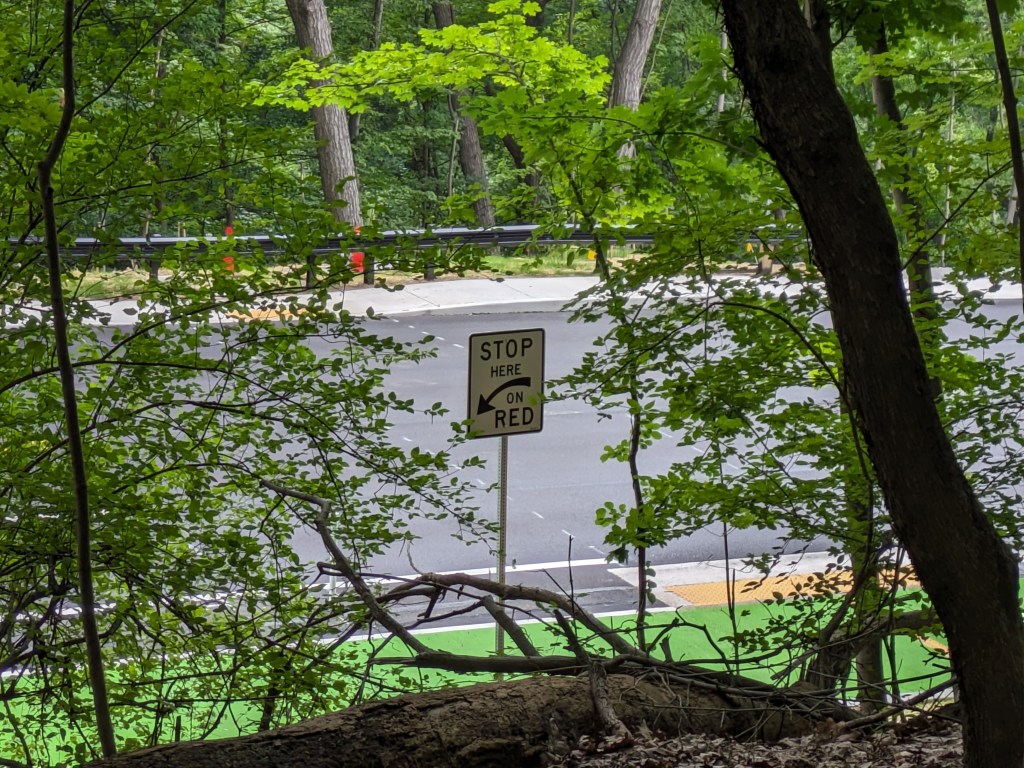
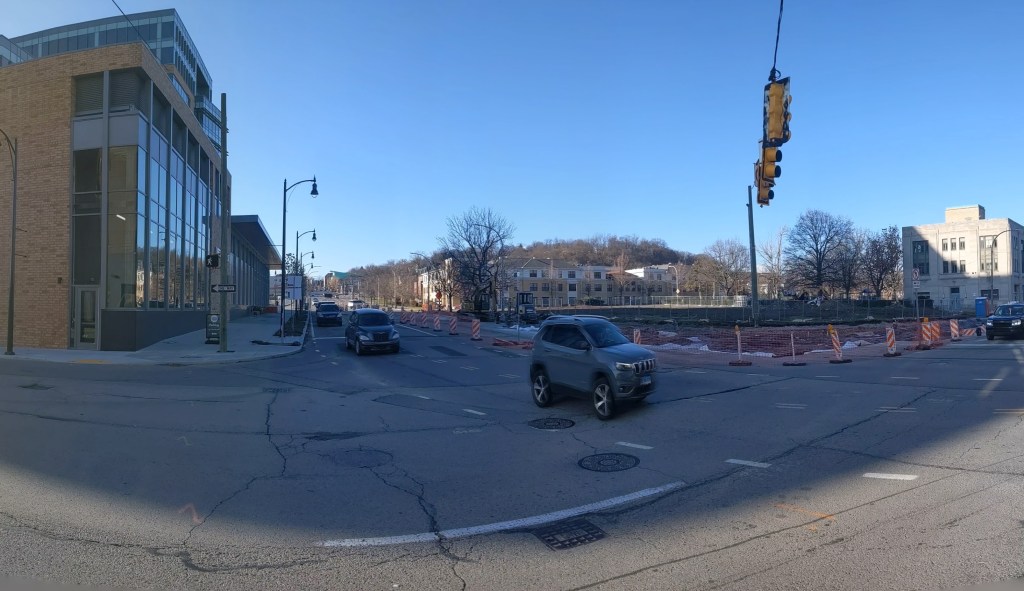
Update 2: While all lanes, the sidewalk, and multi-modal path are now open, there is evidence of some more work to be done. A little beyond the western end of the bridge, there are the preliminary markings for a crosswalk. Also, a “stop here on red” sign was installed, though it currently faces the park, not the traffic. Both of these suggest that a new traffic light will be installed to create a safe pedestrian crossing.
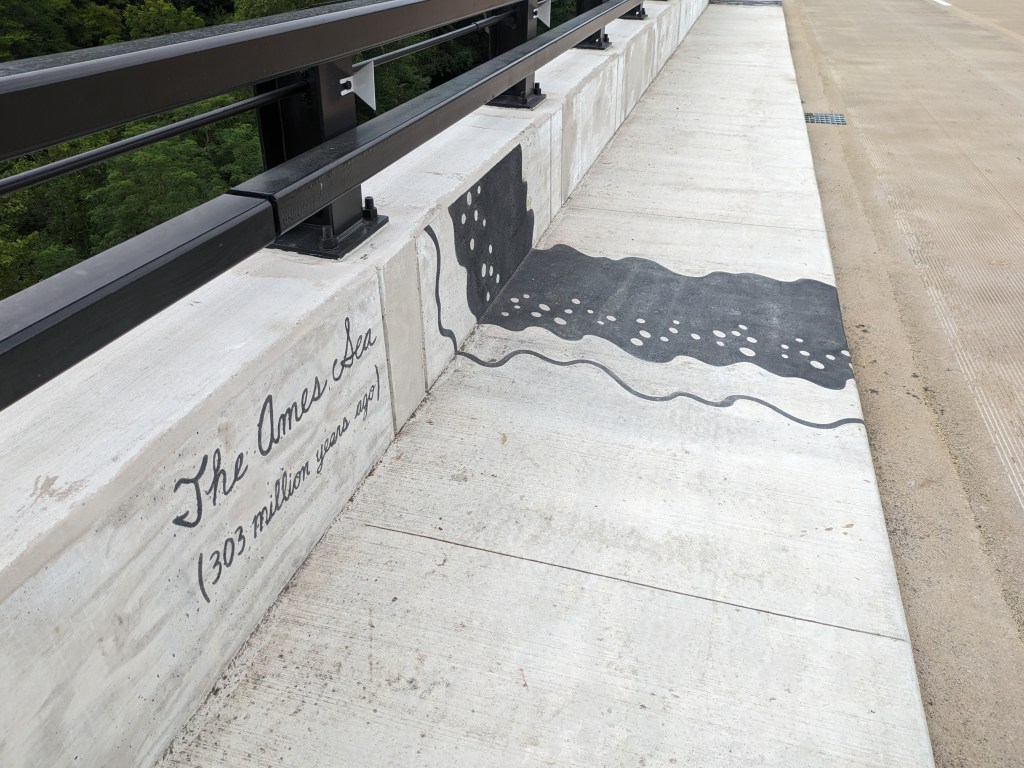
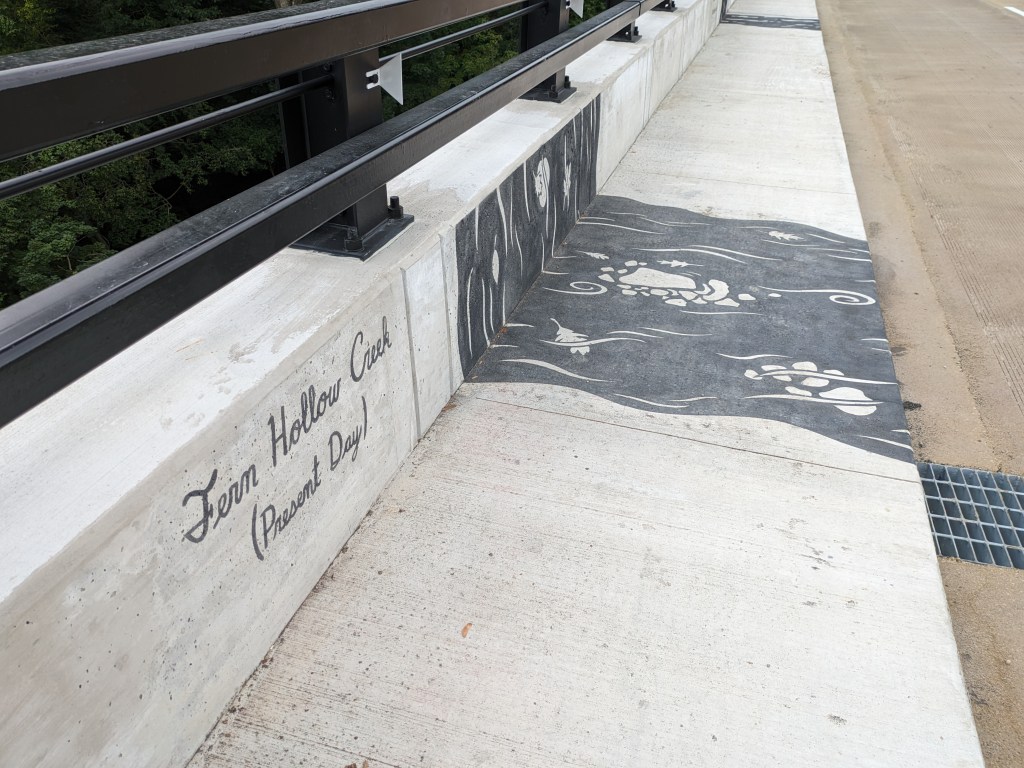
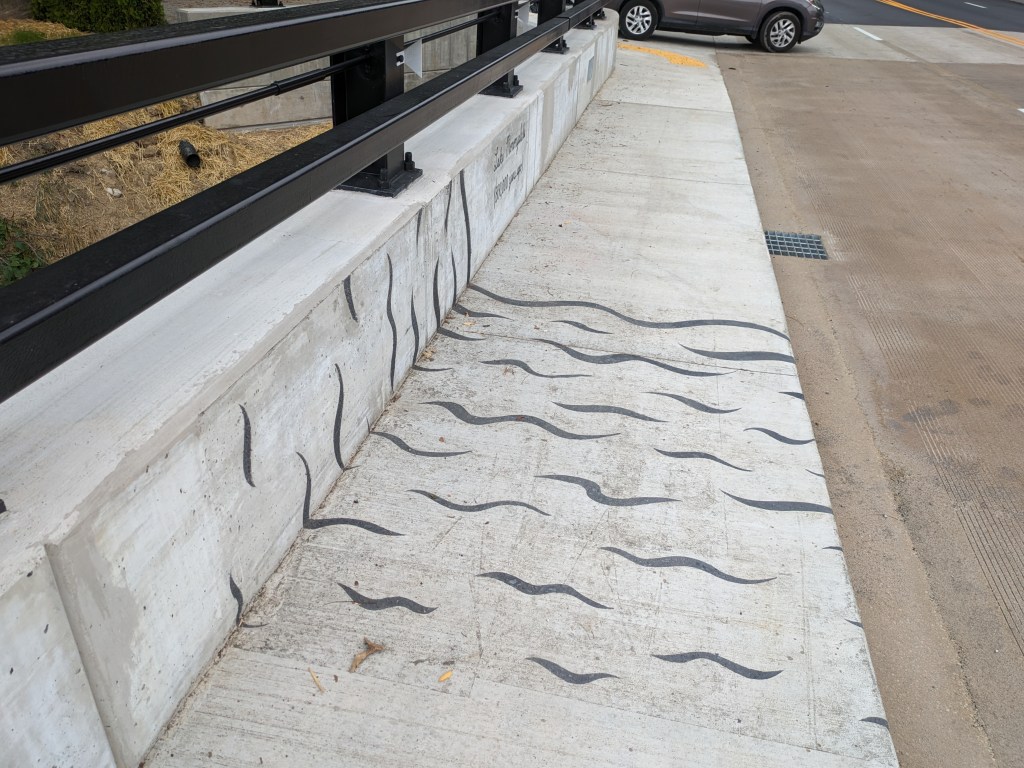
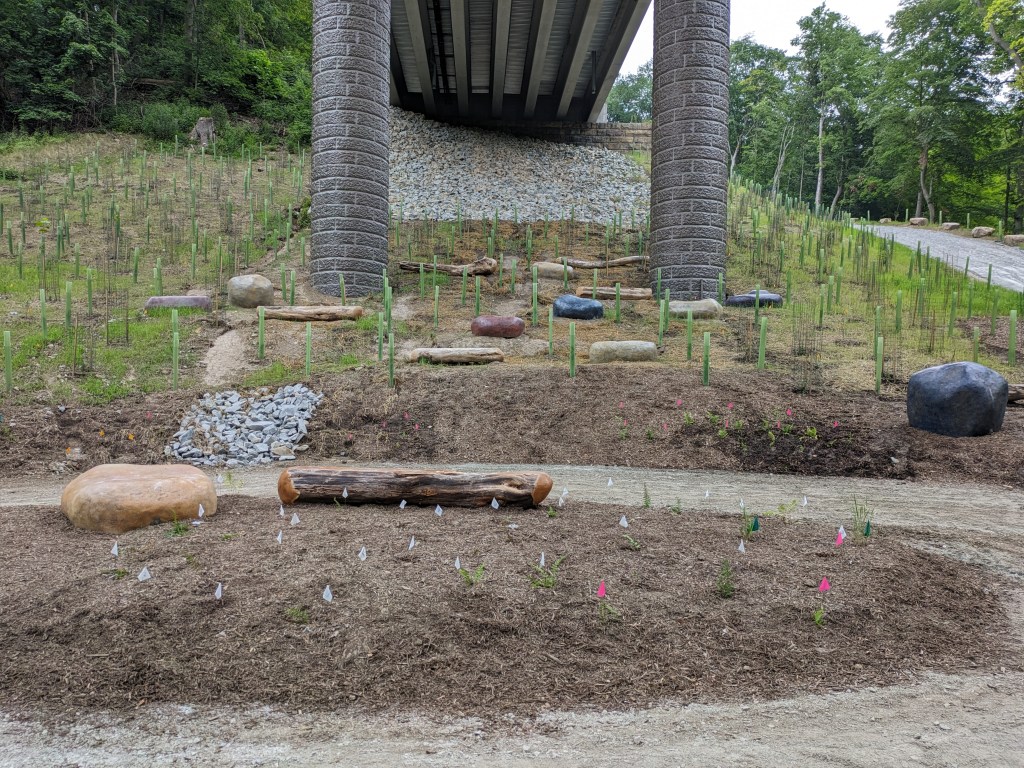
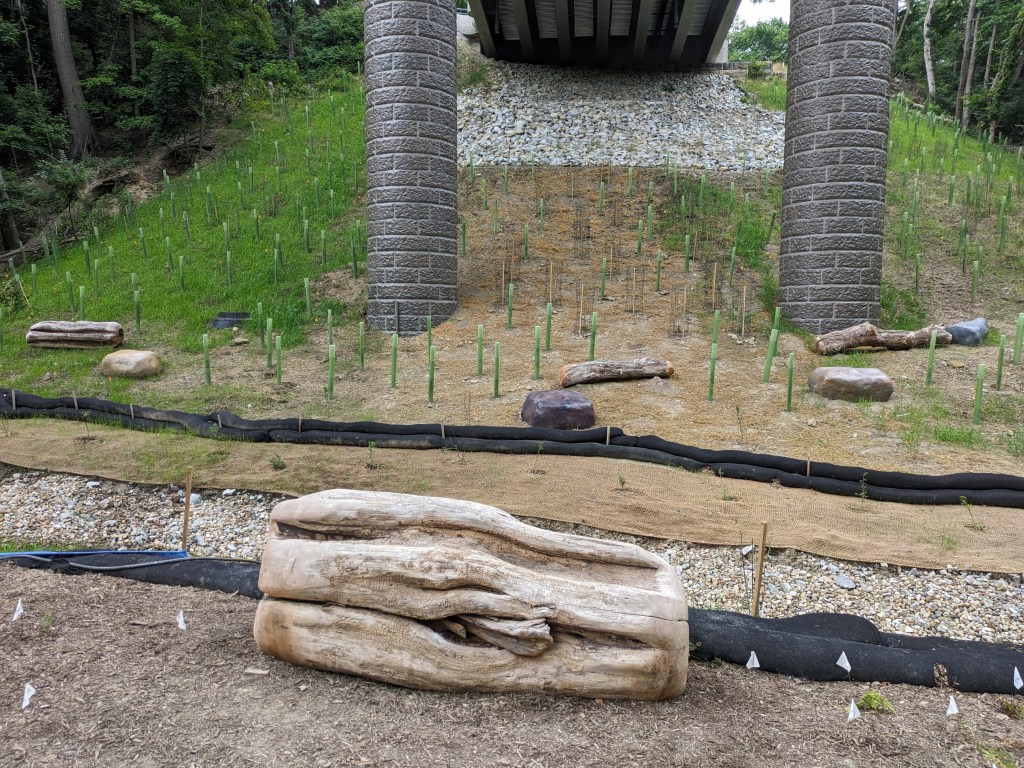
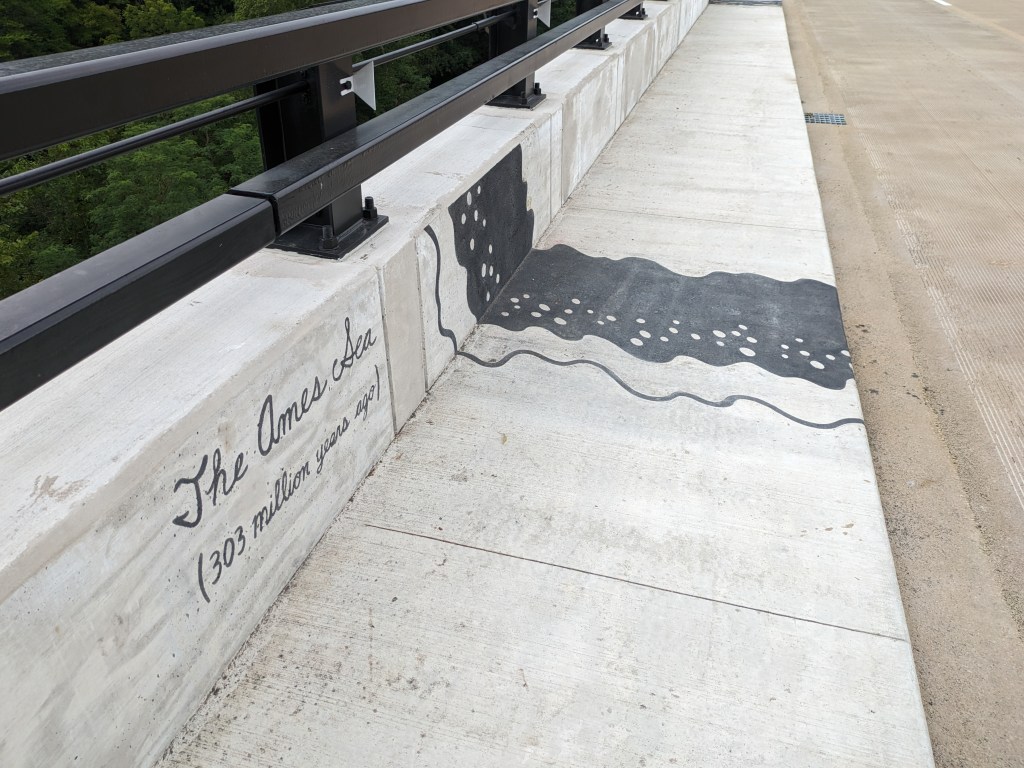
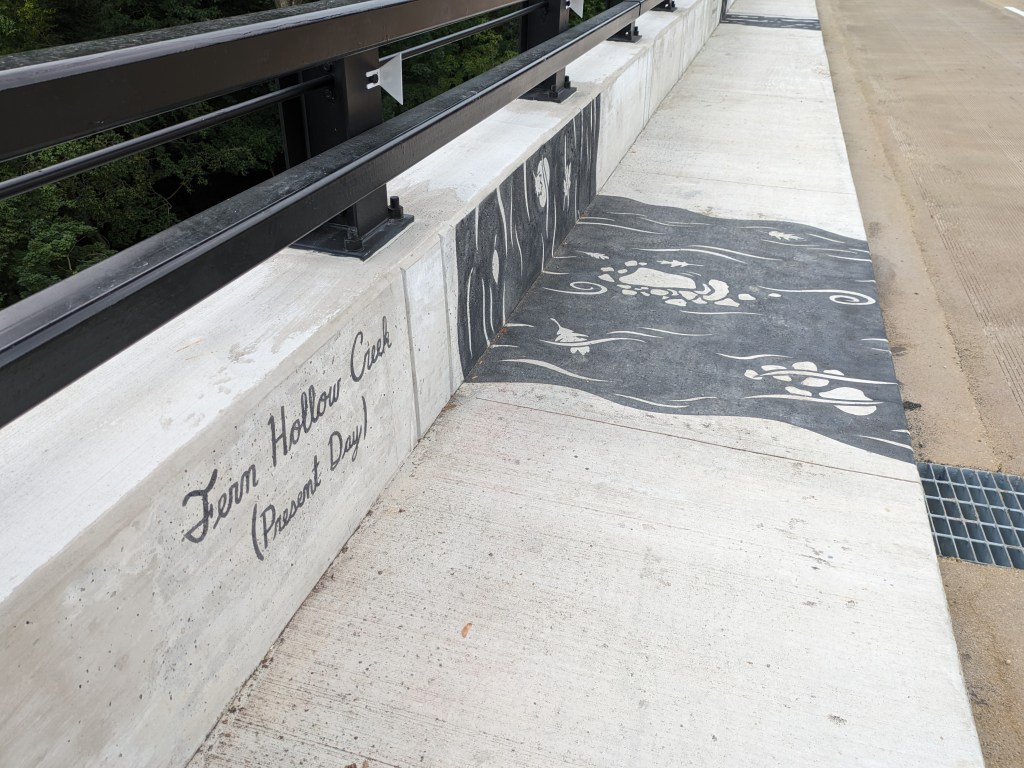
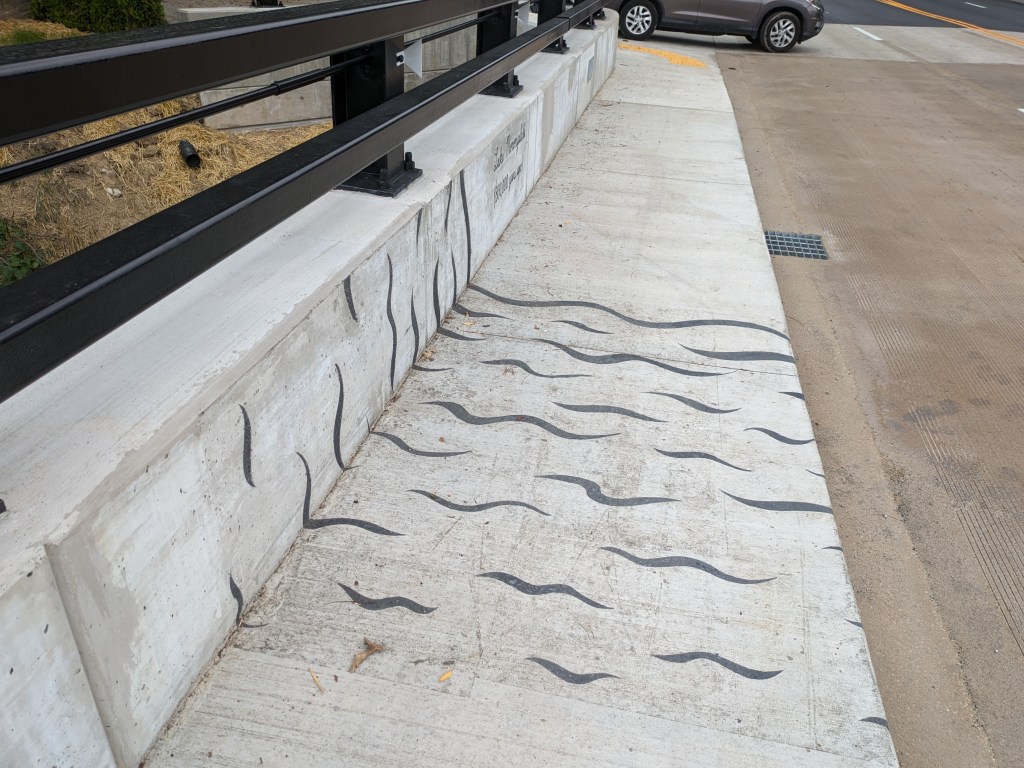
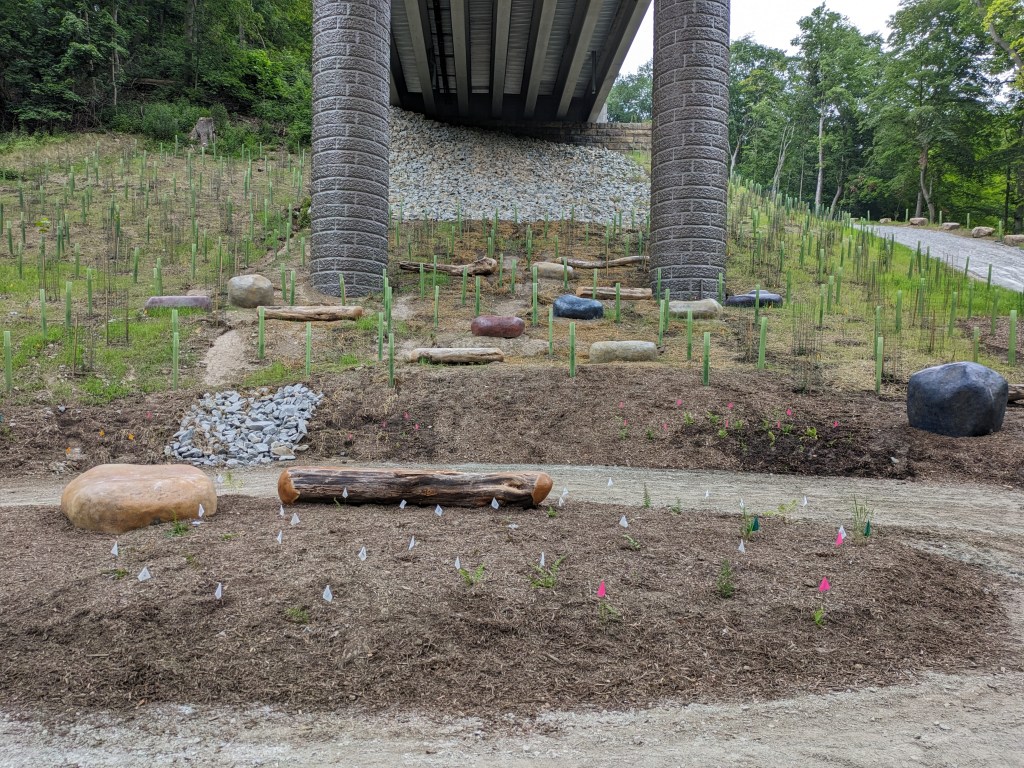
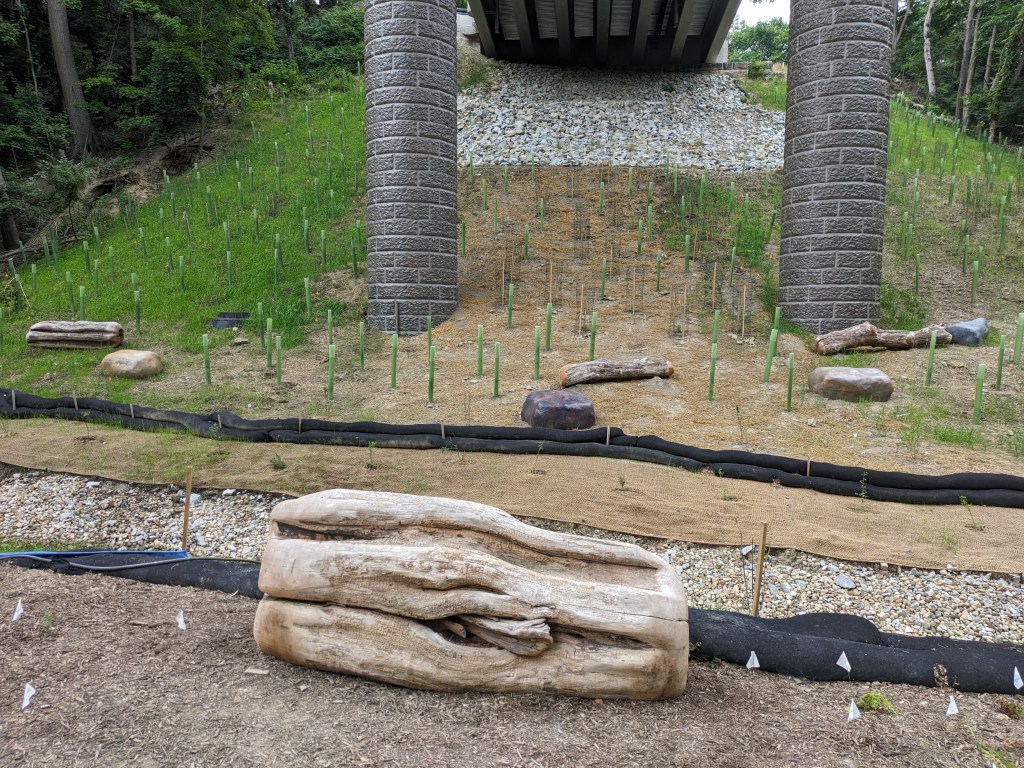
Update 3: John Peña’s A History of Fern Hollow Creek was installed on the bridge and Carin Mincemoyer’s Trail Meander was installed under the bridge. Mincemoyer’s alternative concept of a rain arch that paid homage to the arch of the former bridge did not move forward as it was found to not be feasible within the time and budget constraints of the project. I enjoyed the historical timeline of the bodies of water on this site illustrated in Peña’s installation – it provides and opportunity to stop and think about the different bodies of water that have shaped the landscape of Pittsburgh over millennia. I haven’t yet cracked the pattern of the order in which they are displayed, if there is one.
Update 4: As I do not currently have any mobility limitations, I was able to take many more pictures from different angles.
Photos: Fern Hollow
Below are the news updates on the Fern Hollow Bridge and other bridge maintenance and replacement efforts in Pittsburgh and Allegheny County.
- The artwork on the bridge was approved by the Public Art + Civic Design Commission in October 26, 2022 (Agenda, Application, Minutes). The artwork for the trail experience under the bridge was approved by the Public Art + Civic Design Commission in March 22, 2023 (Agenda, Application, Minutes).
- PennDOT’s project page regarding the reconstruction of the bridge has not been updated since March 2022, except to add a sentence at the beginning to say that the bridge is now complete and operational prior to my last update in January, despite the fact that the bridge was fully closed again for a month in June 2023 to “complete all remaining bridge work.” (Mayor’s Press Release, June 8, 2023; WESA, June 8, 2023; Pittsburgh Magazine, June 9, 2023; Roads & Bridges, June 9, 2023; WPXI, June 11, 2023; WTAE, June 12, 2023)
- Preliminary findings have been released in the National Transportation Safety Board’s ongoing investigation. Corrosion and deterioration of Fern Hollow Bridge’s uncoated weathering steel components is the key finding along. In addition, while the annual inspection of the bridge had identified maintenance activities that would have addressed these issues for over a decade, the maintenance was not completed.
- The City created a Commission on Infrastructure Asset Reporting and Investment in March 2022, but no one has been appointed to the commission and it hasn’t been added yet to the city’s website listing all Boards and Commissions. Earlier this year, Mayor Gainey (WESA, June 26, 2023) and Councilwoman Strassburger (Pittsburgh Union Progress, April 3, 2023) both discussed the value of the commission – when it is operational. Neither discussed why the Mayor hasn’t appointed anyone to the board yet (Post-Gazette, June 8, 2023).
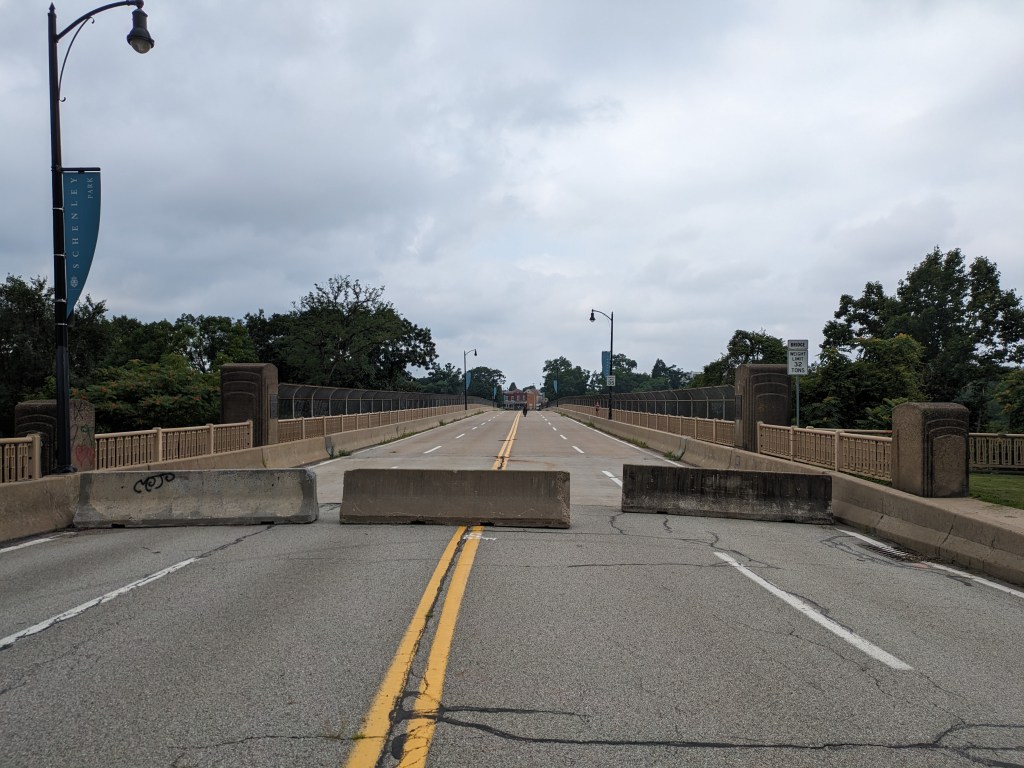
- The temporary closure of the Charles Anderson Bridge turned into a long-term closure as expedited funding was negotiated to move the full rehabilitation forward sooner. The project may take until 2025 or 2027 and will include a new 2-way bike lane. The Panther Hollow Overpass will also be repaired while the Charles Anderson Bridge is closed because the overpass “is approaching the end of its functional life” and the road is already closed. (Mayor’s Press Release, March 16, 2023; KDKA, March 17, 2023; KDKA, March 23, 2023; WTAE, April 18, 2023; Patch, April 18, 2023; Post-Gazette, April 18, 2023; WPXI, April 19, 2023; WESA, June 1, 2023; Pittsburgh Engage project page)
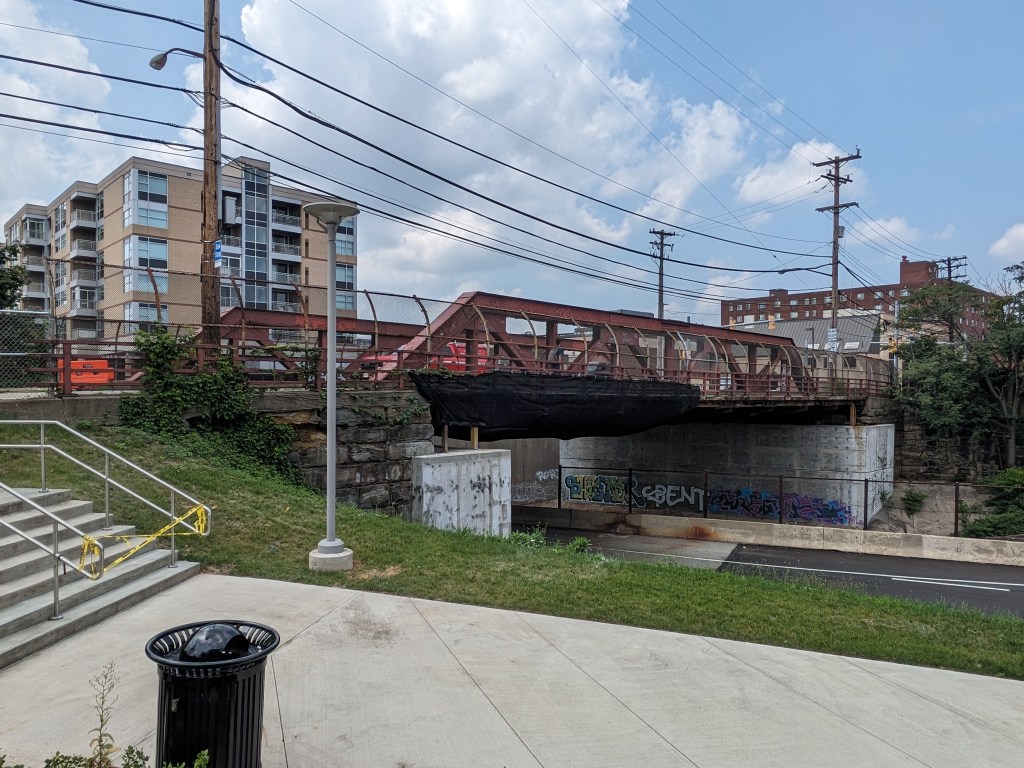
- Pittsburgh’s Swindell Bridge, which closed from July to September 2022 due to falling debris, closed for about a week in April to set-up platforms for future construction and then closed again in July to install new beams. One of the articles says that this will finish the work on the Swindell Bridge, while another says that a full rehabilitation project is yet to come. Pittsburgh’s Engage site only shows the public meeting from April. (Triblive, April 22, 2023; Mayor’s Press Release, April 21, 2023; WTAE, April 27, 2023; Mayor’s Press Release, April 27, 2023; KDKA, July 9, 2023; Pittsburgh Engage page; Mayor’s Press Release, July 7, 2023; Post-Gazette, July 10, 2023)
- In searching for new news on the South Negley Avenue Bridge, I didn’t find anything new, but I found an article from 2015 that said the renovation of the bridge was scheduled to start 2 years from then – that has come and gone with no new start date in sight. In addition to not finding anything new about what is happening to this poor condition bridge, it’s not clear if the closure of the west sidewalk of the South Negley Avenue Bridge from 2022 officially ended or if pedestrians took matters into their own hands and moved the barriers aside themselves. (The Philadelphia Tribune, February 2, 2015)
- Construction began on the 30th Street Bridge rehabilitation in April 2023. (Triblive, April 22, 2023; Mayor’s Press Release, April 21, 2023; Pittsburgh Engage page)
- There’s evidence of that the construction of the new Davis Avenue Bridge is moving forward from the approval of the Public Art + Civic Design (PACD) Commission in March to the listing in the Construction Journal for bids. (Triblive, March 24, 2023; Construction Journal, June 9, 2023; Bridge Engage Page; Public Art Engage page; PACD Agenda, Application, Minutes)
- Maintenance work on Swinburne Bridge was scheduled for May 2023. Full rehabilitation will happen later, after the Charles Anderson Bridge is reopened as the Swinburne Bridge is part of the detour route. (Mayor’s Press Release, May 19, 2023)
- The Lincoln Avenue and Fremont Street bridges were closed indefinitely for repair January 2023 by PennDOT to the surprise of Millvale, PA – a small town across the 40th Street Bridge from Pittsburgh – the borough is seeking funding for the repairs (Borough’s Announcement, January 23, 2023)
Photos: Other Bridges
Historic Pittsburgh Bridge Disasters
According to Bob Regan’s 2006 book “The Bridges of Pittsburgh,” Pittsburgh is no stranger to bridge disasters:
- 1845 – The original Smithfield Street Bridge burned down
- 1851 – The 16th Street Bridge burned down
- 1865 – Two spans of the 16th Street Bridge was washed away in a flood
- late 1880s – The 6th Street/St. Clair Street Bridge burned down
- 1903 – The Wabash Bridge collapsed during construction
- 1918 – The 16th Street Bridge burned down (again)
- 1921 – The 30th Street Bridge burned down
- 1927 – The Mount Washington Roadway Bridge collapsed during construction
Map of bridges discussed in the Bridge Collapse series:
Additional Resources:
Both PennDOT and the Federal Highway Administration have interactive maps of bridges for the state and country respective, and their inspection statuses. Pittsburgh now has the static Comprehensive Bridge Asset Management Program Report of the 147 bridges owned by the City of Pittsburgh.
Bridges in Pittsburgh with community engagement pages for pending rehabilitation or replacement projects:
- 28th Street Bridge
- 30th Street Bridge
- Charles Anderson Bridge
- Davis Avenue Bridge
- Swinburne Bridge
- Swindell Bridge
Previous Fern Hollow Bridge Posts:
Keeping an Eye on Penn Plaza: 2022 Recap
What’s New in 2022
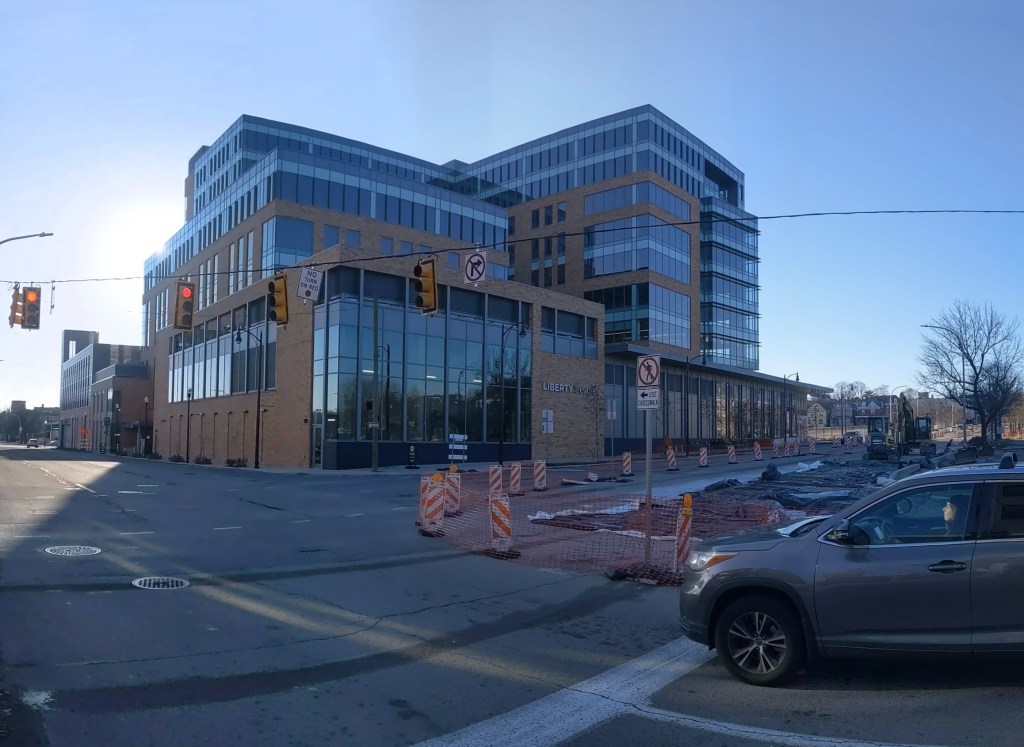
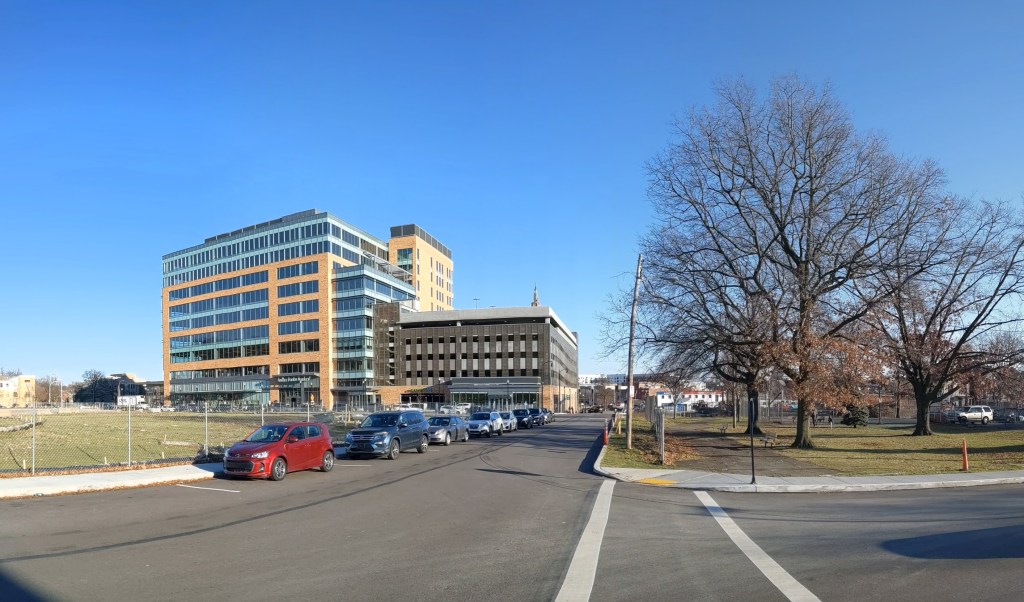
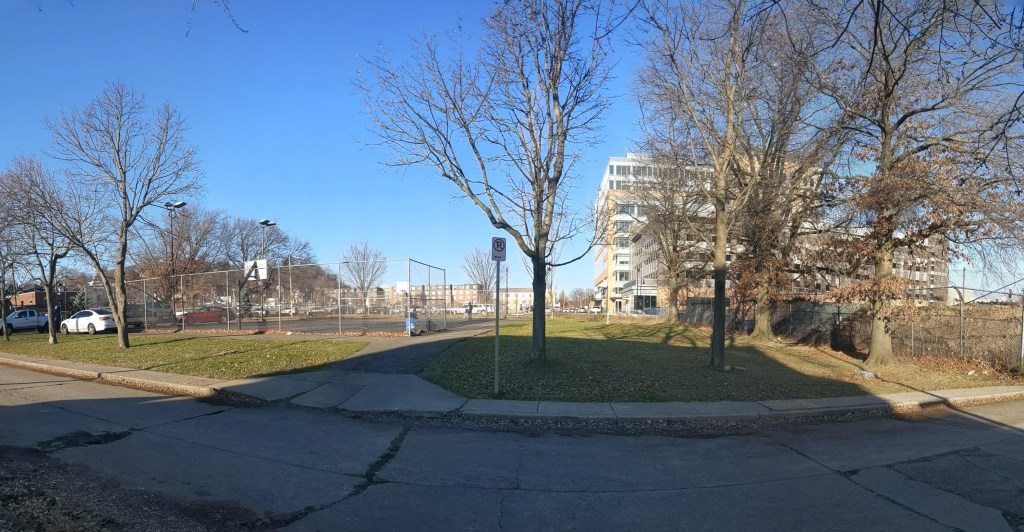
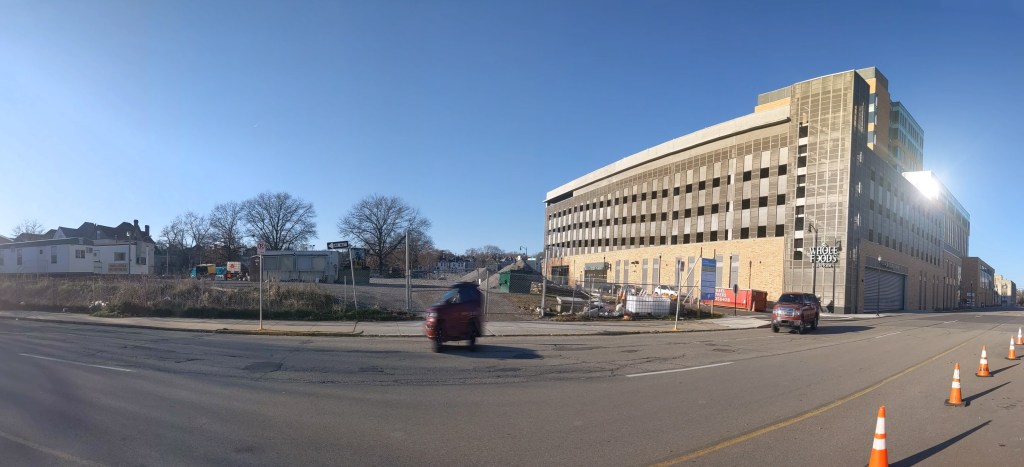
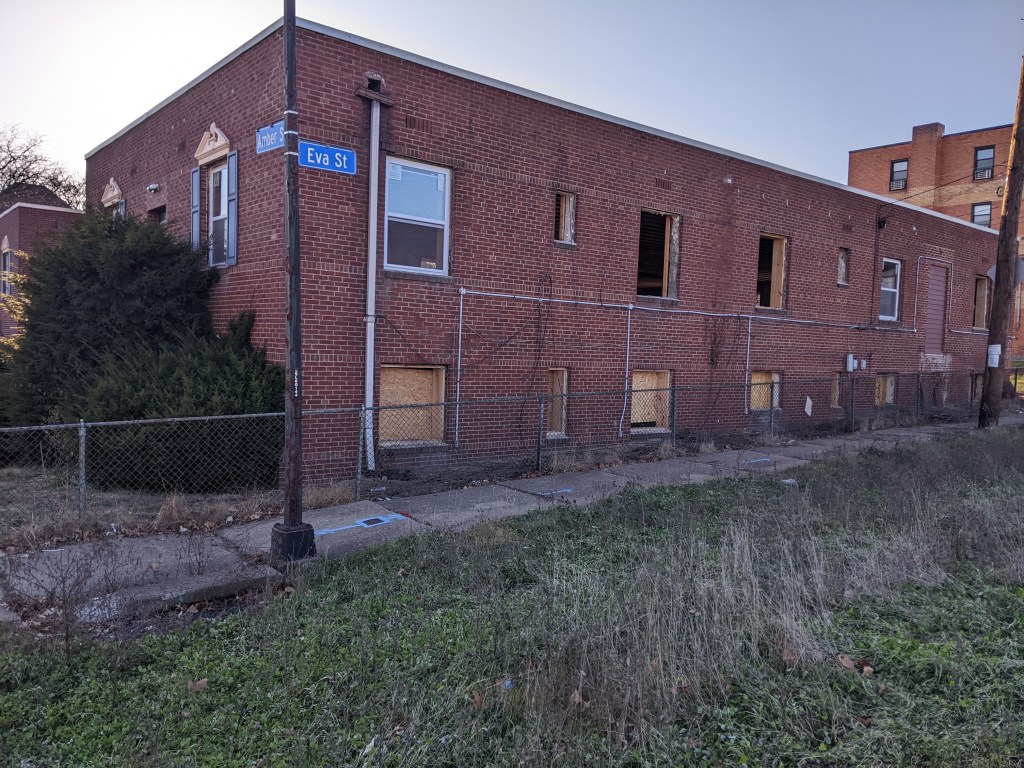
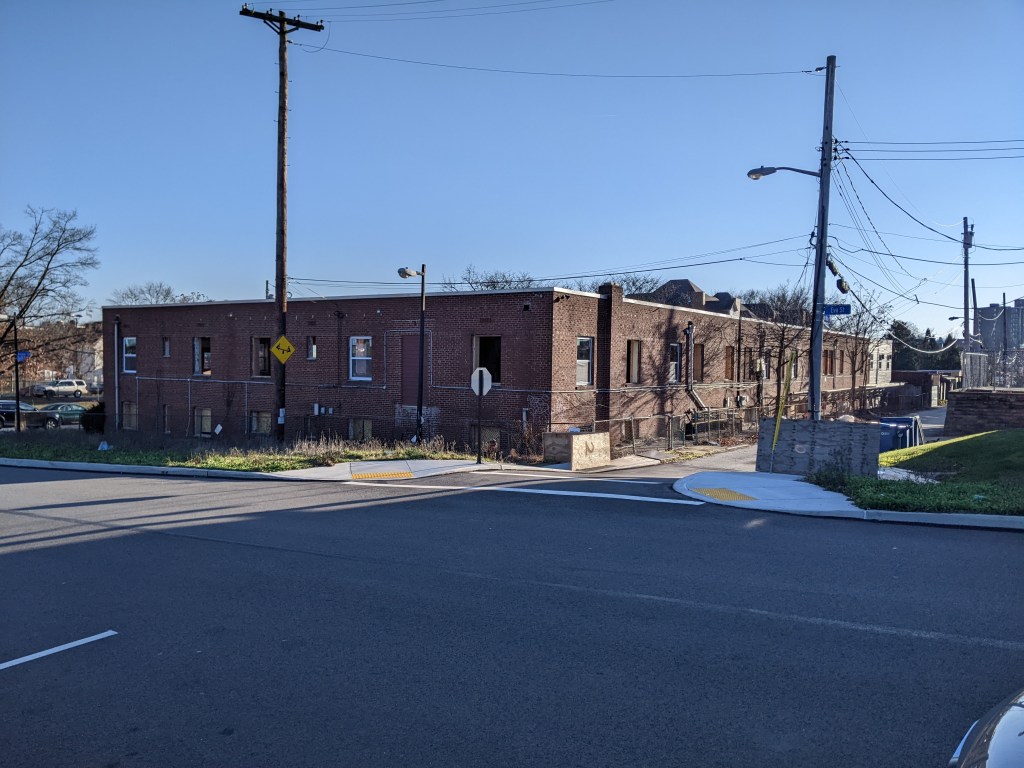
Phase 1 of the Penn Plaza redevelopment opened in 2022, seven years after the initial eviction notices went to the low-income residents of the former Penn Plaza Apartments. The redevelopment is a new retail/office complex that is being constructed in place of the former 519-unit affordable housing complex.
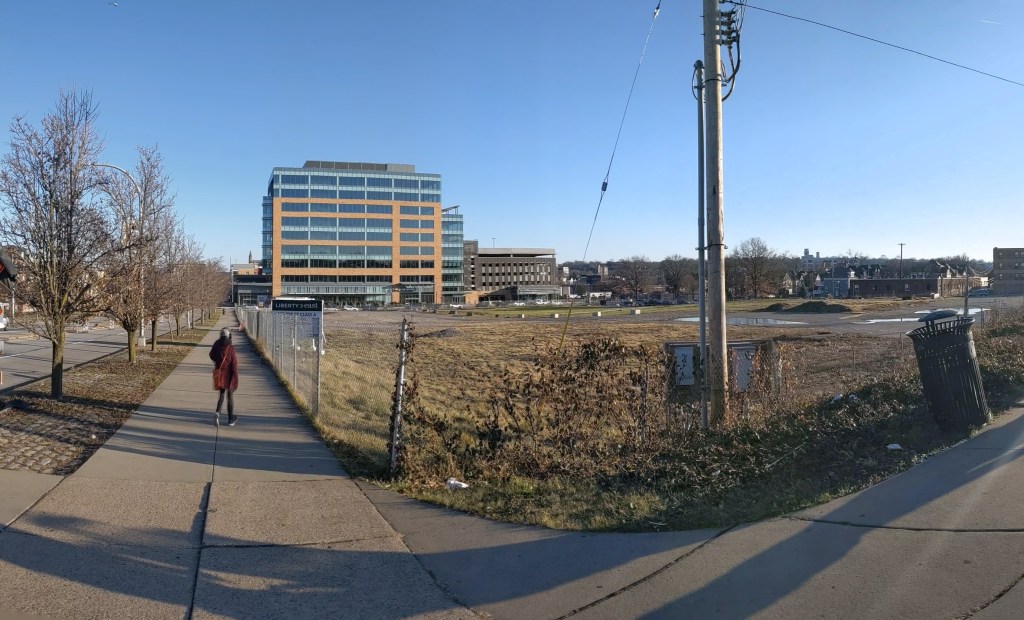
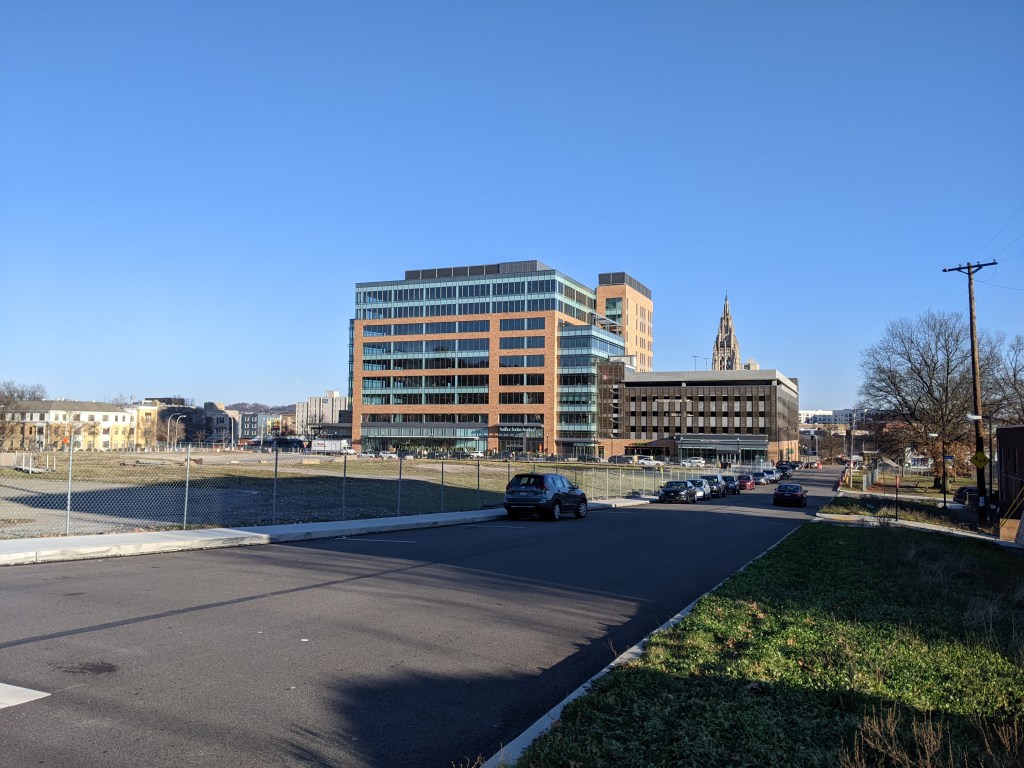
The new building is called Liberty East. Whole Foods is the anchor retail tenant and Duolingo is the first office tenant. An area about twice the size of the footprint of this building remains an untouched meadow with broken pavement scattered throughout and surrounded by a 6-foot high chain link fence. One day, future phases of this redevelopment will begin. In the meantime, changes are starting on land surrounding the site.
- Across Penn Avenue, the East Liberty Lutheran Church sold its property in August, seven years after first listing it. By December, the site was completely demolished and leveled – ready for whatever comes next.
- On the other side of Penn Plaza, a two-story, garden apartment building is showing the first signs of renovation.
- Behind the new building, Euclid Ave and, further down, Station Street are in the initial stages of being converted back to two-way after the 1960s Urban Renewal project that created the Penn Circle ring road.
- On the opposite site of East Liberty’s commercial core, the affordable Giant Eagle closed for the redevelopment of that shopping plaza.
Background
The former Penn Plaza Apartments was a group of large of apartments buildings that served a low-income population. After years of neglecting these apartments, the owner gave the remaining 200 residents notice to vacate within 90 days in the summer of 2015. By then, the surrounding neighborhood of East Liberty was a hopping place to live with low vacancy rates and the average rent much higher than what these residents could afford. There was a large outcry at the time, which only got worse as the owner’s plans for the site were understood. The owner wanted to swap some land with the City and change the zoning district to build a large scale mixed-use development: 54,600 sq ft of retail and 246,090 sq ft of office with accessory parking (see the application materials starting on page 54 from the final Planning Commission review and approval). After months of negotiation with the City and the community, the land and the zone change were given to the development while the affordable housing crisis in Pittsburgh only got worse and the former residents were forced to uproot their lives.
The Penn Plaza Support and Action Coalition has more information on what was promised and what happened as the residents were forced to find new housing.
Photos: The Site
Photos: The Surroundings
Penn Plaza in the News
The site:
- Duolingo signs lease (Pittsburgh Business Times, November 29, 2021)
- Whole Foods preps to move (Pittsburgh Business Times, July 21, 2022)
- Whole Foods opens (Pittsburgh Business Times, August 10, 2022)
The surroundings:
- East Liberty Lutheran Church’s sale (Pittsburgh Business Times, August 2, 2022)
- Giant Eagle closure (East Liberty Development, June 17, 2022)
- Echo Realty presented the redevelopment of the Giant Eagle shopping center to Pittsburgh’s Planning Commission (Pittsburgh Business Times, November 15, 2022) and got approval (Public Source, November 29, 2022; Pittsburgh Business Times, November 29, 2022)
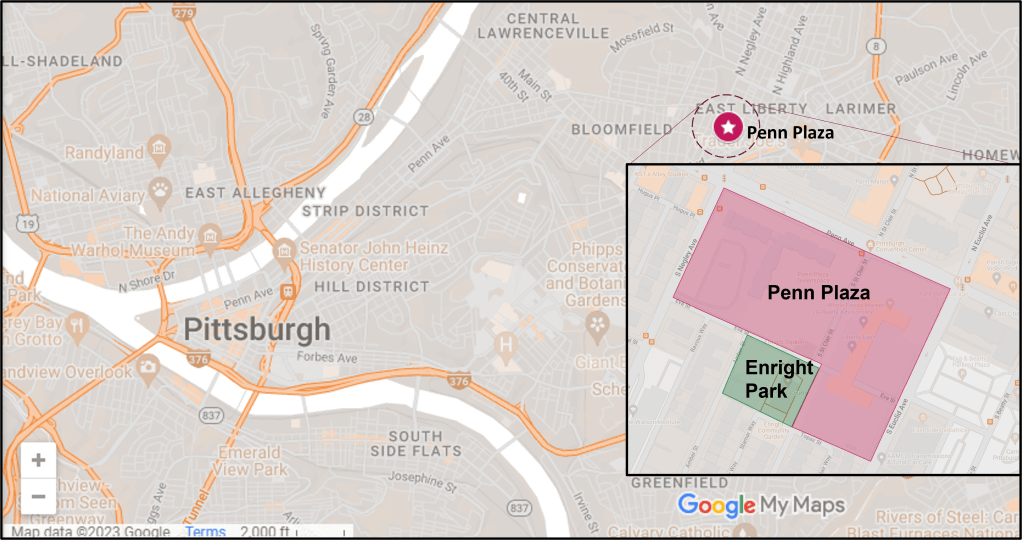
Locating Penn Plaza
Previous Posts in the Series
Keeping an Eye on Penn Plaza – Jun. 2022
Keeping an Eye on Penn Plaza – Apr. 2021
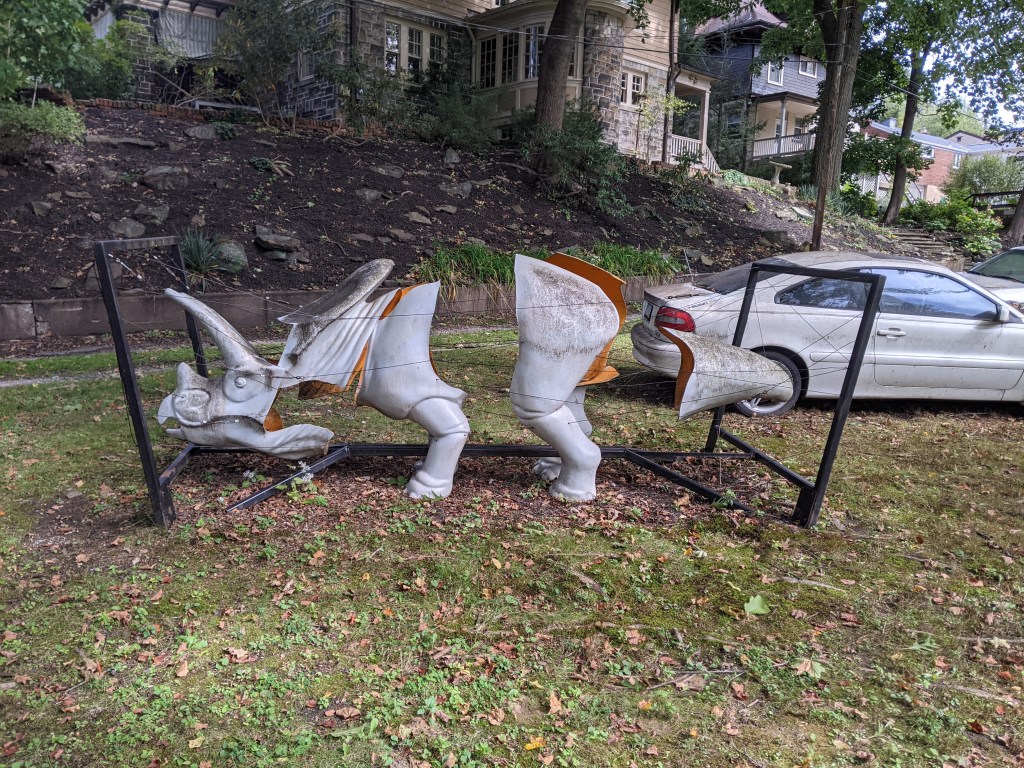
Pittsburgh DinoMite Parade 24
Urban Renewal in the Stroudsburgs
After WWII, while the federal government was building highways — sometimes through communities — and subsidizing and incentivizing the construction and purchase of detached single-family dwellings — that is, if you were of the “right” race, ethnicity, and economic level, — there was a growing sense that cities, and perhaps even towns, weren’t safe places to live. As people and jobs, or jobs and people, or some people and jobs starting leaving cities in large numbers, the cities started looking for ways to reinvent themselves to reattract people and jobs in order to survive. Pittsburgh was a leader at that time, inventing and defining the process of Urban Renewal. Other cities like Bethlehem looked up to Pittsburgh and tried to adopt the strategies and techniques of Urban Renewal used in Pittsburgh. Often these cities, as illustrated by Bethlehem, lacked the resources and power to pull off Urban Renewal on the same scale as Pittsburgh.
Revisiting the once familiar environs of Stroudsburg (pop. 5,950) and East Stroudsburg (pop. 9,669), I realized that even these small towns adopted practices and principals of Urban Renewal. And similar to the pairing of Allentown (pop. 125,944) and Bethlehem (pop.75,624), the larger of the two municipalities implemented more Urban Renewal projects while the smaller implemented more historic preservation practices.
Below is a very biased sample of the the Urban Renewal practices I believe I identified in the Stroudsburgs:
Urban Renewal Practice #1 – The Ring Road
Both boroughs contain a partial or complete loop of one-way streets around portions of their downtowns. This traffic pattern now appears to me as strongly reminiscent of the circles Pittsburgh built around important commercial neighborhoods – which subsequently nearly died, possibly because they were already dying, but probably aided by being choked off by these ring roads. In Stroudsburg and East Stroudsburg, it didn’t appear that the ring road has the same sort of death grip on the commercial enterprises they encircled. Several of the business I remembered were still operating and I didn’t notice significant numbers of vacant properties – though the couple vacant businesses I noticed were in East Stroudsburg. However, they weren’t areas that were tempting to explore more closely because they were sites developed along the second Urban Renewal practice.
Urban Renewal Practice #2 – Auto-oriented Uses
Both boroughs contained drive-through businesses in the center of their ring roads. In addition, strip malls are off to the right as you enter each borough on the ring road. In Stroudsburg, the auto-oriented uses felt like they were tightly centered on the ring road; nearby and spilling into the ring road was a dense, walkable downtown. On the other hand, in East Stroudsburg, it felt like the auto-oriented uses were spilling beyond the immediate environs of the ring road and into what was presumably once a much more extensive dense, walkable downtown.
Urban Renewal Practice #3 – Demolition for Underutilized Parking Lots
Part of what made the experience in East Stroudsburg feel more auto-oriented was the larger number of visible paved lots, presumably for parking, but largely empty. While I was most likely day-dreaming about the plot of my latest story featuring either princesses or cowboys when I previously spent time in downtown East Stroudsburg, there was a feeling of familiarity in the near empty parking lots suggesting that I would have felt uncomfortable if they were actually parked to capacity in the same way I felt uncomfortable passing locations where trees I used to know had been cut down.



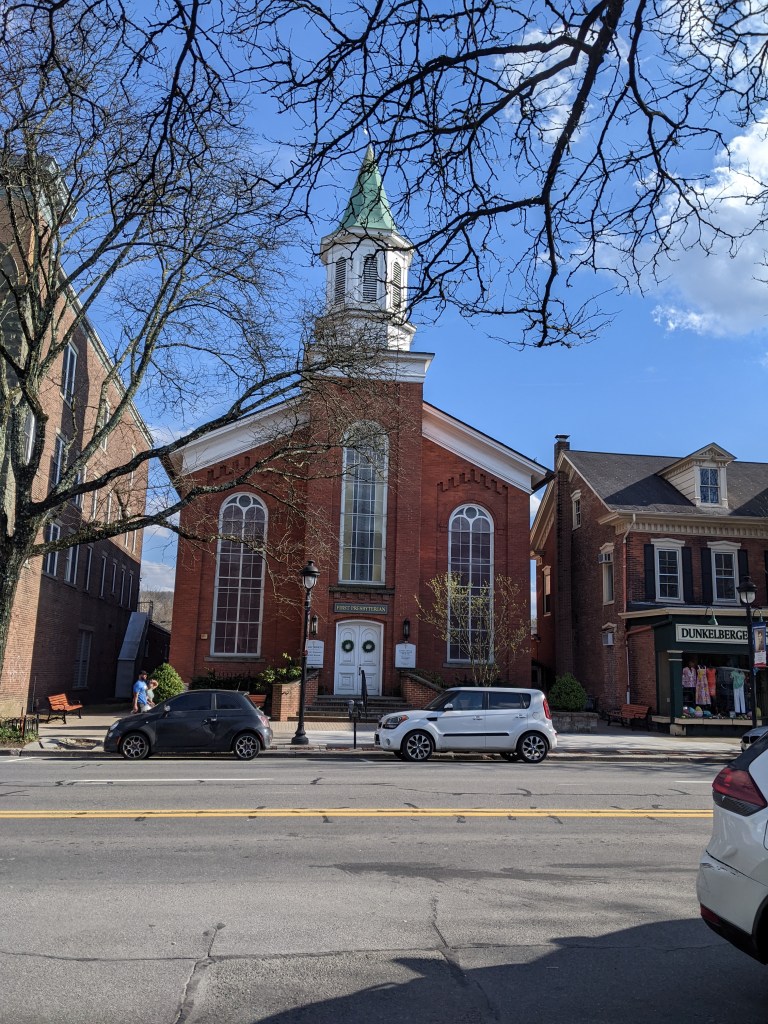
The Story of the Spires – Stroudsburg
One of the key ingredients for the stability component of “home” is safety. In the aftermath of 9/11, there was a concern about the safety of living in cities and living in New York in particular. The Pennsylvania boroughs of Stroudsburg and East Stroudsburg were among the places considered safe by those leaving New York City. Knowing this going in and comparing it to the lessons learned from Bethlehem, I assumed that the religious buildings would reflect a sense of stability.
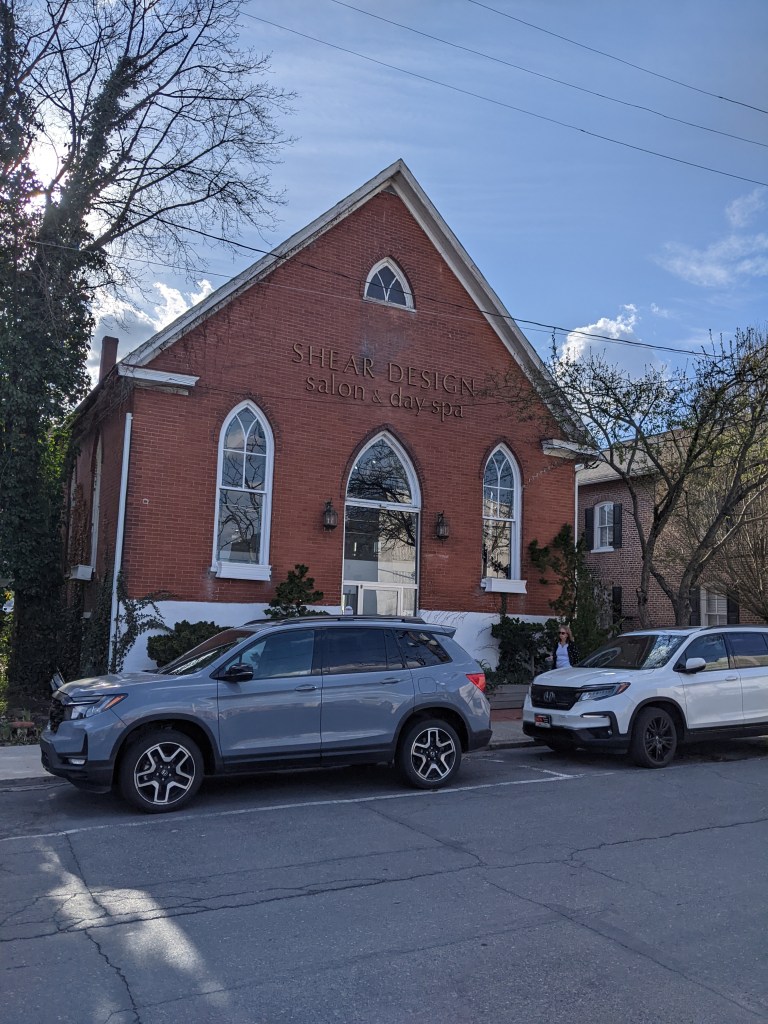
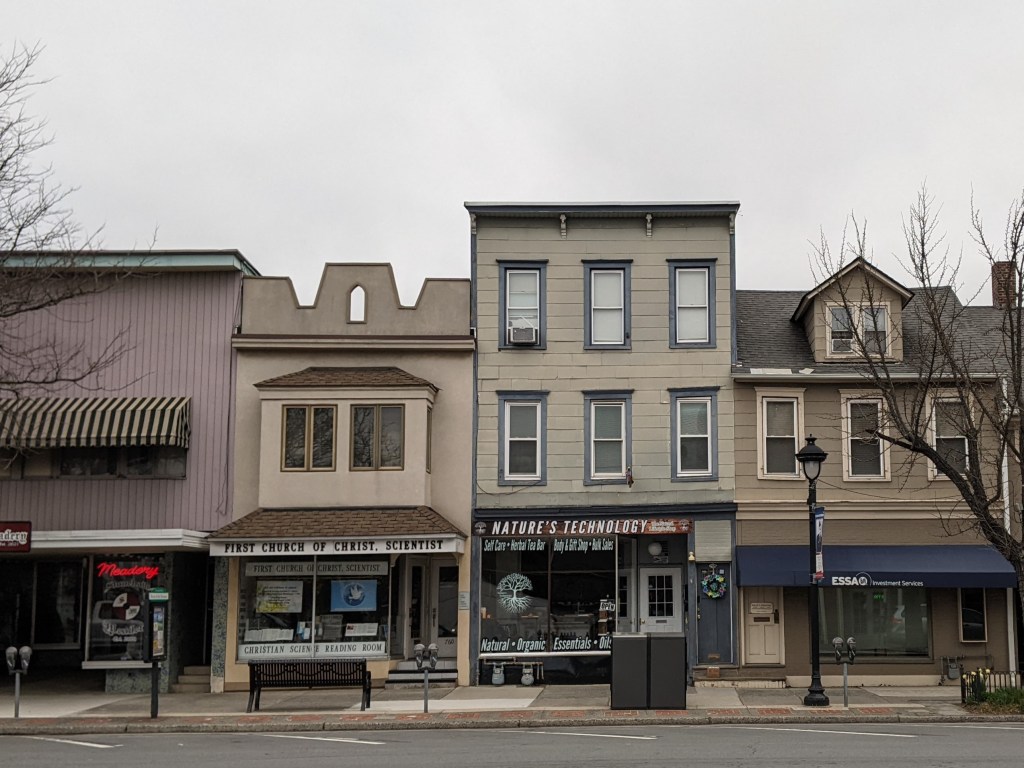
Of the two boroughs, Stroudsburg has a more centralized concentration of religious buildings that was easy for me to explore on foot within the limitations of my post-injury recovery phase. The results of this survey confirmed my hypothesis. Of the seven buildings I found, only one was converted to a secular use. Another one appeared to be having a renovation of it’s primary entrance but was still looked actively used as a church. (Facebook confirmed that it is still active with a video of the Polish language mass from a few days before the date I looked it up.) A third building was a storefront that is a First Church of Christ, Scientist.
Comparing Stroudsburg with other Pennsylvania towns where I’ve explored the status of religious buildings, it fits the pattern well. Stroudsburg’s peak population was in 1950, the same as Pittsburgh and Wilkinsburg. Below is an updated chart of the population loss for these cities and a broad impression of the state of their religious buildings.
| City | Population Loss Since Peak (Peak Year) | Status of Religious Buildings |
| Bethlehem | 1% (1960) | Primarily active sacred uses |
| Erie | 26% (1960) | Primarily active sacred uses |
| Homestead | 85% (1920) | Significant numbers closed or converted to secular uses |
| Pittsburgh | 55% (1950) | Significant numbers closed or converted to secular uses |
| Stroudsburg | 14% (1950) | Primarily active sacred uses |
| Wilkinsburg | 49% (1950) | Significant numbers closed or converted to secular uses |
Pittsburgh DinoMite Parade 23
Best Bridge – Bridge Madness 2023
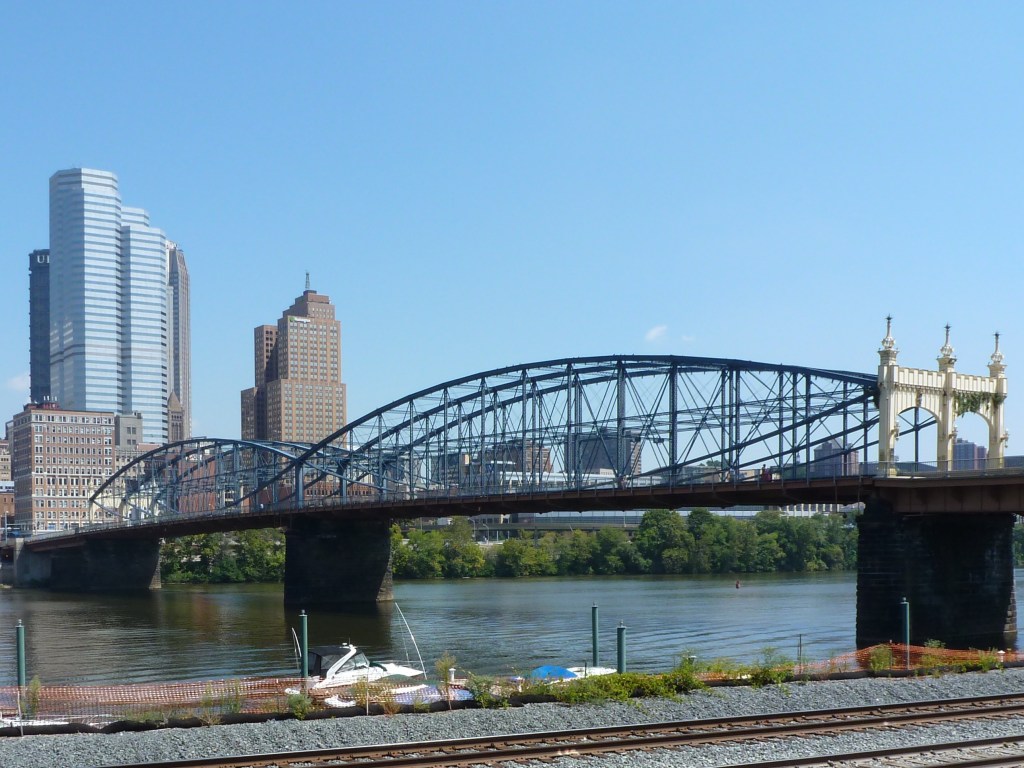

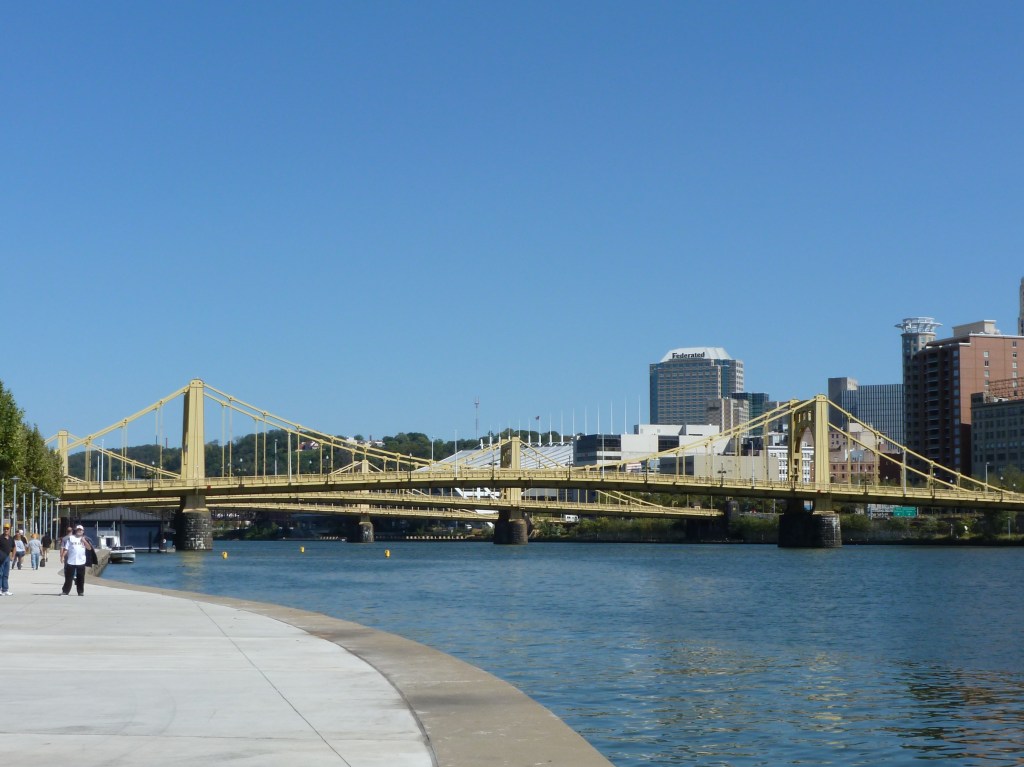
Smithfield Street Bridge wins the 2023 Bridge Madness Tournament with 88% of the votes.
Thank you for participating in the 2023 Bridge Madness Tournament. While there were some close contests throughout the tournament, in the end, the Smithfield Bridge emerged as the clear winner with 88% of the votes to the 16th Street Bridge’s 12%.
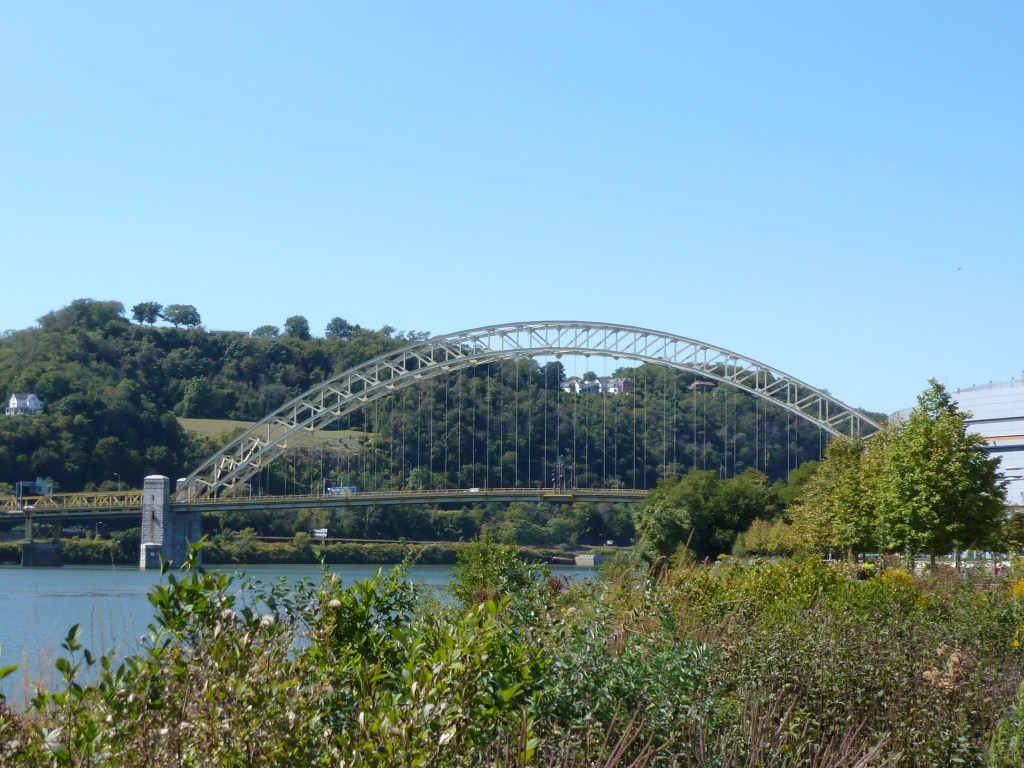
Bridge Madness 2023 featured bridges or groups of bridges that are accessible to vehicles and pedestrians. From east to west, these bridges on the Allegheny and Ohio Rivers are the Highland Park Bridge, the 62nd Street or R.D. Fleming Bridge, the 40th Street or Washington’s Crossing Bridge, the 31st Street Bridge, the 16th Street or David McCullough Bridge, the Three Sisters Bridges (6th Street, 7th Street, and 9th Street), the Fort Duquesne Bridge, and the West End Bridge. From east to west, these bridges on the Monongahela River are the Homestead Greys Bridge, the Glenwood Bridge, the Hot Metal Bridges, the Birmingham Bridge, the South 10th Street Bridge, the Liberty Bridge, the Smithfield Bridge, and the Fort Pitt Bridge.
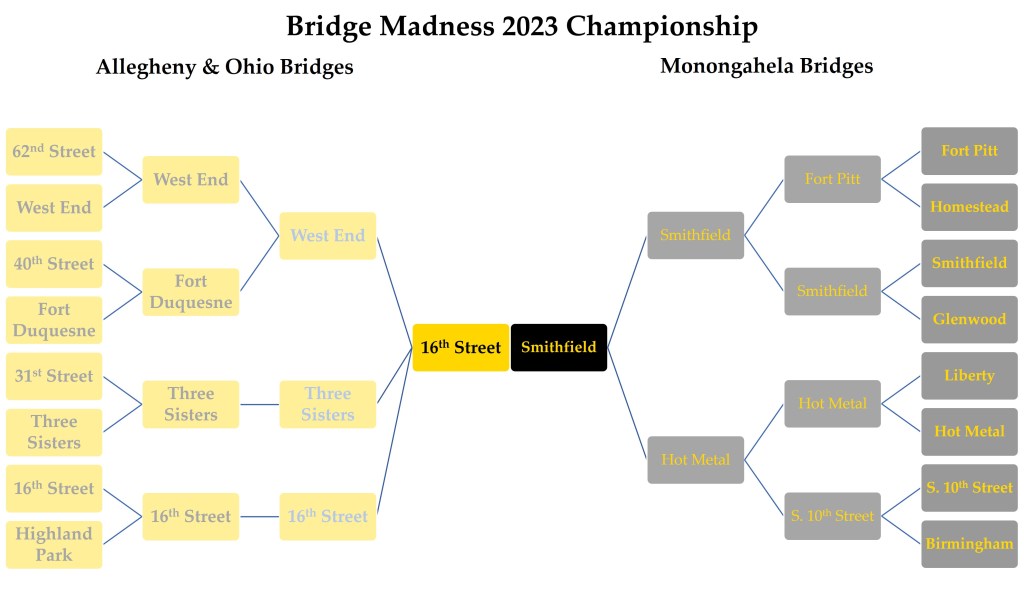
Bridge Madness 2023 – Championship

The results are in from the Final Four match-ups in 2023’s Bridge Madness Tournament. The tournament features bridges or groups of bridges that are accessible to vehicles and pedestrians. From east to west, these bridges on the Allegheny and Ohio Rivers are the Highland Park Bridge, the 62nd Street or R.D. Fleming Bridge, the 40th Street or Washington’s Crossing Bridge, the 31st Street Bridge, the 16th Street or David McCullough Bridge, the Three Sisters Bridges (6th Street, 7th Street, and 9th Street), the Fort Duquesne Bridge, and the West End Bridge. From east to west, these bridges on the Monongahela River are the Homestead Greys Bridge, the Glenwood Bridge, the Hot Metal Bridges, the Birmingham Bridge, the South 10th Street Bridge, the Liberty Bridge, the Smithfield Bridge, and the Fort Pitt Bridge.
In the Allegheny and Ohio Conference
Bracket 7 was the 16th Street Bridge (46%) vs. the Three Sisters Bridges (37%) vs. the West End Bridge (17%).
In the Monongahela Conference
Bracket 7 was the Smithfield Bridge (55%) vs. the Hot Metal Bridges (45%).
The winners are matched up below for the Championship. Vote for your favorite bridge by noon on March 29, then check back on March 30 for the announcement of the winner.
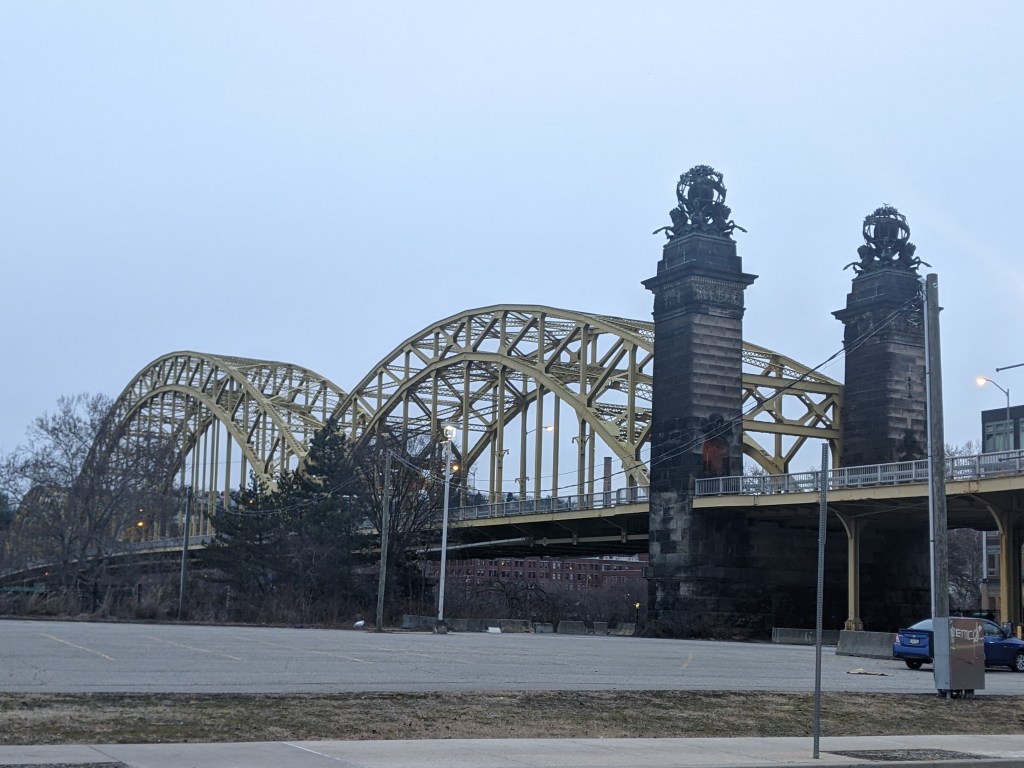


Bridge Madness 2023 – Final Four(ish)
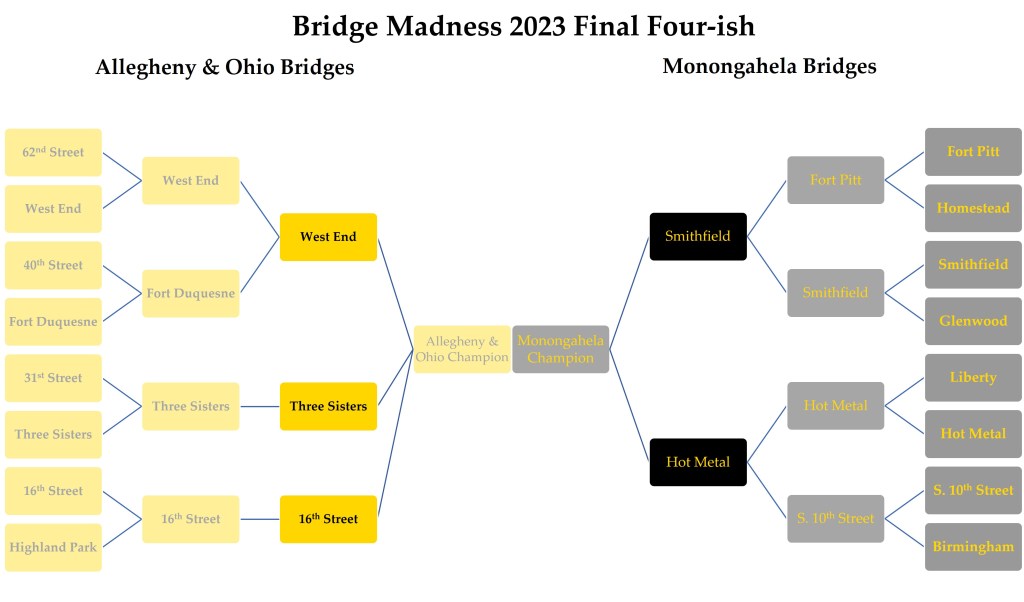
The results are in from the Elite Eight match-ups in 2023’s Bridge Madness Tournament. The tournament features bridges or groups of bridges that are accessible to vehicles and pedestrians. From east to west, these bridges on the Allegheny and Ohio Rivers are the Highland Park Bridge, the 62nd Street or R.D. Fleming Bridge, the 40th Street or Washington’s Crossing Bridge, the 31st Street Bridge, the 16th Street or David McCullough Bridge, the Three Sisters Bridges (6th Street, 7th Street, and 9th Street), the Fort Duquesne Bridge, and the West End Bridge. From east to west, these bridges on the Monongahela River are the Homestead Greys Bridge, the Glenwood Bridge, the Hot Metal Bridges, the Birmingham Bridge, the South 10th Street Bridge, the Liberty Bridge, the Smithfield Bridge, and the Fort Pitt Bridge.
In the Allegheny and Ohio Conference
Bracket 5 was the West End Bridge (63%) vs. the Fort Duquesne Bridge (34%).
Bracket 6 was the Three Sisters Bridges (50%) vs. the 16th Street Bridge (50%).
In the Monongahela Conference
Bracket 5 was the Smithfield Bridge (79%) vs. the Fort Pitt Bridge (21%).
Bracket 4 was the Hot Metal Bridges (71%) vs. the South 10th Street Bridge (293%).
The winners in these brackets are matched up below for the Final Four. Vote for your favorite bridges below by noon on March 26, then check back on March 27 for the Championship.





































































